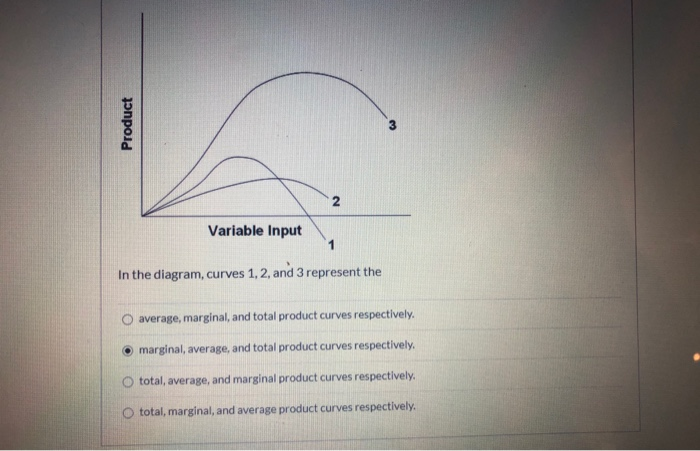
39 in the diagram, curves 1, 2, and 3 represent
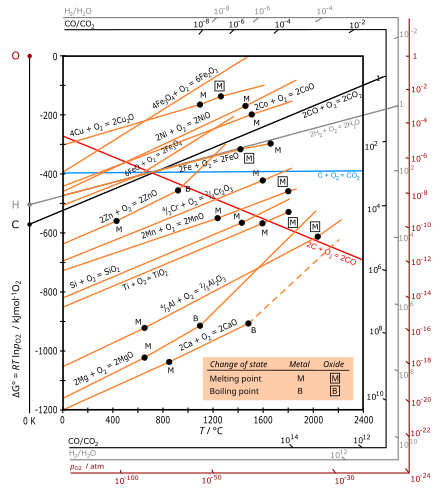
Chapter 9 - 10 Phase Diagrams • Indicate phases as function of T, Co, and P. • For this course:-binary systems: just 2 components.-independent variables: T and Co (P = 1 atm is almost always used). • Phase Diagram The above diagram suggests that: curves 1, 2, and 3 represent the: when marginal product lies above average product, average product is rising Suppose that a business incurred explicit costs of $1 million and implicit cost of $200,000 in a specific year.
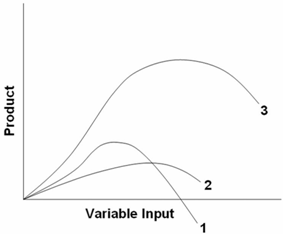
In the diagram, curves 1, 2, and 3 represent the: marginal, average, and total product curves respectively. In the figure, curves 1, 2, 3, and 4 represent the: MC, ATC, AVC, and AFC curves respectively. The diagram suggests that: when marginal product lies above average product, average product is rising.
In the diagram, curves 1, 2, and 3 represent
In the above diagram curves 1 2 and 3 represent the a. 24. In the above diagram curves 1, 2, and 3 represent the:A. average, marginal, and total product curves respectively. B. marginal, average, and total product curves respectively. C. total, average, and marginal product curves respectively. D. total, marginal, and average product curves ... In the diagram curves 1,2,3 represent. total fixed cost, total variable cost, and total cost respectively. If a firm wanted to know how much it would save by producing one less unit of output, it would look to: MC. A device 'X' is connected to an ac source V=V0sinωt. The variation of voltage, current and power in one cycle is shown in the following graph:a) Identify the device 'X'.b) Which of the curves A, B and C represent the voltage, current and the power consumed in the circuit? Justify your answer.c) How does its impedance vary with frequency of the ac source?
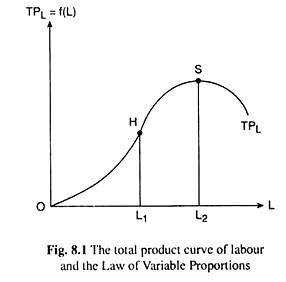
In the diagram, curves 1, 2, and 3 represent. suppose we want to customize the graph above by making the x curve a red line, x2 curve a dashed line, the x3 curve an orange line, and the x4 curve a thick line, we would input: Plot x, x^2, x^3, x^4 , x,-1, 1 , PlotStyle Æ Red, Dashed, Orange, Thick -1.0 -0.5 0.5 1.0-1.0-0.5 0.5 1.0 And now we can readily tell one graph from another. 3 2 x lny O 1.5,1.2 5.24,2.7 The variables xand ysatisfy the equation y2 = Aekx, where Aand kare constants.The graph of lnyagainst xis a straight line passing through the points 1.5, 1.2 and 5.24, 2.7 as shown in the diagram. Find the values of Aand kcorrect to 2 decimal places.[5] In the above diagram curves 1, 2, and 3 represent the: A) average, marginal, and total product curves respectively. B) marginal, average, and total product curves respectively. C) total, average, and marginal product curves respectively. D) total, marginal, and average product curves respectively. Answer: B In Fig. 13.12 the curves Q 0 - Q 1 and Q 2 are isoquants depicting a representative production function. The isocost lines KL, K'L' and K"L" represent the minimum costs of producing each of the three output levels, since they are tangent to the respective isoquants. Since we do not assume any change in the factor-price ratio up to ...
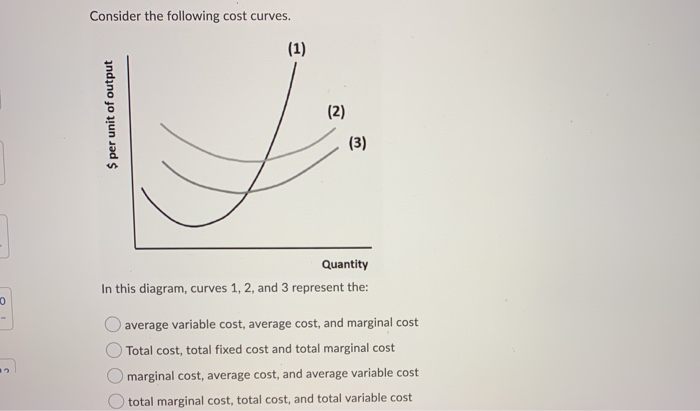
13. In the diagram below, curves 1, 2, and 3 represent: A. average variable cost, marginal cost, and average fixed cost respectively. B. total variable cost, total fixed cost, and total cost respectively. C. total fixed cost, total variable cost, and total cost respectively. In the above diagram the range of diminishing marginal returns is. Curves 1 2 and 3 represent marginal average and total product curves respectively. Marginal Product Of Labor Wikipedia When marginal product lies above average product average product is rising. In the diagram total product will be at a maximum at. The average product ap when ... Gradients of straight-line graphs - Intermediate and Higher tier Finding the gradient. The gradient of a straight line describes the slope or steepness of the line. In the figure, curves 1, 2, 3, and 4 represent the: MC, ATC, AVC, and AFC curves respectively. Refer to the diagram. This firm's average fixed costs are: the vertical distance between AVC and ATC. ... Curve (1) in the diagram is a purely competitive firm's: total economic profit curve.
3 Version 0.1 Turn over 0 2 In the diagram below, SRPC 1 and SRPC 2 represent short-run Phillips curves and LRPC represents the long-run Phillips curve. Which one of the following would explain a movement from point X to Y? A A fall in taxation B An increase in government expenditure C A cut in real interest rates 11. In the above diagram curves 1, 2, and 3 represent the: A) average, marginal, and total product curves respectively. B ) marginal, average, and total product curves respectively. C) total, average, and marginal product curves respectively. D) total, marginal, and average product curves respectively. 12. Set Symbols. A set is a collection of things, usually numbers. We can list each element (or "member") of a set inside curly brackets like this: Common Symbols Used in Set Theory. Symbols save time and space when writing. Download scientific diagram | A typical UCST-type phase diagram, curve 1, curve 2 and curve 3 represent crystallization temperature curve, spinodal curve and binodal curve, respectively from ...
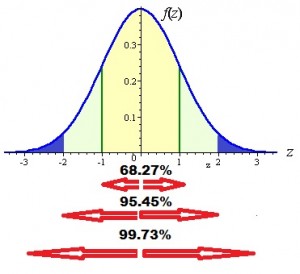
Properties of a Normal Curve 1.All Normal Curves have the same general bell shape. 2.The curve is symmetric with respect to a vertical line that passes through the peak of the curve. 3.The curve is centered at the mean which coincides with the median and the mode and is located at the point beneath the peak of the curve.
Solved In The Above Diagram Curves 1 2 And 3 Represent Average Variable Cost Marginal Cost And Average Fixed Cost Respectively Variable Cost Course Hero
In the above figure, curves 1, 2, 3, and 4 represent the: A. ATC, MC, AFC, and AVC curves respectively. B. AFC, MC, AVC, and ATC curves respectively. ... The above diagram shows the short-run average total cost curves for five different plant sizes of a firm. In ...
C = 100 + .5 Y_D I = 100 + .1 Y - 500 i G = 100 T = .2 Y The public holds one-third of its money in currency (c = 1/3) and two-thirds of its money in checkable deposits. Banks hold one-quarter of ...
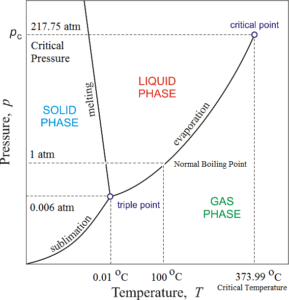
Consider the phase diagram for carbon dioxide shown in Figure 5 as another example. The solid-liquid curve exhibits a positive slope, indicating that the melting point for CO 2 increases with pressure as it does for most substances (water being a notable exception as described previously). Notice that the triple point is well above 1 atm, indicating that carbon dioxide cannot exist as a liquid ...
In the diagram, curves 1, 2, and 3 represent the: 18. The question is based on the following table that provides information on the production of a product that requires on variable input. Refer to the above table. Marginal product is zero when the total product is: 19.
Calculated phase diagram of the MgO-Al 2 O 3 -SiO 2 system. The thick curves represent three-phase equilibria with the liquid phase. The labeled areas show the liquidus surfaces for various solids.
4.1.1 Recognize a function of two variables and identify its domain and range. 4.1.2 Sketch a graph of a function of two variables. 4.1.3 Sketch several traces or level curves of a function of two variables. 4.1.4 Recognize a function of three or more variables and identify its level surfaces. Our first step is to explain what a function of ...
In the diagram, curves 1, 2, and 3 represent the: marginal, average, and total product curves respectively. The basic difference between the short run and the long run is that: at least one resource is fixed in the short run, while all resources are variable in the long run.
Basics 3 4.16 kV Bus 1-Line : Basics 4 600 V 1-Line : Basics 5 480 V MCC 1-Line : Basics 6 7.2 kV 3-Line Diagram : Basics 7 4.16 kV 3-Line Diagram : Basics 8 AOV Elementary & Block Diagram : Basics 9 4.16 kV Pump Schematic : Basics 10 480 V Pump Schematic : Basics 11 MOV Schematic (with Block included) Basics 12 12-/208 VAC Panel Diagram
Real Number Venn Diagram. In Mathematics, set is an ordered group of objects and can be denoted in a set builder form or roster form. Generally, sets are denoted in curly braces {}. For example, A = { 1,2,3,4} is a set. The set of real numbers includes the set of rational numbers and the set of irrational numbers.
In the diagram, what do Curves 1, 2, and 3 represent? a. Average, marginal, and total product respectively b. Marginal, average, and total product respectively c. Total, average, and marginal product respectively d. Total, marginal, and average product respectively; Question: In the diagram, what do Curves 1, 2, and 3 represent? a.
A device 'X' is connected to an ac source V=V0sinωt. The variation of voltage, current and power in one cycle is shown in the following graph:a) Identify the device 'X'.b) Which of the curves A, B and C represent the voltage, current and the power consumed in the circuit? Justify your answer.c) How does its impedance vary with frequency of the ac source?
In the diagram curves 1,2,3 represent. total fixed cost, total variable cost, and total cost respectively. If a firm wanted to know how much it would save by producing one less unit of output, it would look to: MC.
In the above diagram curves 1 2 and 3 represent the a. 24. In the above diagram curves 1, 2, and 3 represent the:A. average, marginal, and total product curves respectively. B. marginal, average, and total product curves respectively. C. total, average, and marginal product curves respectively. D. total, marginal, and average product curves ...

Simpler And Faster Covid 19 Testing Strategies To Streamline Sars Cov 2 Molecular Assays Ebiomedicine

Managing The Software Enterprise The Organisational And Business Context 1 4 Return On Investment Openlearn Open University M882 1
Processes Of Excitation And Deactivation Of Excitation Energy In Organic Wavelength Transformers Cooperating With Solar Photovoltaic Cells
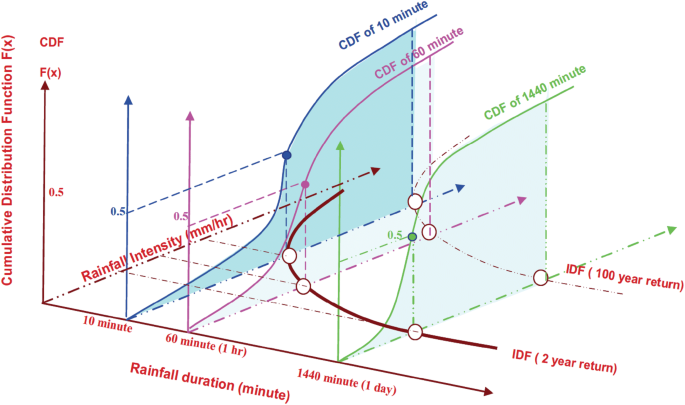
Deriving Intensity Duration Frequency Idf Curves Using Downscaled In Situ Rainfall Assimilated With Remote Sensing Data Geoscience Letters Full Text
Past Papers Solutions Cambridge International Examinations Cie As A Level Mathematics 9709 Pure Mathematics 1 P1 9709 01 Year 2018 Oct Nov P1 9709 11 Q 7 O A Level Solutionso A Level Solutions
Exact Dispersion Relations For The Hybrid Plasmon Phonon Modes In Graphene On Dielectric Substrates With Polar Optical Phonons

/marginal_rate_of_substitution_final2-893aa48189714fcb97dadb6f97b03948.png)
/supply_curve_final-465c4c4a89504d0faeaa85485b237109.png)

















0 Response to "39 in the diagram, curves 1, 2, and 3 represent"
Post a Comment