40 identify the structures labeled a, b, and c in the diagram of a sarcomere above.
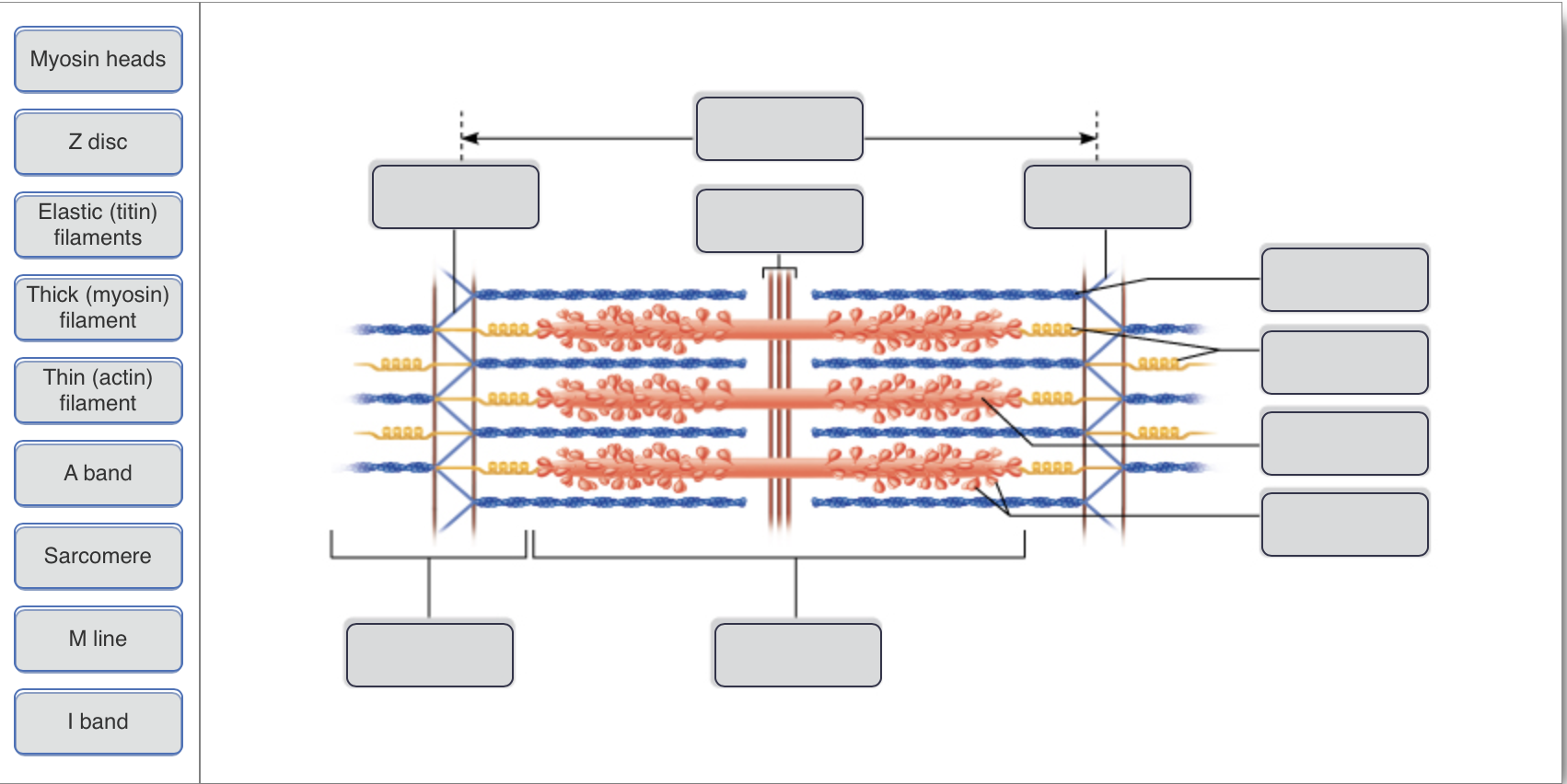
Drag the labels onto the diagram to identify the structures and functions of the nephron. This is likely because of the visual distance between the label and input field. Reaction diagrams for an endothermic process in the absence (red curve) and presence (blue curve) of a catalyst. To label the diagram and swimlanes, click a shape that contains placeholder text, and then type the label ... 18 Jun 2016 — Label the thick and thin filaments in figs. A b and c above. 10 2 Skeletal Muscle Anatomy Physiology. Skeletal muscle is the muscle type ...
Identify the structures labeled a b and c in the diagram of a sarcomere above. This means it is the most basic unit that makes up our skeletal muscle. Which of the labeled structures on the diagram holds muscles with similar functions together allows free. B and c in the diagram of a sarcomere above. Label each of the lines.

Identify the structures labeled a, b, and c in the diagram of a sarcomere above.
Drawing labelled diagrams of the structure of a sarcomere ... striated banding pattern should be identified (A band = dark region ; I band = light region).Missing: above. | Must include: above. Identify the structures labeled a b and c in the diagram of a sarcomere above. The thin bands contract while the thick bands stay the same as a group observe the diagram in model 2 and describe possible reasons why there is a limit to the amount of shortening that can occur in a sarcomere during muscle contraction. Identify the structures labeled a b and c in the diagram of a sarcomere above. The brain stem connects the brain with the the brain stem connects the brain to the spinal cord. This flashcard is meant to be used for studying quizzing and learning new information. Skeletal muscle is the muscle type that initiates all of our voluntary movement. A ...
Identify the structures labeled a, b, and c in the diagram of a sarcomere above.. Identify the structures labeled "1."; A) mitochondria. B) glycogen. C) ATP ... Interactions between actin and myosin filaments of the sarcomere are ... Identify The Structures Labeled A, B, And C In The Diagram Of A Sarcomere Above. (Correct Answer Below). Identify The Structures Labeled A, B, And C In The ... Drag the labels onto the diagram to identify the structures. Feb 02, 2021 · To diagram a sentence, start by drawing a horizontal line with a vertical line through the middle. Excel provides several options for the placement and formatting of data labels. The infundibulum (pituitary stalk) is now visible in the Part A - Animal cell structures and functions To understand how cells function as ... When performing column chromatography to purify a protein of interest, one needs an assay to identify which fractions that contain the protein of interest. True or False: As discussed in lecture, we use a different assay for each different protein that we purify (For instance, the assay for protein A will be different than the assay for protein B which will be different than the assay for ...
12.07.2021 · A labeled diagram of the abdomen and some of its organs. The abdomen is an important region of the body, as it contains various vital blood vessels and organs (such as the digestive organs ... 3) Identify the specific structure indicated by Label G. A) Muscle fascicle B) Triad C) Myofibril D) Sarcomere E) Myofilament In the picture above of a sarcomere, what is the name of the area labeled A? (#1) a. z disk b. H zone c. I band d. A band. b. H zone. A)A B)B C)C D)D 6.The map below shows four locations, A, B, C, and D, on the continent of South America. Which location is the first to experience sunset on September 23? A)winter B)spring C)summer D)fall 7.The diagram below represents Earth in space on the first day of a season. Which season is beginning in New York State on the
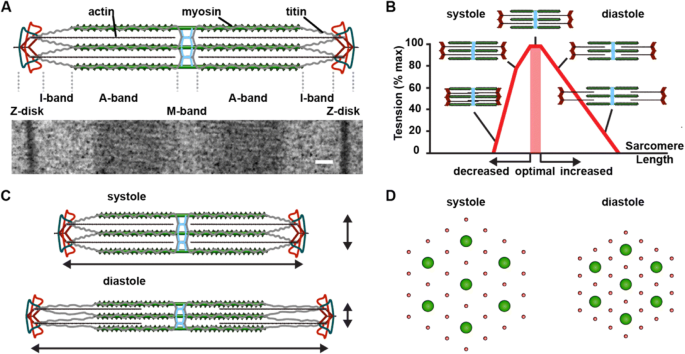
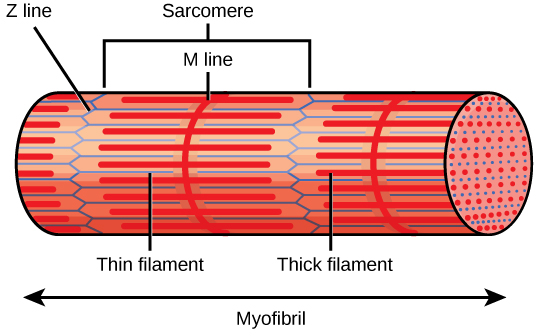
Academia.edu is a platform for academics to share research papers. Identify each structure in the diagram (sarcomere, titin, thin filament, thick filament). A= Sarcomere B= Titin C= Thin Filament D= Thick Filament.Missing: above. | Must include: above. Describe the structure and function of a bursa. 9. Define the following terms: A) Actin: 1) My C) Sarcomere: D) Myofilament: 10. Label the diagram below. Sarcomere Z line Z line Thick filaments Thin filaments 1 band H zone A band I band 11. A muscle is made up of many contractile cells called muscle fibers. Identify the structures labeled a b and c in the diagram of a sarcomere above. Which of the figures a b or c represents a cross section in the h zone. Model 3 muscle contraction 13. Draw and label a diagram to show the structure of a sarcomere including z lines actin filaments myosin filaments with heads and the resultant light and dark bands.
(Labeled A, T, C, or G) Alternating sugar and phosphate units form the two sides of a ladder-shaped arrangement with the rungs or steps each formed by a pair of nucleotide bases. Figure 2 below shows the structural formula of DNA in greater detail.

Structure And Interactions Of Myosin Binding Protein C Domain C0 Cardiac Specific Regulation Of Myosin At Its Neck Sciencedirect
Formula Lewis Electron-Dot Diagram : Ethanethiol CH 3 CH 2 SH : Ethane : CH 3 CH 3: Ethanol CH 3 CH 2 OH : Ethyne : C 2 H 2 (a) Draw the complete Lewis electron-dot diagram for ethyne in the appropriate cell in the table above. See the lower right cell in the table above. One point is earned for the correct Lewis structure.
A sarcomere is defined as the region of a myofibril contained between two cytoskeletal structures called Z-discs (also called Z-lines), and the striated appearance of skeletal muscle fibers is due to the arrangement of the thick and thin myofilaments within each sarcomere (Figure 10.2.2).
01.09.2011 · Schematic diagram of the gross organization of muscle tissue and muscle ECM-tendon organization. (A) ... (C) Central region of ... multiple reaction monitoring may be used in the future to quantify proteins from labeled cell types in muscle. 107 This method can detect and quantify peptides in multiplex format using a triple quadrupole instrument. An advantage to this method is that it might be ...
19.06.2015 · (B) C. elegans viewed through the dissecting microscope. The two adults are moving in this view. Tracks in the plate indicate where animals have traveled on the bacterial lawn. (C) An adult hermaphrodite is viewed in a compound microscope. In all pictures, anterior is to the left and ventral is on the bottom. C. elegans moves on either its left or right side; in this image the surface facing ...
B. Which of the labeled structures on the diagram holds muscles with similar ... C. In the figure above, what letter correctly identifies tropomyosin?
Academia.edu is a platform for academics to share research papers.
potassium b. calcium c. troponin d. tropomyosin 2. Which of the following substances acts at the neuromuscular junction to excite the muscle fibers of a motor unit? a. acetylcholine b. ATP c. creatine phosphate d. serotonin 3. When throwing a baseball, an athlete’s arm is rapidly stretched just before throwing the ball. Which of the following structures detects and responds to that stretch ...
Identify the structures labeled A, B, and C in the diagram of a sarcomere above. A is a "blue" filament, attached to the Z line at the ends of a sarcomere. Rating: 5 · 1 review
Autophagy (or autophagocytosis; from the Ancient Greek αὐτόφαγος autóphagos, meaning "self-devouring" and κύτος kýtos, meaning "hollow") is the natural, conserved degradation of the cell that removes unnecessary or dysfunctional components through a lysosome-dependent regulated mechanism. It allows the orderly degradation and recycling of cellular components.
Identify the structures labeled a b and c in the diagram of a sarcomere above. The brain stem connects the brain with the the brain stem connects the brain to the spinal cord. This flashcard is meant to be used for studying quizzing and learning new information. Skeletal muscle is the muscle type that initiates all of our voluntary movement. A ...
Identify the structures labeled a b and c in the diagram of a sarcomere above. The thin bands contract while the thick bands stay the same as a group observe the diagram in model 2 and describe possible reasons why there is a limit to the amount of shortening that can occur in a sarcomere during muscle contraction.
Drawing labelled diagrams of the structure of a sarcomere ... striated banding pattern should be identified (A band = dark region ; I band = light region).Missing: above. | Must include: above.

Cardiac Myosin Binding Protein C Interaction With Actin Is Inhibited By Compounds Identified In A High Throughput Fluorescence Lifetime Screen Journal Of Biological Chemistry

Sarcomere Integrated Biosensor Detects Myofilament Activating Ligands In Real Time During Twitch Contractions In Live Cardiac Muscle Journal Of Molecular And Cellular Cardiology
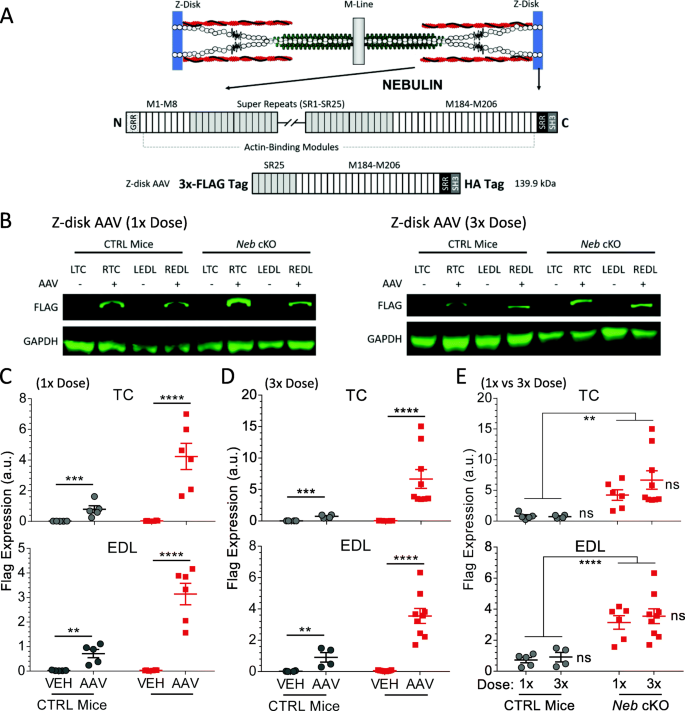
Expressing A Z Disk Nebulin Fragment In Nebulin Deficient Mouse Muscle Effects On Muscle Structure And Function Skeletal Muscle Full Text
A Stochastic Simulation Of Skeletal Muscle Calcium Transients In A Structurally Realistic Sarcomere Model Using Mcell

Amino Terminus Of Cardiac Myosin Binding Protein C Regulates Cardiac Contractility Journal Of Molecular And Cellular Cardiology
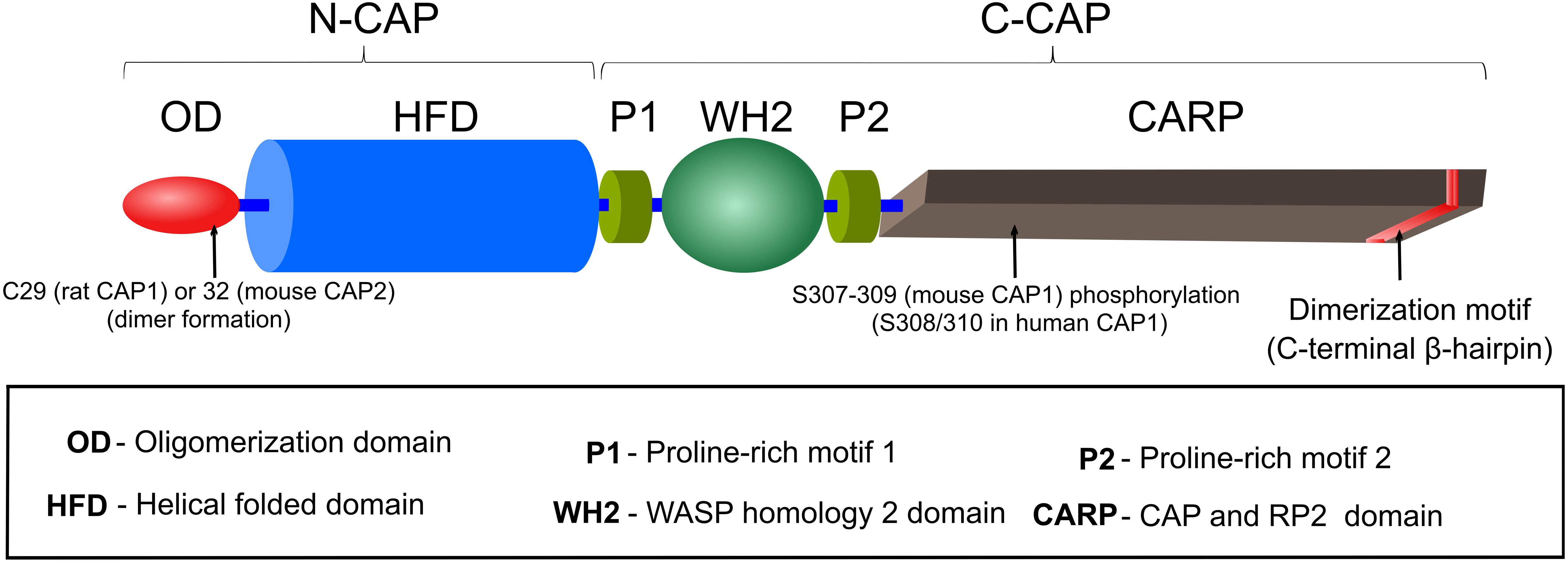
Frontiers Capt N Of Actin Dynamics Recent Advances In The Molecular Developmental And Physiological Functions Of Cyclase Associated Protein Cap Cell And Developmental Biology


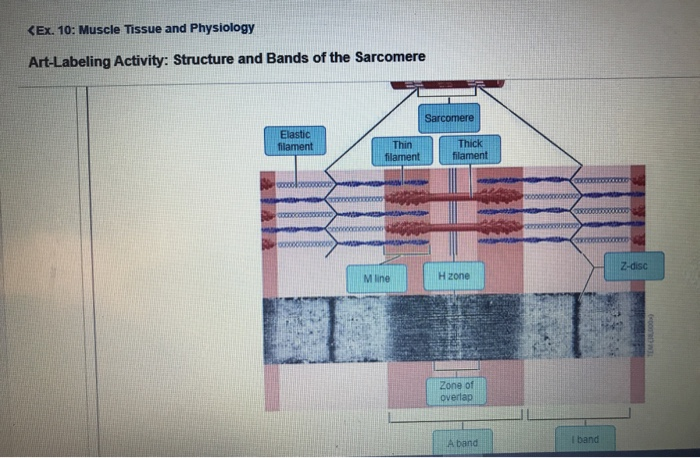

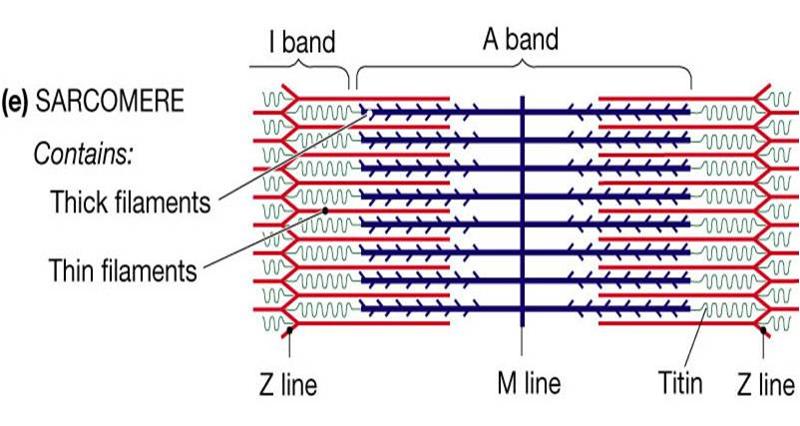
















0 Response to "40 identify the structures labeled a, b, and c in the diagram of a sarcomere above."
Post a Comment