37 draw a ray diagram for the following situation
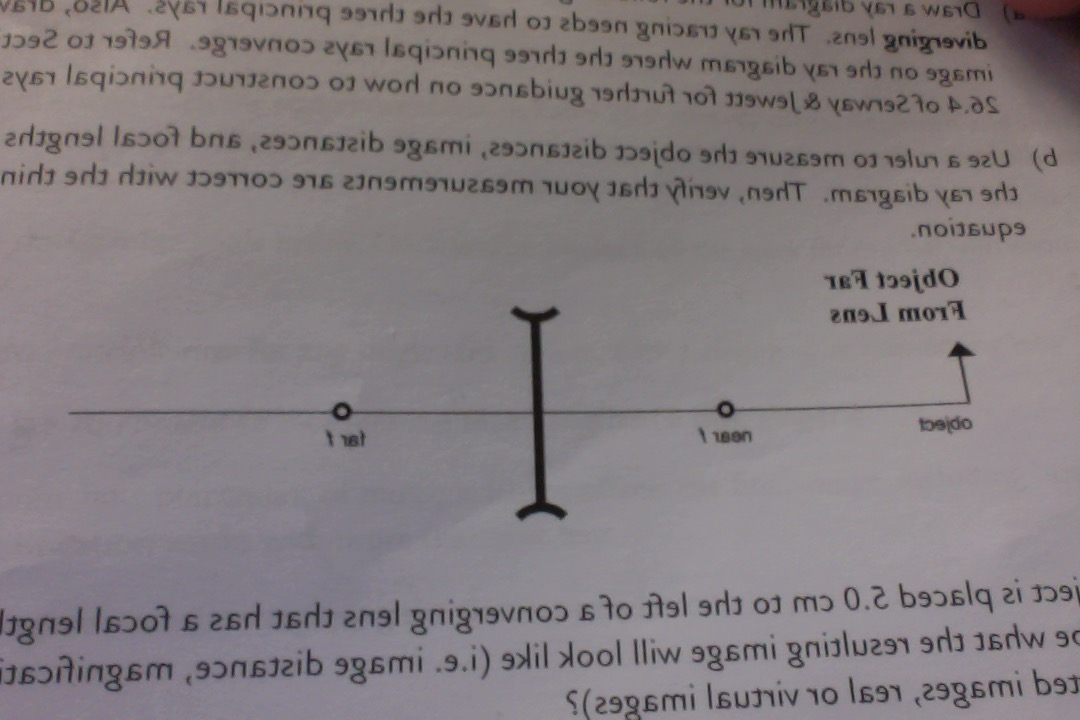
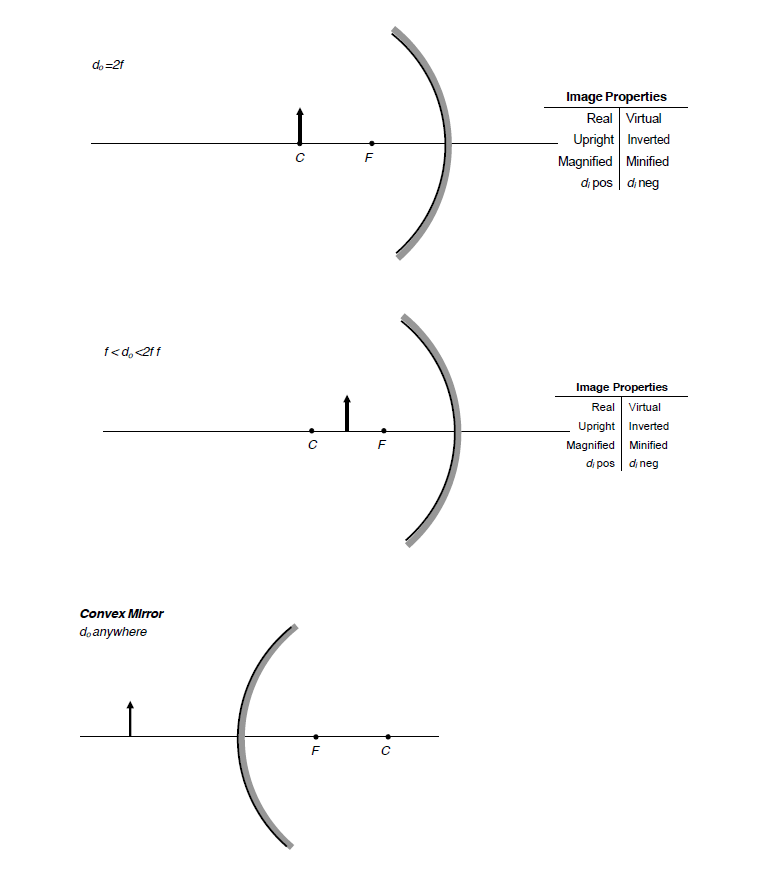
Question: a) Draw a ray diagram for the following situation involving a converging lens. The ray tracing needs to have the three principal rays. Also, draw the image on the ray diagram where the three principal rays converge. b) Use a ruler to measure the object distances, image distances, and focal lengths for the ray diagram. A ray diagram shows the path of light from an object to mirror to an eye. A ray diagram for a convex mirror shows that the image will be located at a position behind the convex mirror. Furthermore, the image will be upright, reduced in size (smaller than the object), and virtual. This is the type of information that we wish to obtain from a ray diagram.
Draw a Ray Diagram to Show the Formation of Image in the Above Situation . CBSE CBSE (English Medium) Class 10. Question Papers 886. Textbook Solutions 17807. MCQ Online Tests 12. Important Solutions 3111. Question Bank Solutions 24345. Concept Notes & Videos 356. Time Tables 12.

Draw a ray diagram for the following situation
Drawing Ray Diagrams - a Step-by-Step Approach. This section of Lesson 2 details and illustrates the procedure for drawing ray diagrams. Let's begin with the task of drawing a ray diagram to show how Suzie will be able to see the image of the green object arrow in the diagram below. For simplicity sake, we will suppose that Suzie is viewing the ... PART 5 - DRAWING RAY DIAGRAMS Draw a ray diagram for each situation, using the 3 principal rays. Use a ruler to measure all dimensions. For each ray diagram identify the following (list near diagram): 1. d i - the image distance (cm ok) 2. is image inverted or upright? 3. is image real or virtual ? 4. is image magnified or reduced? Draw a ray diagram for concave mirror when object is placed between focus and centre of curvature. Also write position, nature and size of image. Medium. View solution >; A point source of light S, placed at a distance L in front of the centre of a plane mirror of width d, hangs vertically on a wall.
Draw a ray diagram for the following situation. 1. Draw a ray diagram to help you figure out how the size of the observed image relates to the distance to the mirror. On the picture below draw the rays coming from your head and your toes, and reflected directly into your eyes. 2. Draw the normal line (perpendicular to the mirror surface) from your eyes. Draw the reflected image. 3. Draw a ray diagram for the following situation (an object far from the lens) involving a diverging lens. The ray tracing needs to have the three principal rays. Also, draw the image on the ray diagram where the three principal rays converge. Draw an entity relationship diagram (ERD) for the following situations: 1. Whenever new patients are seen for the first time, they complete a patient information form that asks their name, address, phone number, and insurance carrier, all of which are stored in the patient information file. Patients can be signed up with only one carrier, but ... Figure shows a ray of light meeting the glass of the window of a car at an angle of incidence of 40 ° °. (i) Assuming that the refractive index of glass is 1.5, find the angle of refraction for this ray in the glass. (ii) Complete the diagram by sketching the path of the ray through the glass and out on the other side.
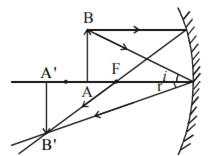
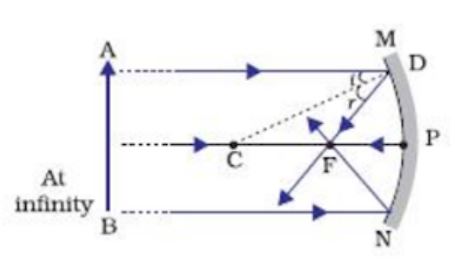
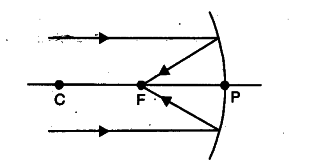
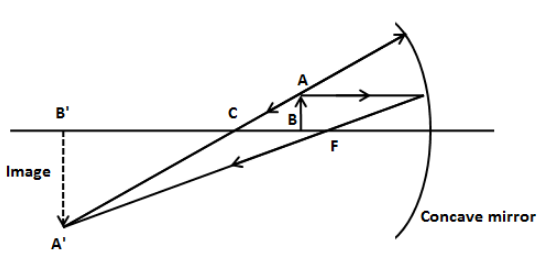
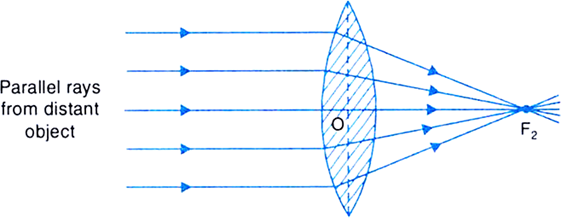
Draw the following diagram, in which a ray of light is incident on a concave/convex mirror, on your answer sheet. Show the path of this ray, after reflection, in each case. (Delhi 2016) Answer: Question 39. AB and CD, two spherical mirrors, form parts of a hollow spherical ball with its centre at O as shown in diagram. a) Draw a ray diagram for the following situation involving a converging lens. The ray tracing needs to have the three principal rays. Also, draw the image on the ray diagram where the three principal rays converge. b) Use a ruler to measure the object distances, image distances, and focal lengths for the ray diagram. The image formed in this situation when object is placed at infinity, has the following characteristics: (1). Real image (2). Inverted image (3). Highly diminished image Additional Information: A lens is basically a carefully grounded piece of transparent material which refracts light rays in such a way as to form an image. Case 1 - Object is Placed at infinity. In this Case, Object AB is kept far away from mirror (almost at infinite distance) So, we draw rays parallel to principal axis. Since ray parallel to principal axis passes through the Focus. Both rays meet at focus after reflection. Hence, Image is formed at Focus. And it is very very small. We can say that.
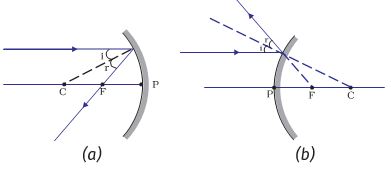
Lens and mirror practice! Draw ray diagrams for each of the following scenarios, and check your results using the lens/mirror equation. Diverging lens, object at {eq}\frac{f}{2}. The rules used for drawing ray diagrams for the formation of an image by a concave mirror are: Rule 1: If the incident ray is parallel to the principal axis then the reflected ray passes through the focus of the concave mirror. Rule 2: If the incident ray passes through the focus of the concave mirror, the reflected ray is parallel to the ... Ray diagram for object located in front of the focal point. A draw a ray diagram for the following situation an object far from the lens involving a diverging lens. Posted one year ago. Through the focal point in front of the lens. A draw a ray diagram for the following situation an object far from the lens involving a diverging lens. Draw ray diagram from the following situation m =+ve (convex mirror) . information about solar light, solar water heating system and solar cooker with diagram . State and prove law of conservation of momentum with diagram. From the ch Health and Hygiene pls tell me the ans for the question *List the factors that affect the health of a person* .

Draw Ray Diagram To Show The Situation When An Incident At A Transparent Curved Surface Dose Not Brainly In
(a) Draw a ray diagram for the following situation involving a converging lens. The ray-tracing needs to have three principal rays. Also, draw the image on the ray diagram where the three principal rays converge.

A With The Help Of A Ray Diagram Show How A Concave Mirror Is Used To Obtain An Erect And Magnified Image Of An Object B Using The Above Ray Diagram Obtain
In order to illustrate the method of drawing a ray diagram for a concave mirror, we will consider the situation in which a real object sits inbetween the centre of curvature of the mirror and the focal point. The bottom of the object will sit on the principal axis, and the top of the object will sit above the principal axis.
Cbse Free Ncert Solution Of 10th Science Light Reflection And Refraction An Object 5 Cm In Length Is Held 25 Cm Away From A 24th November 2021 Saralstudy
Draw ray diagrams to represent the nature, position and relative size of the image formed by a convex lens for the object placed: (a) at 2F 1 (b) between F 1 and the optical centre O of lens: Draw ray diagrams to show image formation. Object at C - concave mirror Object beyond 2f - convex lens Object at infinity - concave lens.

Draw A Ray Diagram To Show The Path Of The Reflected Ray In Each Of The Following Cases A Ray Of Light Incident On A Convex Mirror A Strikes At Its Pole
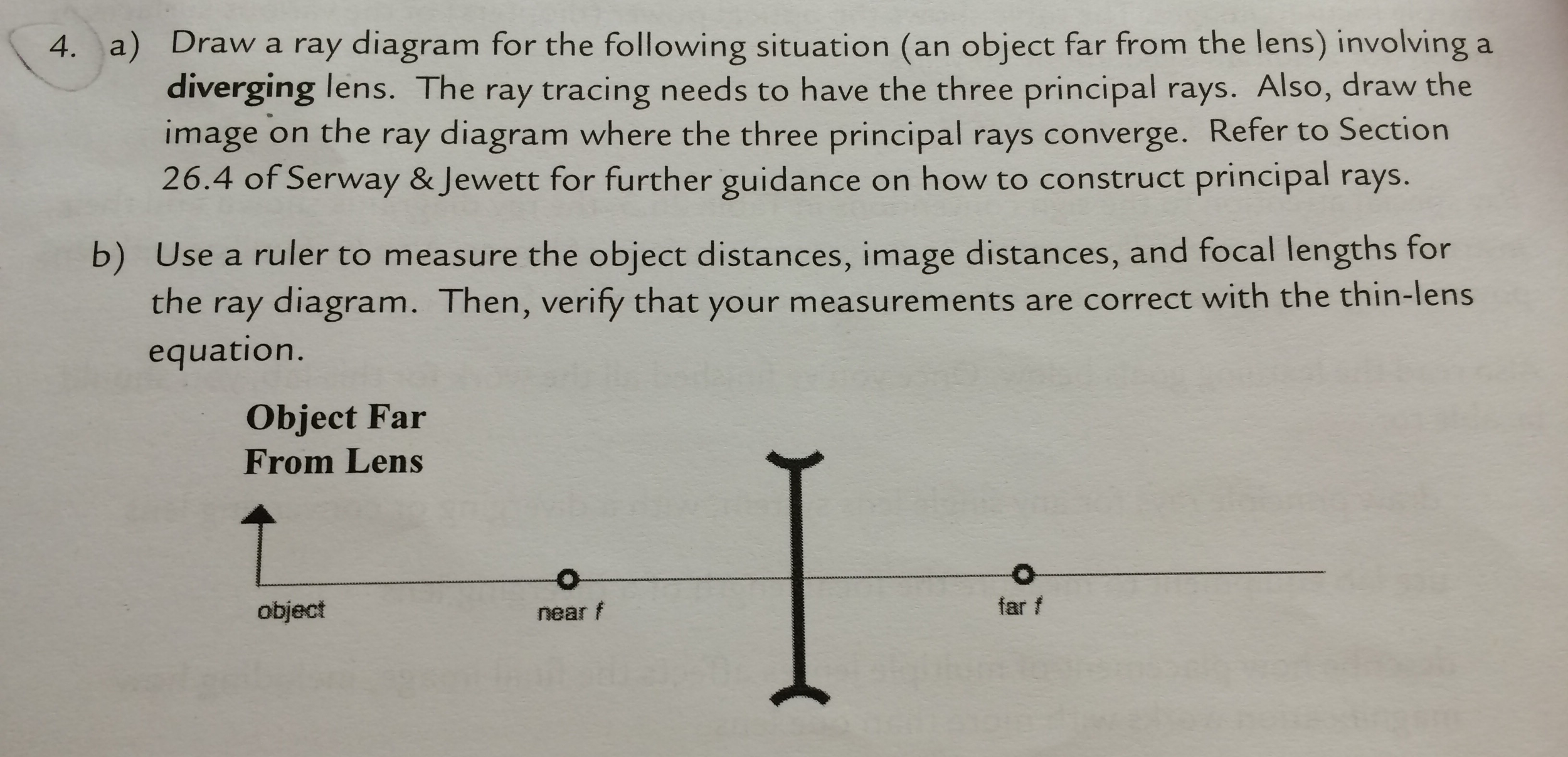
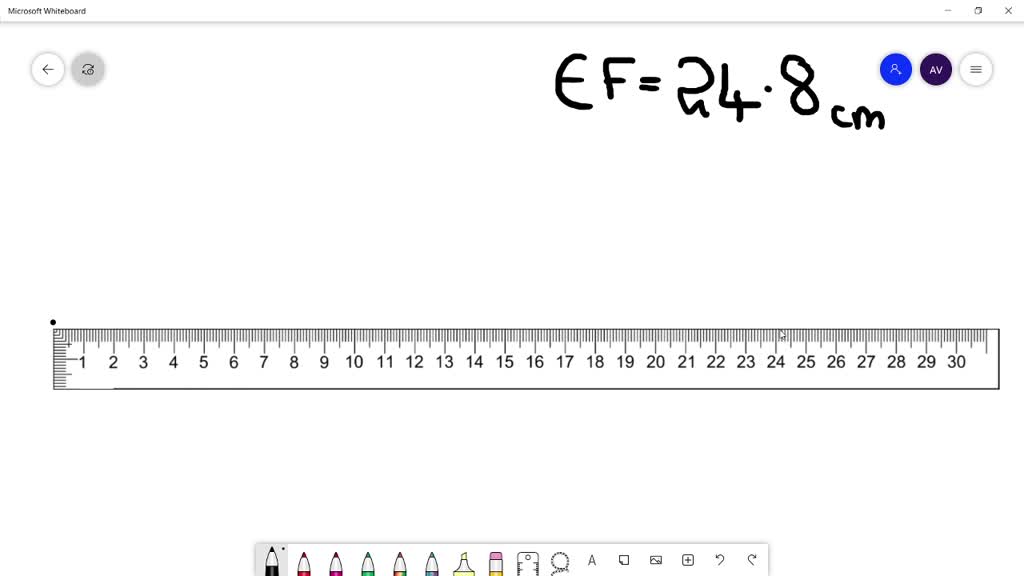
Problem: A) Draw a ray diagram for the following situation (an object far from the lens) where the three principle waves converge.B) Use a ruler to measure the object distances, image distances, and focal lengths for the ray diagram. Then verify that your measurements are correct with the thin-lens equation.
Once the method of drawing ray diagrams is practiced a couple of times, it becomes as natural as breathing. Each diagram yields specific information about the image. The two diagrams below show how to determine image location, size, orientation and type for situations in which the object is located at the 2F point and when the object is located ...
Two situations involving objects and diverging lenses are shown below. Draw three principal rays for these two situations. Also, draw the image on the ray diagram where the three principal rays converge and then describe the image in the space provided (i.e. relative location, magnification, orientation, etc.).
Draw A Ray Diagram In Each Of The Following Cases To Show The Formation Of Image When The Object Is Placed I Between Optical Centre And Principal Focu Physics Topperlearning Com
Draw ray diagrams showing the image formation by a concave lens when an object is placed (a) at the focus of the lens (b) between focus and twice the focal length of the lens (c) beyond twice the focal length of the lens - Get the answer to this question and access a vast question bank that is tailored for students.
Nov 26, 2021 · a) Draw a ray diagram for the following situation involving a converging lens. Subject: Physics Price: 2.85 Bought 3. Share With. a) Draw a ray diagram for the following situation involving a converging lens. The a) ray tracing needs to have the three principal rays. Also, draw the image on the ray diagram where the three principal rays converge.
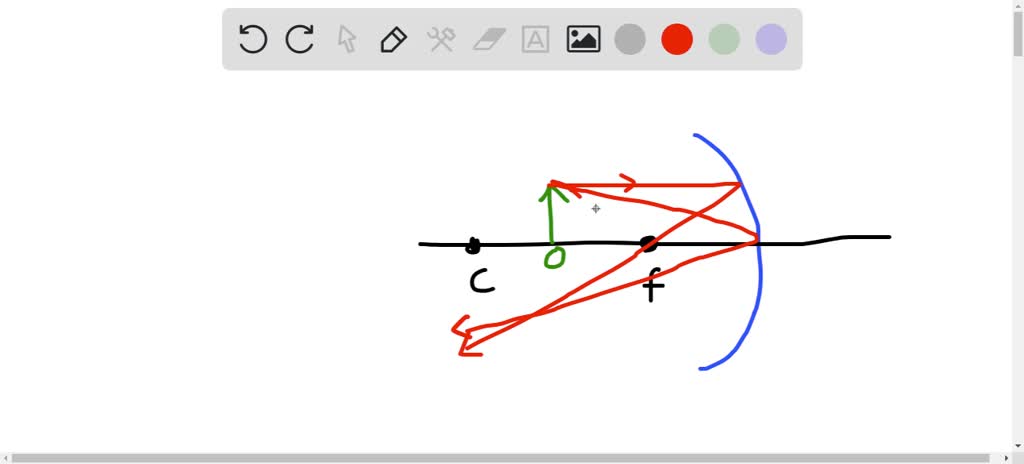
Solved Draw A Ray Tracing Diagram For The Following Situation An Object Is Placed Between The Focal Point F And A Concave Mirror Also Indicate If The Image Is Real Or Virtual And If
(c) Draw a ray diagram to show the formation of image in above situation. a) Optical centre is the point lying on the principal axis of a lens through which light passes through without undergoing any deviation.

Draw The Ray Diagram For Convergent Mirror When Object Is Placed Perpendicular On The Principal Axis Brainly In
First, we draw a ray parallel to principal axis. So, it passes through focus after refraction. We draw another ray which passes through Optical Center. So, the ray will go through without any deviation. Where both rays meet is point A'. And the image formed is A'B'. This image is formed between F 2 and 2F 2. We can say that.
Once the method of drawing ray diagrams is practiced a couple of times, it becomes as natural as breathing. Each diagram yields specific information about the image. The two diagrams below show how to determine image location, size, orientation and type for situations in which the object is located at the center of curvature and when the object ...
A) Draw a ray diagram for the following situation ( an object far from the lens) involving a diverging lens. The ray tracing needs to have the three principal rays. B) Use a ruler to measure the object distances, image distances, and focal lengths for the ray diagram. Then verify that your measurements are correct with the thin-lens equation.
Ray diagrams help us trace the path of the light for the person to view a point on the image of an object. Ray diagram uses lines with arrows to represent the incident ray and the reflected ray. It also helps us trace the direction in which the light travels. Plane Mirror vs Spherical Mirrors.
Draw A Ray Diagram To Show Image Formation When The Concave Mirror Produces A Real Inverted And Magnified Image Of The Object Zigya
A draw a ray diagram for the following situation an object far from the lens involving a diverging lens. Step by step method for drawing ray diagrams. If an object is located between the focal point and converging lens the image will be. Through the center of the lens. Also draw the image on the ray diagram where the three principal rays converge.

The Following Figure Shows A Concave Mirror With Its Pole P Focus F And Center Of Curvature C Draw A Ray Diagram To Show The Formation Of The Image Of An Object
A) Draw a ray diagram for the following situation (an object far from the lens) involving a diverging lens.The ray tacing needs to have the three principal rays.Also draw the image on the ray diagram where the three principle waves converge.. B) Use a ruler to measure the object distances, image distances, and focal lengths for the ray diagram.
Jul 15, 2018 · A draw a ray diagram for the following situation an object far from the lens involving a diver. The first picture below shows how to draw a ray diagram. A ray diagram for an object that is between f and 2f. Also draw the image on the ray diagram where the three principal rays converge. Through the focal point in front of the lens.
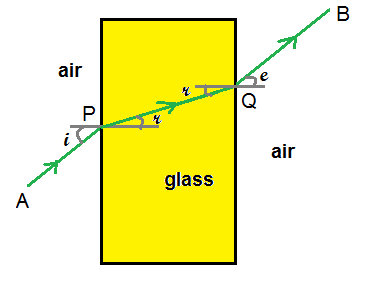
Draw A Ray Diagram To Show The Refraction Of Light Through The Glass Slab And Mark Angle Of Refraction And The Lateral Shift Suffered By The Ray Of Li Science
Draw a ray diagram for concave mirror when object is placed between focus and centre of curvature. Also write position, nature and size of image. Medium. View solution >; A point source of light S, placed at a distance L in front of the centre of a plane mirror of width d, hangs vertically on a wall.
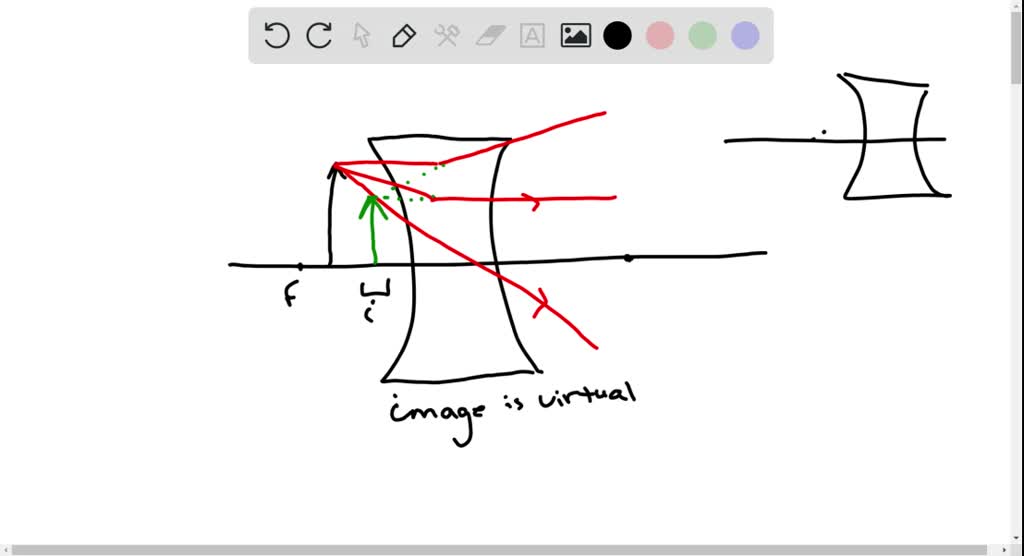
Solved Draw A Ray Tracing Diagram For The Following Situation An Object Is Placed Between The Focal Point F And The Convex Lens Also Indicate If The Image Is Real Or Virtual And
PART 5 - DRAWING RAY DIAGRAMS Draw a ray diagram for each situation, using the 3 principal rays. Use a ruler to measure all dimensions. For each ray diagram identify the following (list near diagram): 1. d i - the image distance (cm ok) 2. is image inverted or upright? 3. is image real or virtual ? 4. is image magnified or reduced?
Drawing Ray Diagrams - a Step-by-Step Approach. This section of Lesson 2 details and illustrates the procedure for drawing ray diagrams. Let's begin with the task of drawing a ray diagram to show how Suzie will be able to see the image of the green object arrow in the diagram below. For simplicity sake, we will suppose that Suzie is viewing the ...
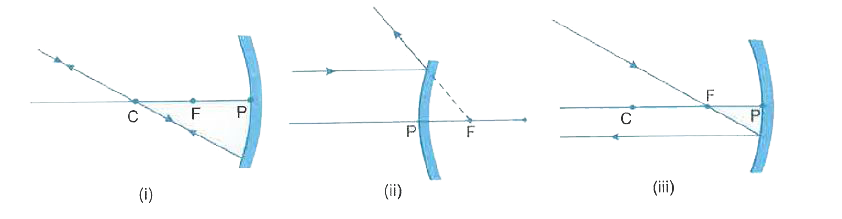
Draw Ray Diagrams For The Following Cases When A Ray Of Light I Passing Through Centre Of Curvature Of A Concave Mirror Is Incident On It Ii Parallel To Principal Axis
Draw A Ray Diagram In Each Of The Following Cases For A Concave Mirror When Magnitude Of Magnification Is Sarthaks Econnect Largest Online Education Community
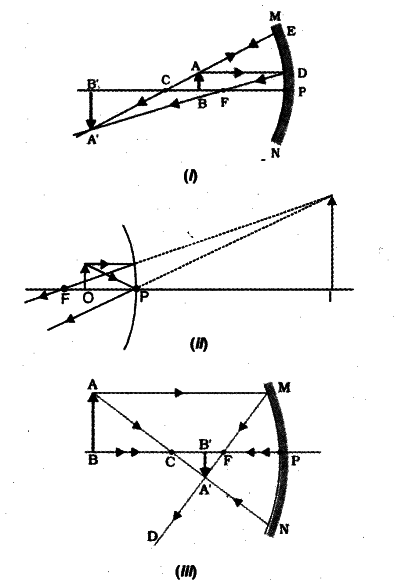
Draw A Ray Diagram In Each Of The Following Cases To Show The Position And Nature Of The Image Formed When Object Is Placed Cbse Class 10 Science Learn Cbse Forum

18 Draw A Ray Diagram For The Following Positions Of The Object Placed In Front Of A Convex Lens 5 Brainly In











0 Response to "37 draw a ray diagram for the following situation"
Post a Comment