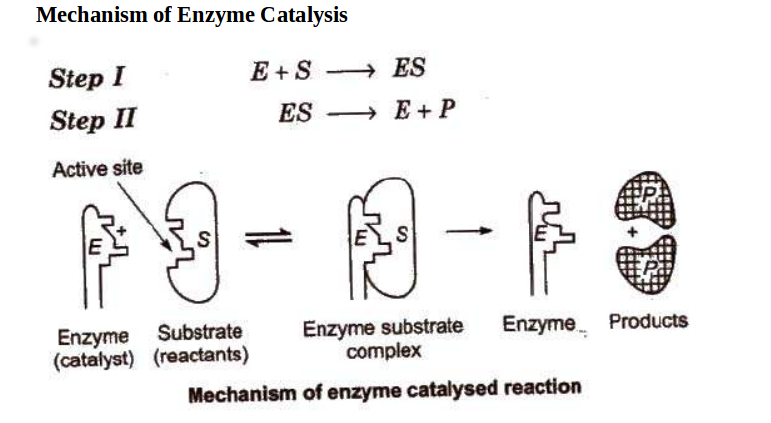
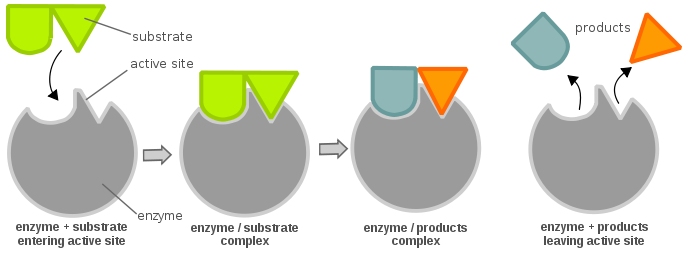
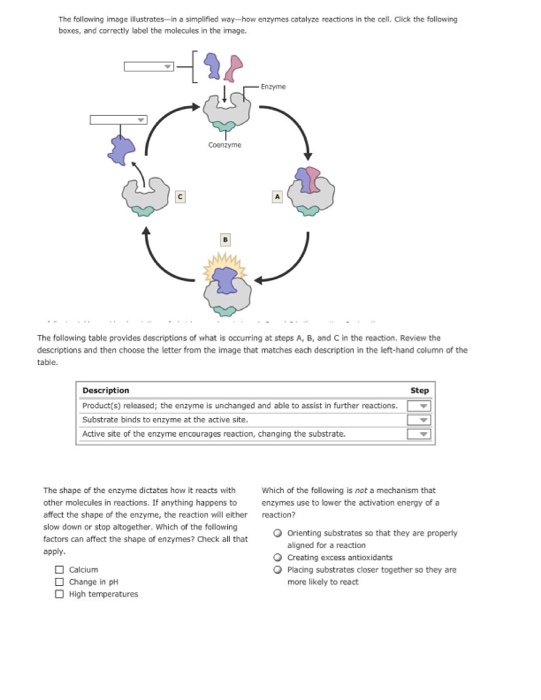
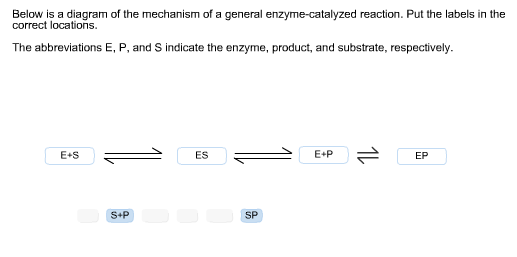
37 below is a diagram of the mechanism of a general enzyme-catalyzed reaction
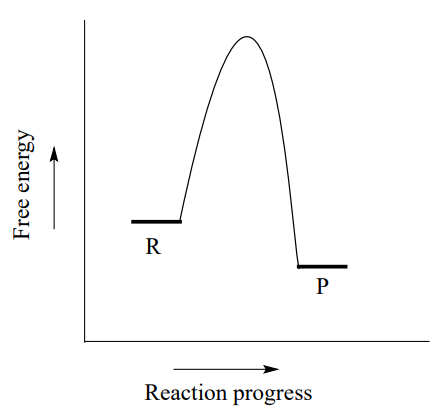
Note that the enzyme (E) is not altered by the reaction, so the chemical equilibrium remains unchanged, determined solely by the thermodynamic properties of S and P.The effect of the enzyme on such a reaction is best illustrated by the energy changes that must occur during the conversion of S to P (Figure 2.22).The equilibrium of the reaction is determined by the final energy states of S and P ... Enzyme catalysis is the increase in the rate of a process by a biological molecule, an "enzyme".Most enzymes are proteins, and most such processes are chemical reactions. Within the enzyme, generally catalysis occurs at a localized site, called the active site.. Most enzymes are made predominantly of proteins, either a single protein chain or many such chains in a multi-subunit complex.
Each enzyme-catalyzed reaction reveals a characteristic K M value, and this value is a measure of the tendency of the enzyme and the substrate to combine with each other. In this sense, the K M value is an index of the affinity of the enzyme for its particular substrate. Some representative K M values are given in Table 8-2.

Below is a diagram of the mechanism of a general enzyme-catalyzed reaction
In fact, typically, an enzyme accelerates the rate of a reaction by factors of at least a million compared to the rate of the same reaction in the absence of the enzyme. Most biological reactions do not occur at perceptible rates in the absence of enzymes. One of the simplest biological reactions catalyzed by an enzyme is the hydration of CO2 ... - An enzyme that temporarily undergoes covalent catalysis as part of its mechanism. - A type of enzyme inhibitor where KM is unaltered. - The type of reaction catalyzed by proteases. - An enzyme that is part of a pigment formation pathway and has a low-temperature optimum. - A protease enzyme with a low pH optimum. Enzyme-catalyzed reaction. In a CSTR, if the reaction is controlled by enzyme catalysis and the kinetics equation follows the Michaelis-Menten equation, substituting the kinetics equation directly into Eq. (3.42) gives the residence time. (11.46) τ = Vr Q0 = ( cs0 − cs) ( Km + cs) rmaxcs = ( cs0 − cs) ( Km + cs) k2cE0cs.
Below is a diagram of the mechanism of a general enzyme-catalyzed reaction. A transition state analog is a stable molecule that resembles the transition state of an enzyme catalyzed reaction, and is a potent _____ of that enzyme. *inhibitor Little can be learned about enzyme reaction mechanisms by examining the corresponding nonenzymatic reactions of model compounds. This is known as the Michaelis-Menten mechanism. The potential energy diagram is shown in the figure. Which of the following sets of identifications is correct?1 answer · Top answer: (1) represents enzyme (E) and substrate (S),(2) represents enzyme - substrate intermediate 1 (ES).(3) represents enzyme product intermediate 2 ... Mechanism of Enzyme Action 1. General properties of enzymes 2. Activation energy and the ... Transition state diagram/reaction coordinate diagram: ... The reaction catalyzed by lysozyme, the hydrolysis of a glycoside, is the conversion of an acetal into a ... Enzyme-catalyzed reactions can be classified according to reactancy, ... reaction is depicted in the following diagram where E' indicates that the enzyme ...
The mechanism for the enzyme-catalyzed reaction would consist of at least two steps, the first step being formation of the enzyme-substrate (ES) complex, which is an intermediate. If the formation of the ES complex is thermodynamically favorable, it would be represented on a reaction coordinate diagram at a lower level along the energy axis. Most modern Biochemistry textbooks, resting on the energetic profile of enzymic reaction, try to bridge the gap between the thermodynamic and the mechanistic description of enzyme action. In this sense, the energy diagram for an enzyme-catalyzed reaction is an invaluable teaching and learning tool. This problem has been solved! Below is a diagram of the mechanism of a general enzyme-catalyzed reaction. Put the labels in the correct locations. The abbreviations E, P, and S indicate the enzyme, product, andsubstrate, respectively. Chemistry questions and answers. Complete the diagram of the mechanism of a general enzyme-catalyzed reaction. The abbreviations E, P, and Sindicate the enzyme, product, and substrate, respectively. ES E+P = EUS Answer Bank SP. Question: Complete the diagram of the mechanism of a general enzyme-catalyzed reaction.
Enzymes have high substrate specificity, and can even show regiospecificity that leads to the generation of stereospecific products. Figure 7.1 Effect of an enzyme on reducint the activation energy required to start a reaction where (a) is uncatalyzed and (b) is an enzyme-catalyzed reaction. Figure from Peter K. Robinson. Question: Below is a diagram of the mechanism of a general enzyme-catalyzed reaction. Put the labels in the correct locations. The abbreviations E, P, ... QUESTION 4: REACTION MECHANISM (5 pts.) (i) Draw a reaction mechanism converting glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate to dihydroxyacetone phosphate, such that an enzyme-catalyzed intermediate is formed. Show each structure: reactant, intermediate, and product. Show the arrows for the flow of electron pairs. [ea. struct. 1 pt., electron arrows 0.5 pt. ea.] The catalyzed reaction is shown as a two-stage process with lower activation energy and is, therefore, faster. It is possible that the unanalyzed reaction proceeds by more than one step and the catalyzed reaction may also consist of several steps. The important point to note is that for the catalyzed reaction there is no step which has higher ...

The Physical Organic Chemistry Of Glycopyranosyl Transfer Reactions In Solution And Enzyme Catalyzed Sciencedirect
and metal ions in the right position for catalysis. In reality, the free energy diagram for an enzyme-catalyzed reaction is considerably more complicated than the exam-ple in Fig. 4.2. Typically an enzyme-catalyzed reaction will involve multiple steps, each with an activation energy that is markedly lower than that for the uncatalyzed reaction.
Figure 1. Experimental observations for a typical enzyme catalyzed reaction (left) and a typical uncatalyzed chemical reaction (right). On the left, the reaction becomes zero order in substrate as the enzyme active site is saturated. On the right, no saturation is observed and the rate continues to be
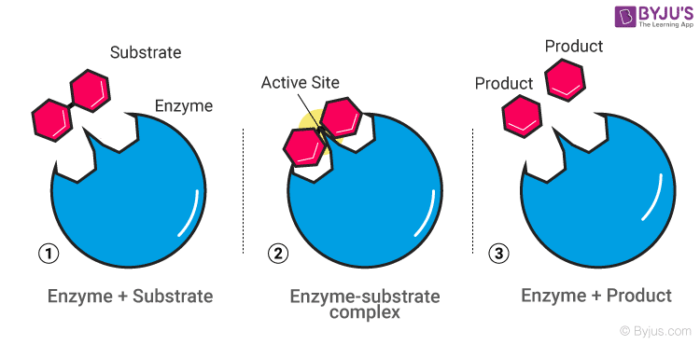
ADVERTISEMENTS: In this article we will discuss about the mechanism of enzyme reaction. In an enzyme-catalysed biochemical reaction, the enzyme molecule binds specifically and reversibly to the substrate molecule resulting in formation and breaking of chemical bonds to produce the product. Thus, there is formation of an unstable enzyme-substrate complex which immediately breaks into the […]
2. Compare the two reaction coordinate diagrams below and select the answer that correctly describes their relationship. In each case the single intermediate is the ES complex. a. The ES complex is given by #2 in (a) and #3 in (b). b. The activation energy for the catalyzed reaction #5 in (a) and is #7 in (b).
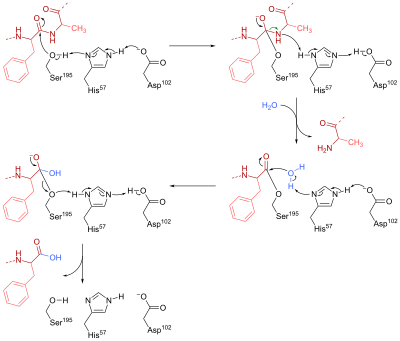
E. extrapolate for the value of reaction rate at infinite enzyme concentration. 11. In the following diagram of the first step in the reaction catalyzed by the protease chymotrypsin, general base catalysis is identified by the numbers _____ and covalent catalysis is the process identified by the numbers _____. 195 Ser B: 5 C 3 OR O R -NH2 2 + 1 ...
Catalysts function by providing an alternate reaction mechanism that has a lower activation energy than would be found in the absence of the catalyst. In some cases, the catalyzed mechanism may include additional steps, as depicted in the reaction diagrams shown in Figure 2. This lower activation energy results in an increase in rate as ...

Energy Diagrams For Enzyme Catalyzed Reactions Concepts And Misconcepts Aledo 2003 Biochemistry And Molecular Biology Education Wiley Online Library
The catalyzed reaction is the one with lesser activation energy, in this case represented by diagram b. Check Your Learning Reaction diagrams for a chemical process with and without a catalyst are shown below. Both reactions involve a two-step mechanism with a rate-determining first step.
Many enzymes catalyze reactions by this type of mechanism. Acetylcholinesterase is used as a specific example in the sequence described below.
When the S P reaction is catalyzed by an enzyme, the ES and EP complexes are intermediates (Eqn 8-1); they occupy valleys in the reaction coordinate diagram (.Fig. 8-4). When several steps occur in a reaction, the overall rate is determined by the step (or steps) with the highest activation energy; this is called the rate-limiting step.
Enzyme Catalysis - An enzyme is a substance which fastens a chemical reaction. A substrate is attracted towards the active site of the enzyme which leads to the catalysis of a chemical reaction and formation of products. Read more about the Reactions and mechanism of enyme catalysis at vedantu.com.
A mechanism is a series of elementary steps whose sum is the overall reaction. An elementary step is a reaction that is meant to represent a single collision or vibration that leads to a chemical ...
specific reaction catalyzed by pepsin is the acid hydrolysis of the peptide bond. This reaction will break down proteins into smaller units to enable the digestive process. Pepsin demonstrates an unusual property for an enzyme; it does not actually form chemical bonds with its substrate. The unique aspect of the pepsin mechanism is the
Solution for The diagram shows the mechanism of a general enzyme‑catalyzed reaction. Put the labels in the correct locations. The abbreviations E, P and S…
Below is an energy diagram illustrating the difference in a catalyzed reaction versus an uncatalyzed reaction. Label the energy diagram and answer the question that follows% (1). Catalyzed reactions have a lower activation energy (rate-limiting free energy of activation) than the corresponding uncatalyzed reaction, resulting in a higher ...
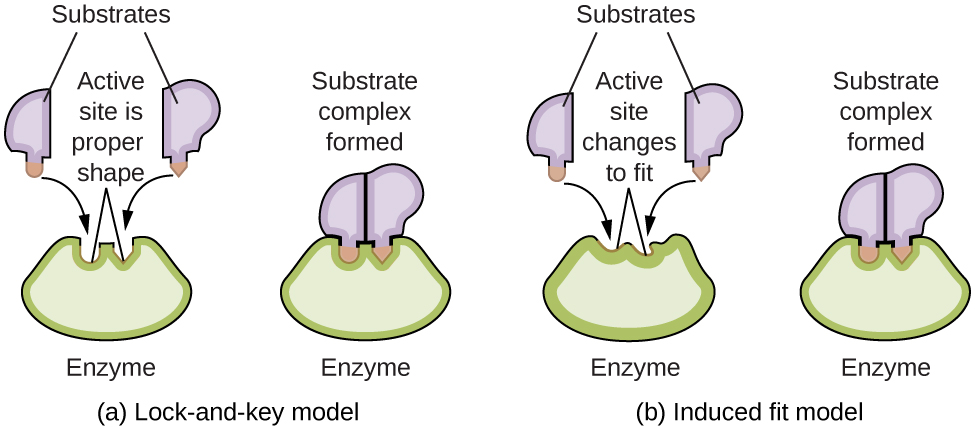
The enzyme active site is the location on the enzyme surface where substrates bind, and where the chemical reaction catalyzed by the enzyme occurs. There is a precise substrate interaction that occurs at the active site stabilized by numerous weak interactions (hydrogen bonds, electrostatic interactions, hydrophobic contacts, and van der Waals ...
Enzyme catalyzed reactions: From experiment to computational mechanism reconstruction ... We have previously described a method for inferring reaction mechanisms and kinetic rate parameters from time course data. Here, we address the limitations in the number of chemical reactions by allowing the introduction of information about chemical ...
Enzyme-catalyzed reaction. In a CSTR, if the reaction is controlled by enzyme catalysis and the kinetics equation follows the Michaelis-Menten equation, substituting the kinetics equation directly into Eq. (3.42) gives the residence time. (11.46) τ = Vr Q0 = ( cs0 − cs) ( Km + cs) rmaxcs = ( cs0 − cs) ( Km + cs) k2cE0cs.
- An enzyme that temporarily undergoes covalent catalysis as part of its mechanism. - A type of enzyme inhibitor where KM is unaltered. - The type of reaction catalyzed by proteases. - An enzyme that is part of a pigment formation pathway and has a low-temperature optimum. - A protease enzyme with a low pH optimum.
In fact, typically, an enzyme accelerates the rate of a reaction by factors of at least a million compared to the rate of the same reaction in the absence of the enzyme. Most biological reactions do not occur at perceptible rates in the absence of enzymes. One of the simplest biological reactions catalyzed by an enzyme is the hydration of CO2 ...
















0 Response to "37 below is a diagram of the mechanism of a general enzyme-catalyzed reaction"
Post a Comment