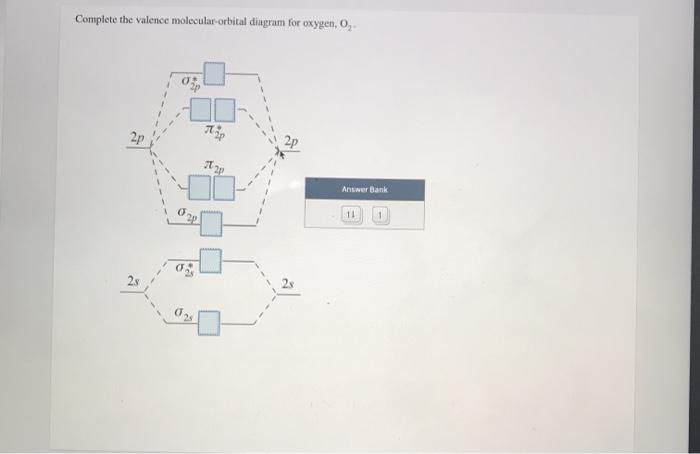
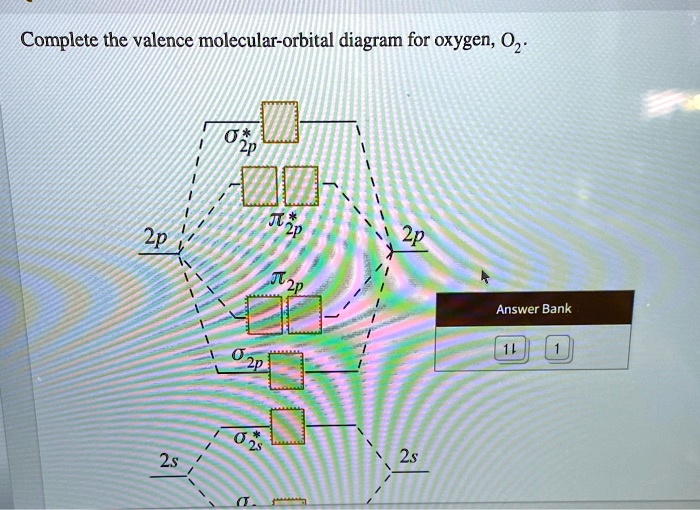
39 complete this valence molecular-orbital diagram for oxygen o2
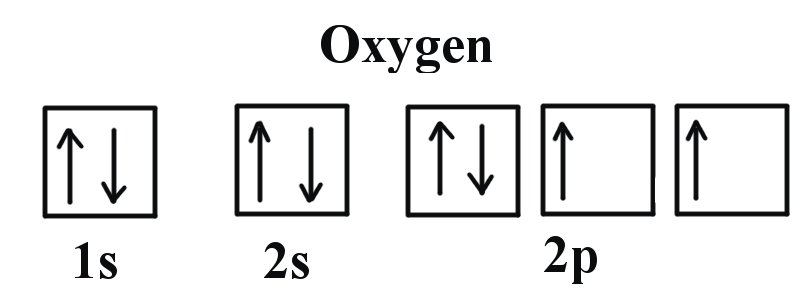
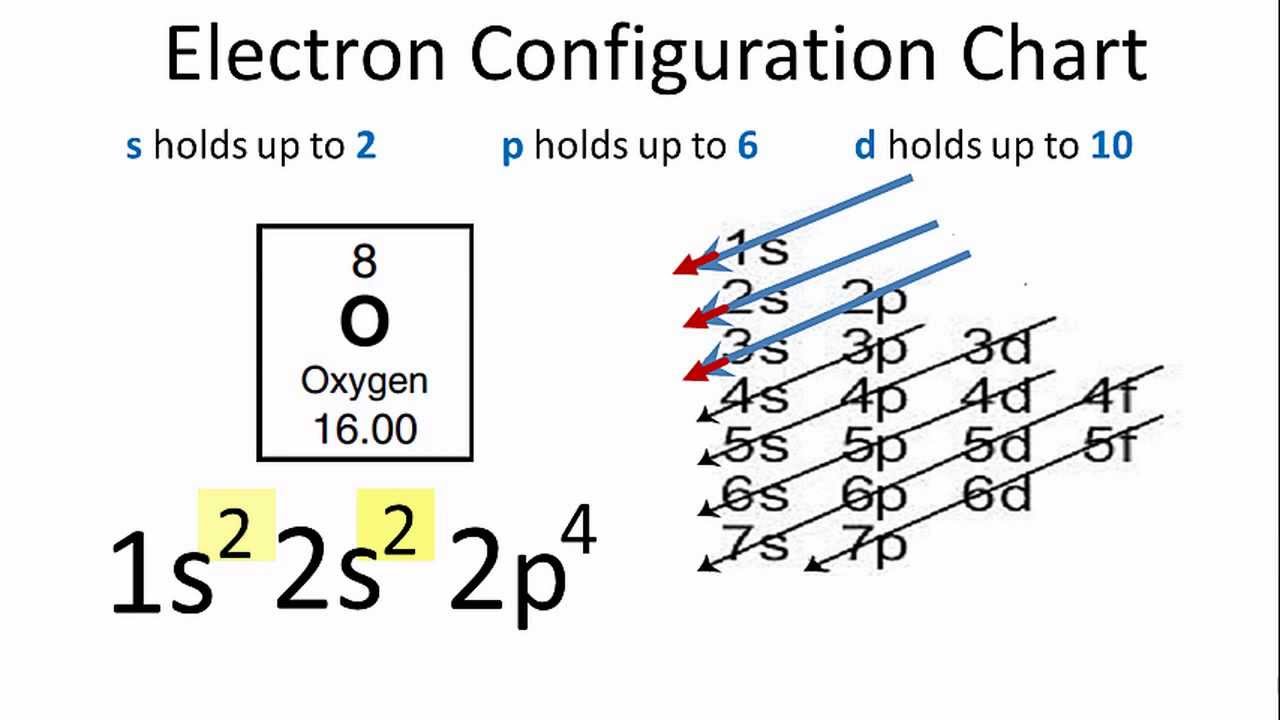
We can use the molecular orbital diagram of oxygen molecules to explain the paramagnetic behaviour of oxygen atoms. We also have to know that for the paramagnetic nature of a molecule, it should contain a minimum of one unpaired electron. Complete answer: The valence bond theory could not explain the paramagnetic nature of oxygen molecules. Oxygen electron configuration is 1s 2 2s 2 2p 4.The period of oxygen is 2 and it is a p-block element. This article gives an idea about the electron configuration of oxygen(O) and orbital diagram, period and groups, valency and valence electrons of oxygen, bond formation, compound formation, application of different principles. The eighth element in the periodic table is oxygen.
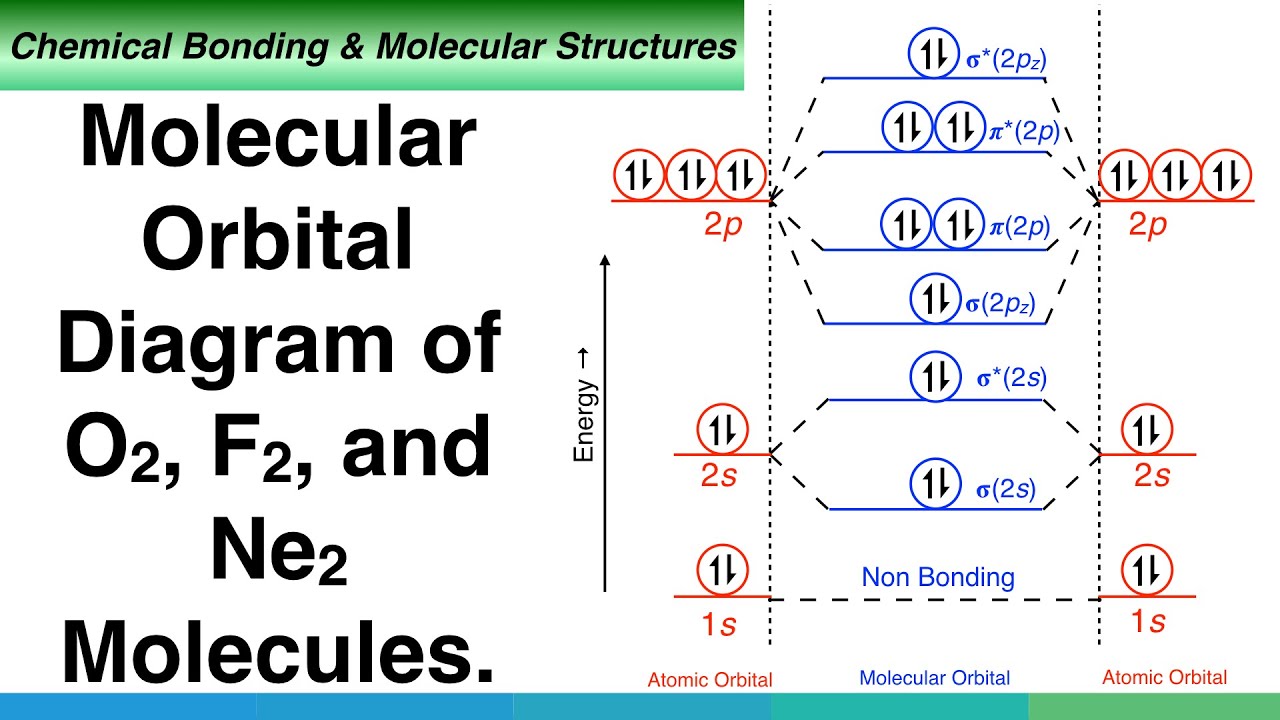
Match. Gravity. place the following molecular orbitals in order of decreasing energy for species of O2, F2, and Ne2. start with the highest energy molecular orbital at the top of the list. Click card to see definition 👆. Tap card to see definition 👆. 1.) o*2p. 2.) pie*2p. 3.) pie2p. 4.) o2p.
Complete this valence molecular-orbital diagram for oxygen o2
number of valence electrons) with O2. Therefore, NF is predicted to be paramagnetic with a bond order of 2. The populations of the bonding (8 electrons) and antibonding (4 electrons) molecular orbitals in the diagram suggest a double bond. c. The 2s, 2s *, 2p, and 2p * orbitals exhibit C v symmetry, with the NF bond axis the infinite-fold Triplet Oxygen Wikipedia . Youll need the molecular orbital MO diagram of O2. Valence electron configuration of o2. 79 211 ratings FREE Expert Solution. The molecular orbital diagram for an O2 molecule would therefore ignore the 1s electrons on both oxygen atoms and pay attention to the interactions between the 2s and 2p valence orbitals. You'll need the molecular orbital (MO) diagram of "O"_2. Begin with the atomic orbitals. Oxygen atom has 2s and 2p valence orbitals and 6 valence electrons: Each oxygen contributes 6, so we distribute 12 valence electrons into the molecule to get "O"_2. Two 2s orbitals combine to give a sigma_(2s) bonding and sigma_(2s)^"*" antibonding MO.
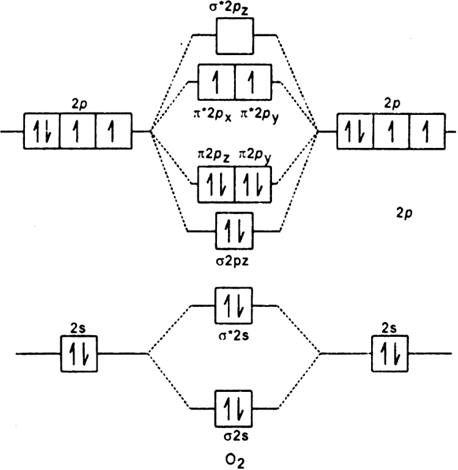
Complete this valence molecular-orbital diagram for oxygen o2. Thus, oxygen molecule has two bonds. i.e., one is bond and one p bond. The last two electrons in p 2 p x ∙ and p 2 p y ∙ orbitals will remain unpaired. Therefore, oxygen molecule has paramagnetic character due to the presence of two unpaired electrons. Question: Complete the molecular orbital diagram for CN. Note that the 1s orbitals are not shown. Identify the bond order of CN. O2 01 OOOOO 25- 0 2s Answer Bank The atomic orbitals on the left side of the molecular orbital diagram are those of The atomic orbitals on the right side of the molecular orbital diagram are those of. electronic state. Complete the molecular orbital diagram for NO by filling in the valence electrons in the occupied orbitals. Sketch the shape of the π and π* orbitals, clearly showing all nodes. Determine the bond order of NO and whether it is paramagnetic or diamagnetic. Marks 6 MO orbital energy level diagram for NO Sketch of the π MO Summary MO Theory • LCAO-MO Theory is a simple method for predicting the approximate electronic structure of molecules. • Atomic orbitals must have the proper symmetry and energy to interact and form molecular orbitals. • Photoelectron spectroscopy provides useful information on the energies of atomic orbitals. • Next we'll see that symmetry will help us treat larger molecules in
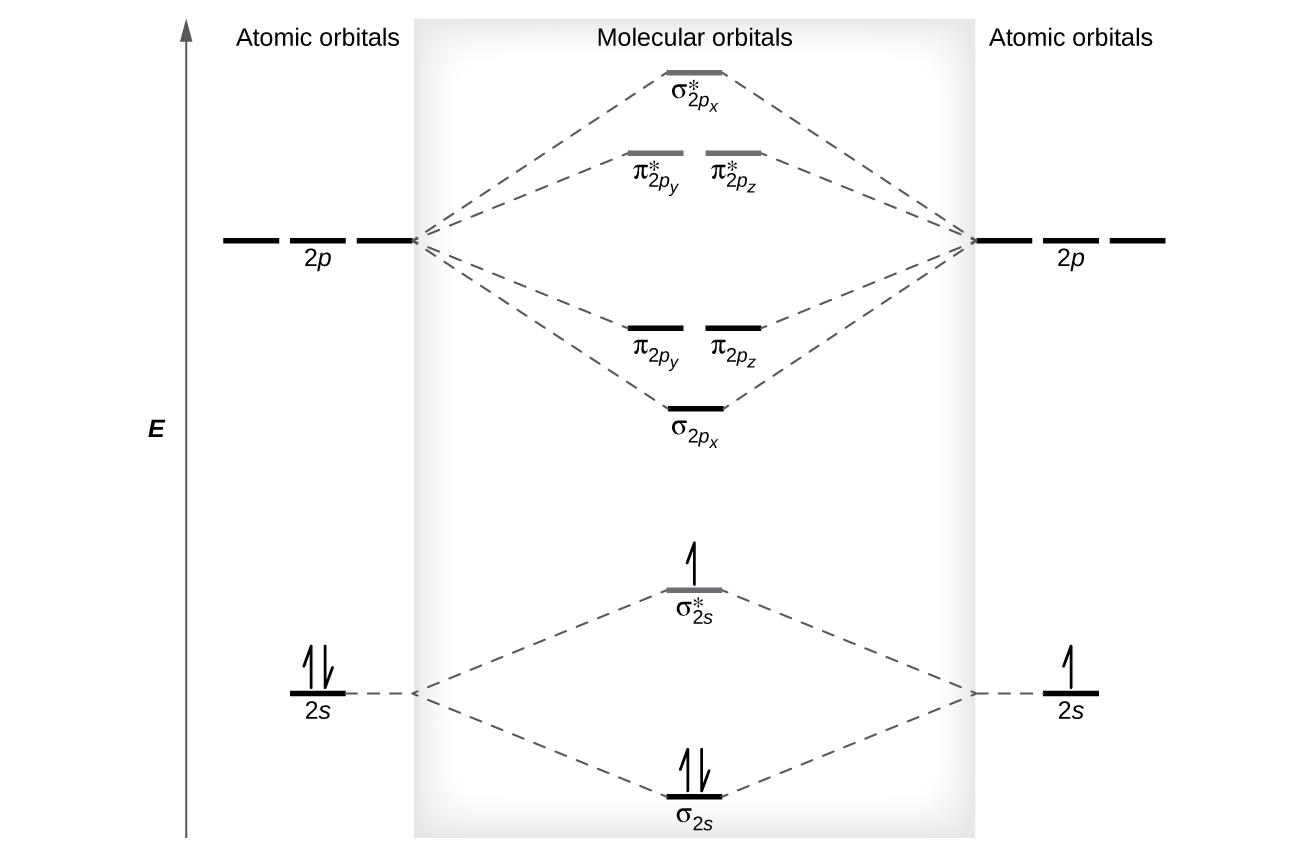
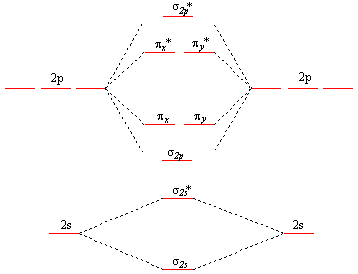
The only orbitals that are important in our discussion of molecular orbitals are those formed when valence-shell orbitals are combined. The molecular orbital diagram for an O 2 molecule would therefore ignore the 1 s electrons on both oxygen atoms and concentrate on the interactions between the 2 s and 2 p valence orbitals. In order to draw oxygen's molecular orbital diagram, you need to start by taking a look at what atomic orbitals you have for an oxygen atom, #"O"#.. As you know, oxygen is located in period 2, group 16 of the periodic table and has an atomic number equal to #8#.This means that the electron configuration of a neutral oxygen atom must account for #8# electrons. Problem Details. Construct the molecular orbital diagram for He 2 and then identify the bond order. Click within the blue boxes to add electrons. Bond order: a) 0. b) 0.5. c) 1. d) 1.5. e) 2. Simple Molecular Orbitals - Sigma and Pi Bonds in Molecules An atomic orbital is located on a single atom. When two (or more) atomic orbitals overlap to make a bond we can change our perspective to include all of the bonded atoms and their overlapping orbitals. Since more than one atom is involved, we refer to these orbitals as molecular orbitals.
Number of valence electrons in Be atom = 2 Thus in the formation of Be 2 molecule, two outer electrons of each Be atom i.e. 4 in all, have to be accommodated in various molecular orbitals in the increasing order of their energies. The electrons in each atomic orbital are represented by arrows. Complete the valence molecular-orbital diagram for oxygen, O, Answer Bank. Complete the valence molecular-orbital diagram for oxygen, O, Answer Bank Construct the molecular orbital diagram for He2 and then identify the bond order. Bond order: Click... Construct the molecular orbital diagram for He2 and then identify the bond order. The molecular orbital diagram for an o 2 molecule would therefore ignore the 1s electrons on both oxygen atoms and concentrate on the interactions between the 2s and 2p valence orbitals. Learn about the molecular orbital diagram for o2 using these free and printable molecular orbital diagram as your reference in understanding the mo of oxygen. Of oxygen is 8. Atoms can either donate or receive electrons only in valence shell. 8 electrons in outermost shell is considered the most stable state of an atom as the shell will be fully occupied. The valency of oxygen is 2 as its electronic configuration is 2,6 and it need 2 electron to complete their octet.

Symmetry Free Full Text Chemical Reasoning Based On An Invariance Property Bond And Lone Pair Pictures In Quantum Structural Formulas Html
Question: Complete the molecular orbital diagram for CN. Note that the 1s orbitals are not shown. Identify the bond order of CN. O2 01 OOOOO 25- 0 2s Answer Bank The atomic orbitals on the left side of the molecular orbital diagram are those of The atomic orbitals on the right side of the molecular orbital diagram are those of.
So, next one electron will go into 1s shell of anti-bonding orbital. Answer to Construct the molecular orbital diagram for H2- and then identify the bond order. Bond order: Click thin the blue boxes. The hydrogen atom is the simplest atom, and its molecule \ (\ce {H2}\) is get a sigma (s) bonding orbital, denoted as s1s in the diagram here.
This means that the electron configuration of a neutral oxygen atom must account for 8 electrons. The molecular orbital diagram for an O2 molecule would therefore ignore the 1s electrons on both oxygen atoms and concentrate on the interactions between the 2s and 2p valence orbitals. image via upload.wikimedia.org. image via upload.wikimedia.org.

Lewis Structure Oxygen Electron Shell Molecular Orbital Diagram Germanium Chemical Element Text Png Pngegg
The o2 mo diagram will have one more electron compared to o2 and the o2 mo diagram will have one fewer electron compared to o2. The molecular orbital diagram for an o2 molecule would therefore ignore the 1s electrons on both oxygen atoms and concentrate on the interactions between the 2s and 2p valence orbitals.
Complete this valence molecular orbital diagram for oxygen o2. Click the blue boxes to add electrons as needed. Complete these structures by adding bonds and lone pairs as necessary. This video shows the construction of a molecular orbital mo diagram for the diatomic molecule o2 using the valence electrons of each oxygen.
Molecular Orbital Diagram for Oxygen Gas (O2).Fill from the bottom up, with 12 electrons total.Bonding Order is 2, and it is Paramagnetic.sigma2s(2),sigma2s*...
Printable O2 molecular orbital diagrams are available for you to guide your study in the molecular orbital lesson.This diagram is a qualitative descriptive tool explaining chemical bonding in molecules in terms of a molecular orbital theory in general and the linear combination of atomic orbitals (LCAO) molecular orbital method in particular.
Atomic oxygen has 6 valence electrons and 4 valence orbitals (2s, 2p x, 2p y, and 2p z). We can draw a Lewis structure of molecular oxygen with a double bond between the oxygen atoms and 2 non-bonding pairs of electrons on each atom. However, experimentally we can determine that O 2 has 2 unpaired electrons. The Lewis structure seems to be ...
A molecular orbital diagram, or MO diagram, is a qualitative descriptive tool explaining chemical bonding in molecules in terms of molecular orbital theory in general and the linear combination of atomic orbitals (LCAO) molecular orbital method in particular.The Hydrogen Molecule Ion H2+Molecular Orbital Diagrams of Diatomic Molecules - Chem
Experts are tested by Chegg as specialists in their subject area. We review their content and use your feedback to keep the quality high. Transcribed image text: Complete this valence molecular-orbital diagram for oxygen, O2. Click the blue boxes to add electrons as needed.
The orbital diagram for a diatomic molecule is. To find the bond order, add the 15 electrons in the molecular orbitals (the blue-colored energy levels in the diagram) one at a time until you have used them up. They completely fill all the orbitals except the highest-energy antibonding sigma 2p orbital.
You'll need the molecular orbital (MO) diagram of "O"_2. Begin with the atomic orbitals. Oxygen atom has 2s and 2p valence orbitals and 6 valence electrons: Each oxygen contributes 6, so we distribute 12 valence electrons into the molecule to get "O"_2. Two 2s orbitals combine to give a sigma_(2s) bonding and sigma_(2s)^"*" antibonding MO.
Triplet Oxygen Wikipedia . Youll need the molecular orbital MO diagram of O2. Valence electron configuration of o2. 79 211 ratings FREE Expert Solution. The molecular orbital diagram for an O2 molecule would therefore ignore the 1s electrons on both oxygen atoms and pay attention to the interactions between the 2s and 2p valence orbitals.

Use Mo Diagrams And The Bond Order From Them To Answer Each Of The Following Questions A Is O2 Stable Or Unstable B Is Be2 Diamagnetic Or Paramagnetic Study Com
number of valence electrons) with O2. Therefore, NF is predicted to be paramagnetic with a bond order of 2. The populations of the bonding (8 electrons) and antibonding (4 electrons) molecular orbitals in the diagram suggest a double bond. c. The 2s, 2s *, 2p, and 2p * orbitals exhibit C v symmetry, with the NF bond axis the infinite-fold
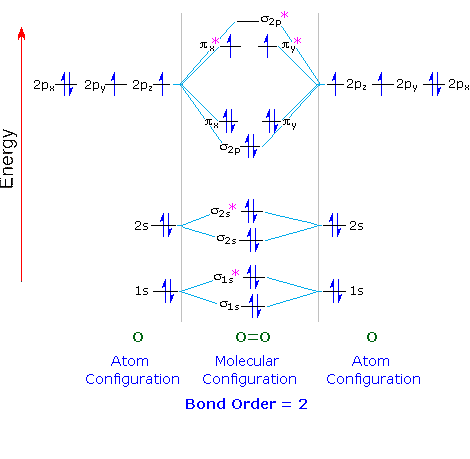
Draw The Molecular Orbital Energy Diagram For Oxygen Molecule O2 And Show That I It Has A Double Bond Ii It Has Paramagnetic Character From Chemistry Chemical Bonding And Molecular Structure Class 11 Cbse

Complete This Molecular Orbital Diagram For Cn Then Determine The Bond Order Note That The 1s Homeworklib

Draw The Molecular Orbital Diagram For Co Based On Your Diagram Why Does Co Always Bond Through The Carbon And Not The Oxygen Atom Study Com

Berkas Valence Orbitals Of Oxygen Atom And Dioxygen Molecule Diagram Svg Wikipedia Bahasa Indonesia Ensiklopedia Bebas















0 Response to "39 complete this valence molecular-orbital diagram for oxygen o2"
Post a Comment