40 crystal field energy level diagram
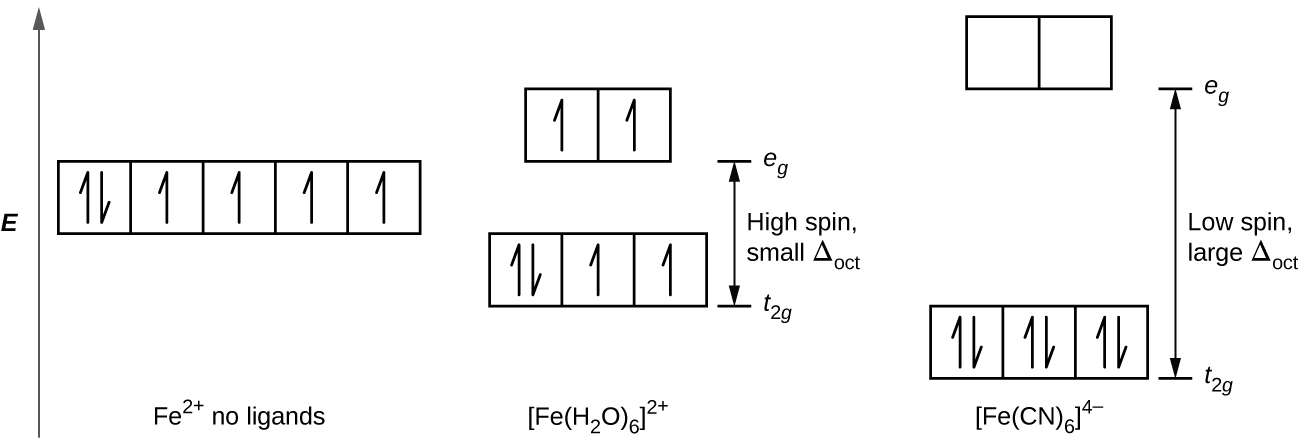
Iron(II) complexes have six electrons in the 5d orbitals. In the absence of a crystal field, the orbitals are degenerate. For coordination complexes with strong-field ligands such as [Fe(CN) 6] 4−, Δ oct is greater than P, and the electrons pair in the lower energy t 2g orbitals before occupying the eg orbitals. With weak-field ligands such as H 2 O, the ligand field splitting is less than ... The crystal field energy-level diagram. Label all orbitals and fill with the appropriate. number of electrons. (b) (2 pts.) Is the complex paramagnetic or diamagnetic? Circle one (c) (2 pts.) Calculate the crystal field stabilization energy (CSFE) in terms of "Dq" (where 10Dq is
A complete 4f{sup n} energy level diagram is calculated for all trivalent lanthanide ions in LaF{sub 3}. The calculated energy levels are compared with experimentally obtained energies. For Ce, Pr, Nd, Eu, Gd, Ho, Er, Tm and Yb many, and in some cases all, energy levels have been observed.

Crystal field energy level diagram
Using crystal field theory, draw energy level diagram, write electronic configuration of the central metal atom/ion and determine the magnetic moment value in the following. ( i ) . [ C o F 6 ] 3 − , [ C o ( H 2 O ) 6 ] 2 + , [ C o ( C N ) 6 ] 3 − For the following, consider a field that has a z-axis that is vertical, a y-axis that is horizontal, and x-axis that is coming out of page. (a) Draw pictures of the d 2 2 2 x -y and d z orbitals (b) Predict the relative energy of d 2 2 crystal field that is along the y-axis x -y in an octahedral crystal field compared to a linear Draw a crystal field energy-level diagram, assign the electron to orbitals, and predict the number of unpaired electrons for {eq}\displaystyle \rm tris(en)cuprate(II) {/eq} ({eq}\displaystyle \rm ...
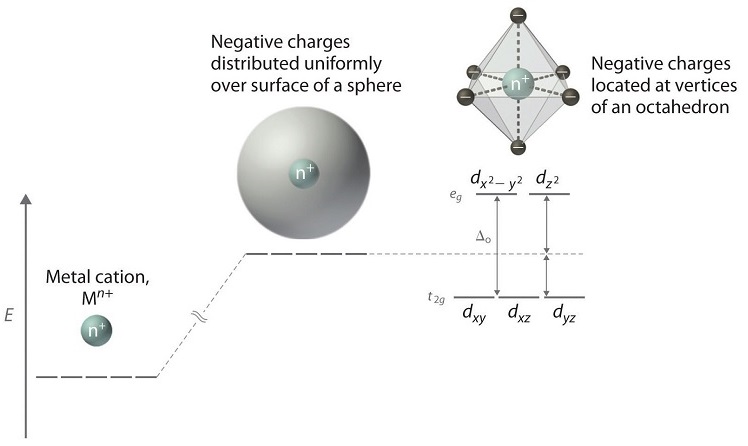
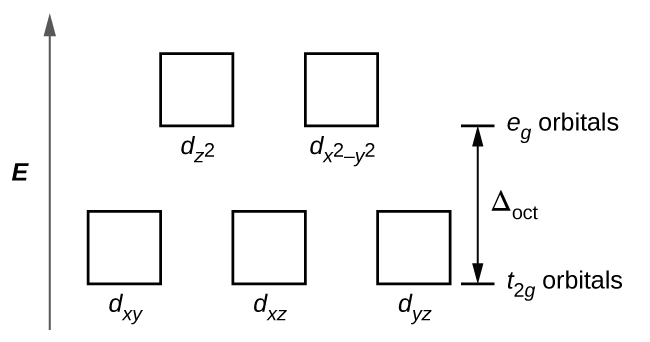
Crystal field energy level diagram. D-orbital splitting diagrams Use crystal field theory to generate splitting diagrams of the d-orbitals for metal complexes with the following coordination patterns: 1. Octahedral 2. Tetrahedral 3. Trigonal bipyramidal 4. Square pyramidal d z2x2-y d xy d yzxz 5. Square planar d z2x2-y d xy d yzxz d z2 d x2-yxy d yz d xz d z2 d x2-y2 d xy d yz d ... Hence, the crystal field splitting Δ o decreases when ligand to metal bonding takes place. The overall molecular orbital energy level diagram for this type of π-bonding in octahedral complexes can be shown as: Buy the complete book with TOC navigation, high resolution images and no watermark. Energy level of hypothetical spherical field Crystal Field Splitting Energy, Δo! The energy gap between t2g and eg levels is designated Δo or 10Dq.! The energy increase of the eg orbitals and the energy decrease of the t2g orbitals must be balanced relative to the energy of the hypothetical spherical field (sometimes called the barycenter ... The degenerate d-orbitals (in a spherical field environment) split into two levels i.e., e g and t 2g in the presence of ligands. The splitting of the degenerate levels due to the presence of ligands is called the crystal-field splitting while the energy difference between the two levels (eg and t2g) is called the crystal-field splitting energy.
Consider the complex ion [Mn (H2O)6]2+. Draw the crystal field energy level diagram and use arrows (that point up or down) to show the placement of d electrons assuming that this is (a) a weak field complex ion (b) stron field complex ion. Our mission is to help you succeed in your Chemistry class. We calculate the crystal field parameters from the crystal structure date and diagonalize the crystal field Hamiltonian to obtain the energy level structure of Cr 3+ ions in LiGa 5 O 8. The ... The most basic crystal field argument includes point-symmetric charges approaching the central metal in a way as the ligands would. Then, any orbitals that are symmetry-equivalent will end up at the same energy, and depending on how much these point towards the point-symmetric approaching charges they will be raised or lowered. Overview of crystal field theory. According to crystal field theory, the interaction between a transition metal and ligands arises from the attraction between the positively charged metal cation and the negative charge on the non-bonding electrons of the ligand. The theory is developed by considering energy changes of the five degenerate d-orbitals upon being surrounded by an array of point ...
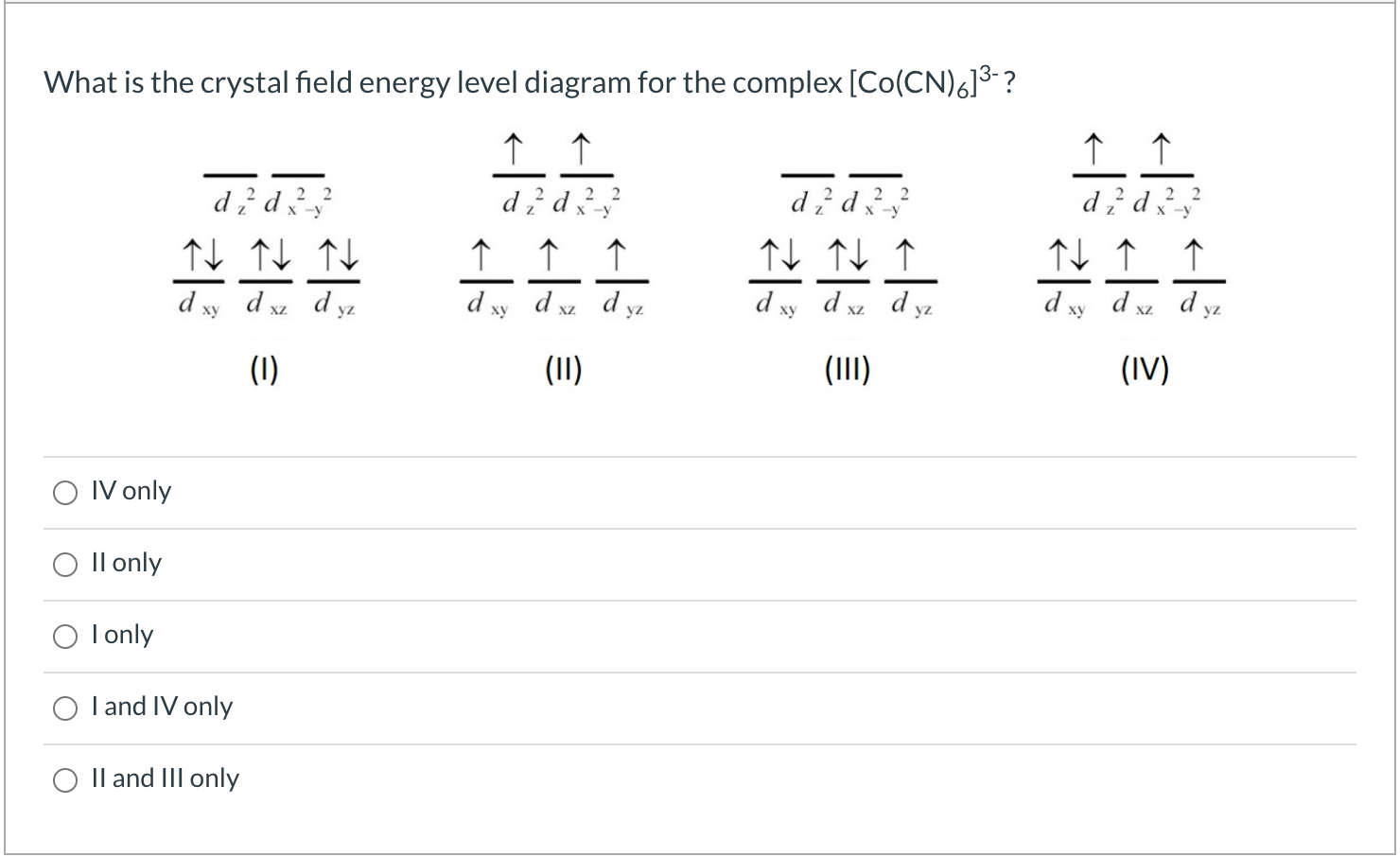
Correct option is. B. Since cyanide ion is a strong field ligand, electrons pair up. All six electrons are present in lower t2g. . energy level. But the two orbitals in the e g set are now lower in energy than the three orbitals in the t 2g set, as shown in the figure below.. To understand the splitting of d orbitals in a tetrahedral crystal field, imagine four ligands lying at alternating corners of a cube to form a tetrahedral geometry, as shown in the figure below. The d x 2-y 2 and d z 2 orbitals on the metal ion at the center of ... About Press Copyright Contact us Creators Advertise Developers Terms Privacy Policy & Safety How YouTube works Test new features Press Copyright Contact us Creators ... CRYSTAL FIELD SPLITTING DIAGRAMS. Their blank d -splitting diagrams within the realm of crystal field theory are: [Ni(CN)4]2−: The d orbitals fill with 8 electrons, then, with a low spin configuration. You can see that an even number of d orbitals will get filled ( dyz,dxz,dz2,dxy) with an even number of 3d electrons.
The simplified energy level diagram for Oj, 02, and 02 in their ground state. When a crystal field is present, the n, and nu levels are not degenerate. Figure 29.2 (a) Octahedral and (b) tetrahedral crystal fields represented as point charges around a central ion. Arrows show the effect of a tetrahedral distortion to the crystal field, (c) d ...

Using Crystal Field Theory Draw Energy Level Diagram Write Electronic Configuration Of The Central Metal Atom Ion And Determine The Magnetic Moment Value In The Following Cof6 3 Co H2o 6 2 Co Cn 6 3
4) Using crystal field theory, draw the crystal field d orbital energy level diagram for each of the following complexes by assigning electrons to 3d orbitals. [Co(en)2]2+ (square planar) [FeF6]3- (octahedral) 5) For the following complex, draw an orbital diagram for the isolated metal ion.
Figure 3.7 Simplified energy level diagram for 3d6 ions (e.g., Fe2+ and Co3+) in an octahedral crystal field. The diagram shows that in a high intensity field the 1Alg crystal field state, corresponding to the low-spin configuration (t2gf, becomes the ground state.
(d) Draw the crystal field energy-level diagram for cisplatinum, labeling the d-orbitals. (e) Predict whether cisplatinum is diamagnetic or paramagnetic? Explain your answer. a) Pt Cl NH3 NH 3Cl Pt Cl NH Cisplatinum Transplatinum b) 90° c) Cisplatinum has four ligands. CN (coordination number) = 4 d) Pt is in group 10.

Draw A Crystal Field Energy Level Diagram Assign The Electron To Orbitals And Predict The Number Of Unpaired Electrons For Tris En Cuprate Ii Low Spin Study Com
Crystal Field Splitting in an Octahedral Field eg Energy 3/5 o o 2/5 o t2g e g - The higher energy set of orbitals (d z2 and d x2-y2) t 2g - The lower energy set of orbitals (d xy, d yz and d xz) Δ o or 10 Dq - The energy separation between the two levels The eThe eg orbitals are repelled by an amount of 0 6orbitals are repelled by an amount of 0.6 Δo The t2gorbitals to be stabilized to the ...
This chemistry video tutorial provides a basic introduction into crystal field theory. It explains how to draw the crystal field splitting diagram of transi...
Crystal field theory describes A major feature of transition metals is their tendency to form complexes. A complex may be considered as consisting of a central metal atom or ion surrounded by a number of ligands. Theinteraction between these ligands with the central metal atom or ion is subject to crystal field theory. Crystal field theory was established in 1929 treats the interaction of metal ion and ligand as a purely electrostatic phenomenon where the ligands are considered as point charges in the vicinity of the atomic orbitals of the central atom. Development and extension of crystal field theory taken into account the partly covalent nature of bonds between the ligand and metal atom mainly through the application of molecular orbital theory. Crystal field theory often termed as ligand field theory.
The difference in energy between the e g and the t 2g orbitals is called the crystal field splitting and is symbolized by Δoct, where oct stands for octahedral. The magnitude of Δ oct depends on many factors, including the nature of the six ligands located around the central metal ion, the charge on the metal, and whether the metal is using 3 ...
Using crystal field theory, sketch the energy-level diagram for the d orbitals in an octahedral field; then fill in the electrons for the metal ion in each of the following complexes. How many unpaired electrons are there in each case? a [V(CN) 6] 3− b [Co(C 2 O 4) 3] 4− (high-spin). c [Mn(CN) 6] 3− (low-spin)

Using Crystal Field Theory Draw Energy Level Diagram Write Electronic Configuration Of The Central Metal Atom Ion And Determine The Magnetic Moment Value In The Following A Cof 6 3 Co H 2 O 6 2 Co Cn 6 3 B Fef 6 3
For each of the following metals, write the electronic configuration of the atom and its 3+ ion: (a) Co. Draw the crystal-field energy-level diagram for the d orbitals of an octahedral complex, and show the placement of the d electrons for each 3+ ion, assuming a weak-field complex.
Using crystal field theory, draw energy level diagram, write electronic configuration of the central metal atom/ion and determine the magnetic moment value in the following : (i) [CoF 6 ] 3- , [Co(H 2 O) 6 ] 2+ , [Co(CN) 6 ] 3-
Find step-by-step Chemistry solutions and your answer to the following textbook question: Draw the crystal-field energy-level diagrams and show the placement of d electrons for each of the following: $[IrCl_6]^{2-}$ (a low-spin complex),.
ligand field is located in the center of the diagram, with the terms due to that electronic ... The following effects lead to a splitting of the energy levels of transition metal atoms, ions (and complexes): - Electron-electron repulsion → spectroscopic terms - Crystal field → spectroscopic terms - Spin-Orbit Interaction → multiplet ...
Draw a crystal field energy-level diagram, assign the electron to orbitals, and predict the number of unpaired electrons for {eq}\displaystyle \rm tris(en)cuprate(II) {/eq} ({eq}\displaystyle \rm ...
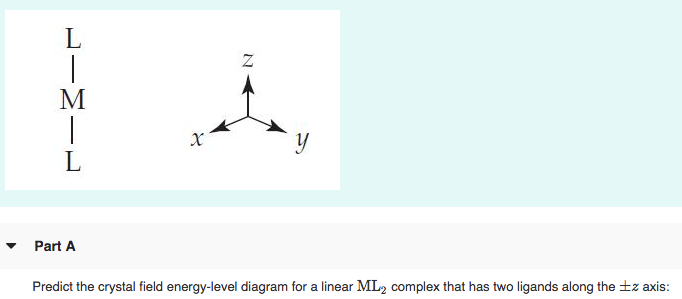
For the following, consider a field that has a z-axis that is vertical, a y-axis that is horizontal, and x-axis that is coming out of page. (a) Draw pictures of the d 2 2 2 x -y and d z orbitals (b) Predict the relative energy of d 2 2 crystal field that is along the y-axis x -y in an octahedral crystal field compared to a linear
Using crystal field theory, draw energy level diagram, write electronic configuration of the central metal atom/ion and determine the magnetic moment value in the following. ( i ) . [ C o F 6 ] 3 − , [ C o ( H 2 O ) 6 ] 2 + , [ C o ( C N ) 6 ] 3 −

Using Crystal Field Theory Draw Energy Level Diagram Write Electric Configuration Of The Central Metal Atom Ion And Determine The Magnetic Moment Value In The Following Complex Fe H2o 6 2
Using Crystal Field Theory Draw Energy Level Diagram Write Electronic Configuration Of The Central Metal Atom Ion Sarthaks Econnect Largest Online Education Community

Using Crystal Field Theory Draw Energy Level Diagram Write Electronic Configuration Of The Central Metal Atom Ion And Determine The Magnetic Moment Value In The Following A Cof 6 3 Co H 2 O 6 2 Co Cn 6 3 B Fef 6 3

Inorganic Chemistry What Does The Crystal Field Splitting Diagram For Trigonal Planar Complexes Look Like Chemist Chemistry Anatomy And Physiology Complex

For Each Of The Following Complexes Draw A Crystal Field Energy Level Diagram Assign The Electrons To Orbitals And Predict The Number Of Unpaired Electrons A Crf 6 3 B V H 2 O 6 3

With Help Of Crystal Field Energy Level Diagram Level Diagram Explain Why The Complex Cr En 3 3 Is Brainly In


















0 Response to "40 crystal field energy level diagram"
Post a Comment