40 terminal velocity free body diagram
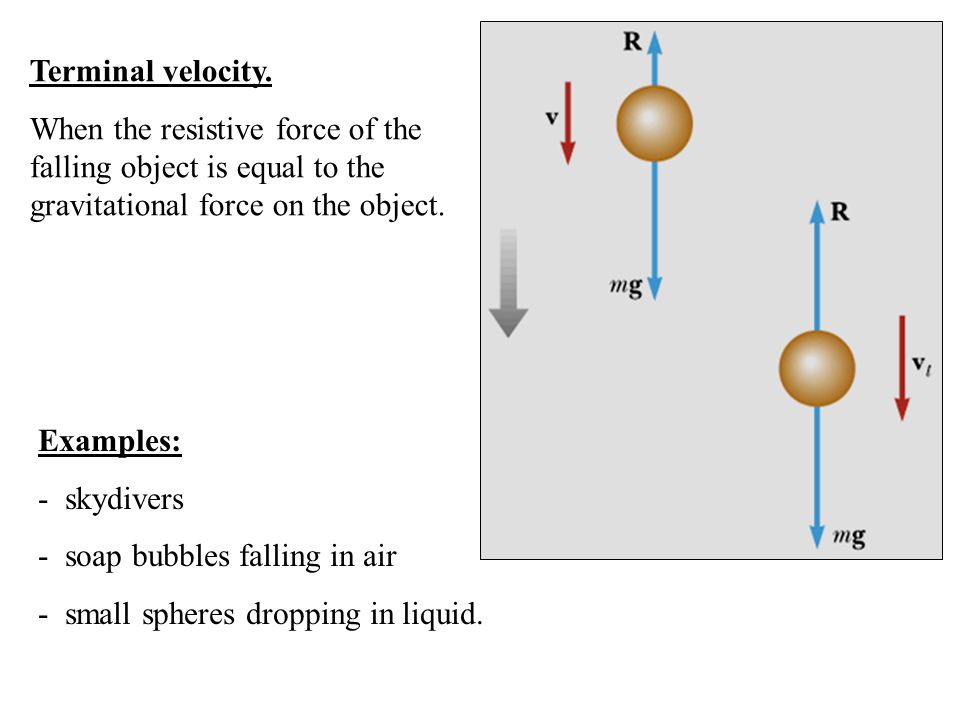
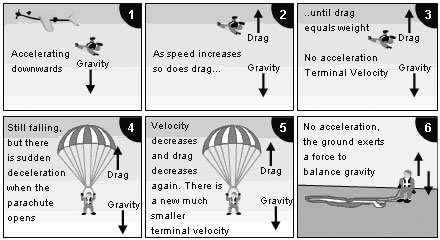
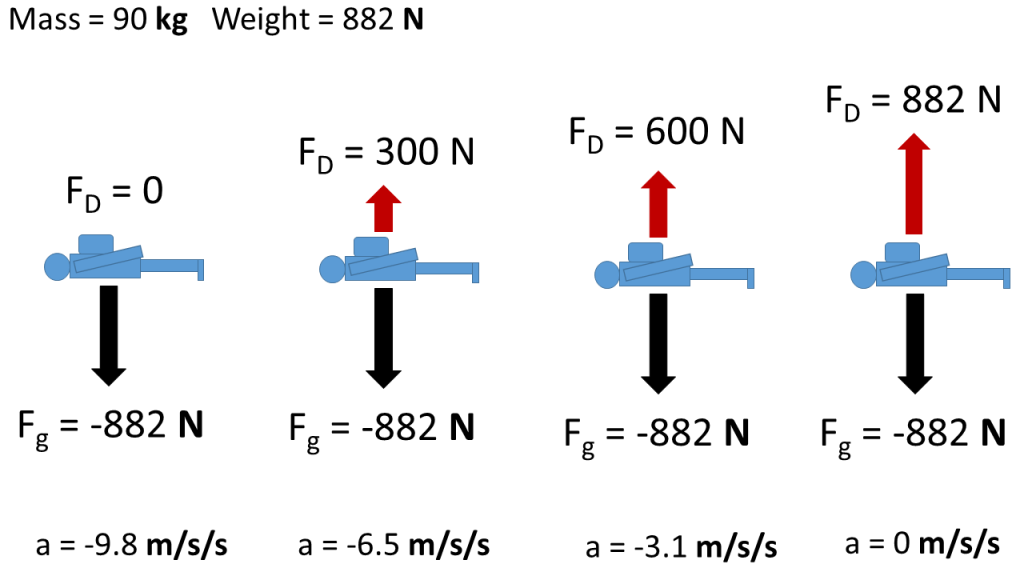
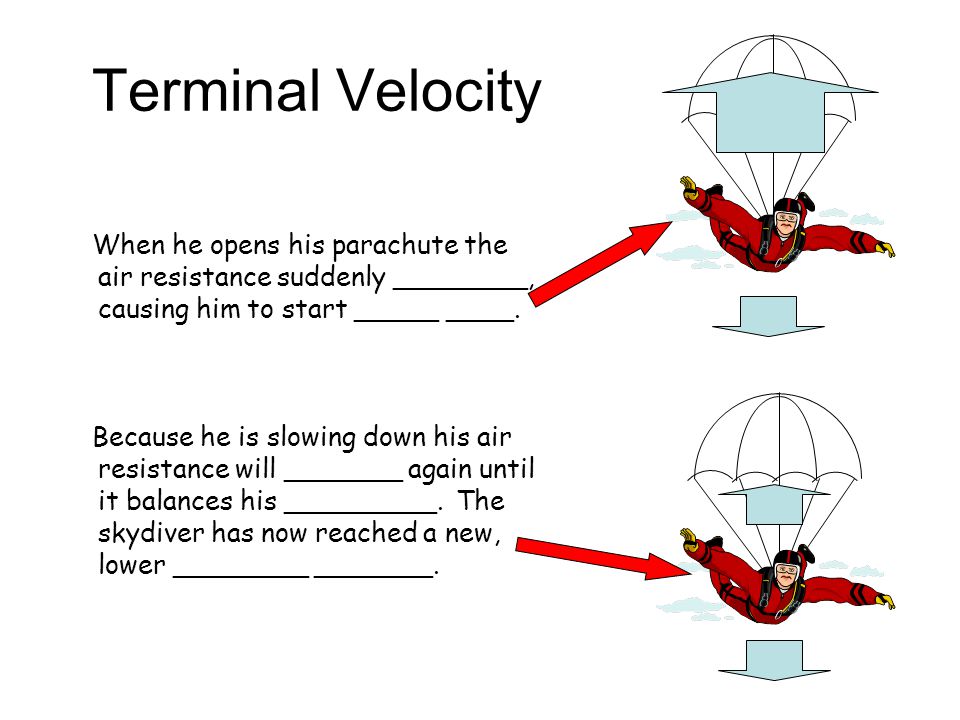
The terminal velocity is the same as the limiting velocity, which is the velocity of the falling object after a (relatively) long time has passed. Similarly, the limiting distance of the boat is the distance the boat will travel after a long amount of time has passed. ... Draw a free-body diagram of the forces to see what the angle . should be.) Free body diagrams of a person with 90 kg mass during a skydive. The initial speed is zero, so drag force is zero. As speed increases, the drag force grows, eventually cancelling out the person's weight. At that point acceleration is zero and terminal velocity is reached. Dynamic Equilibrium
An Easy Guide to Understand Free Body Diagrams in Physics. Every macroscopic and microscopic body or object in the universe exerts different forces on the surroundings, as well as experiences the effect of various forces on it. It is possible to study such physical entities with the help of a free body diagram.
Terminal velocity free body diagram
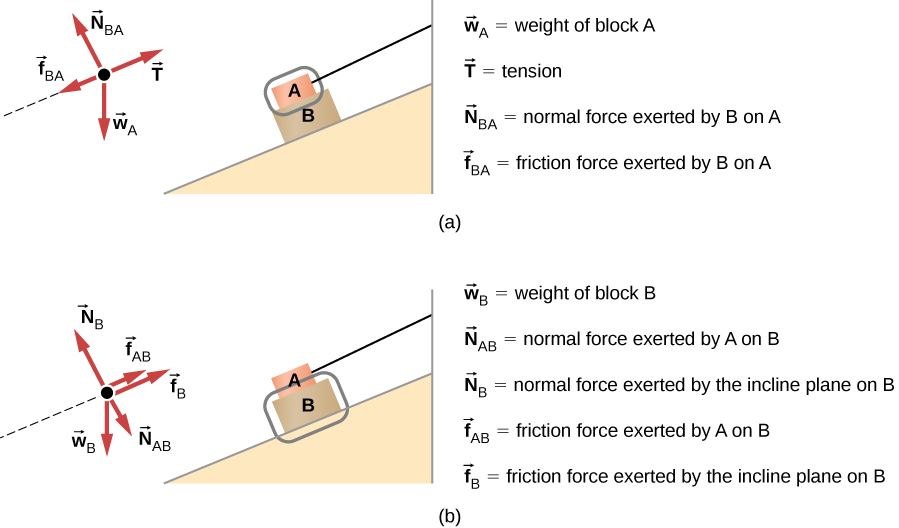
Terminal velocity is the maximum speed achieved by an object freely falling through a gas or liquid. At terminal velocity, the forces acting on the object are balanced so it is no longer accelerating. Terminal velocity Falling objects. There are two main forces which affect a falling object at different stages of its fall: The weight of the object - this is a force acting downwards, caused by ... Figure 5.32 (a) The free-body diagram for isolated object A. (b) The free-body diagram for isolated object B. Comparing the two drawings, we see that friction acts in the opposite direction in the two figures. Because object A experiences a force that tends to pull it to the right, friction must act to the left. Because object B experiences a component of its weight that pulls it to the left ...
Terminal velocity free body diagram. Construct free-body diagrams for the following physical situations. Label all forces (e.g, Fgrav, Fnorm, Fapp, Ffrict, Fair, Ftens, etc. ). a. A physics book rests upon a level table. b. A skydiver is falling and has reached a terminal velocity. c. A large crate is being pushed leftward at a constant velocity. d. A sledder has reached The figure below shows a free-body diagram of this. Where: g is the acceleration due to gravity, which is 9.8 m/s 2 m is his mass D is the drag force acting upwards W is the force of gravity pulling him down v is the speed at which he falls v t is the constant (terminal) speed he reaches when D = W It is easy to understand why his speed ... A free body diagram with 2 forces: the first pointing downward labeled F Subscript g Baseline 20 N and the second pointing upward labeled F Subscript air Baseline 20 N. Explanation: This is because at terminal velocity, the ball stops accelerating and the net force on the ball is zero. Terminal Velocity =V = [ (2 * W) / (K*r*A)] 1/2[formula for Terminal Velocity] here K = Drag Coefficient of the falling object (it depends on the inclination of the shape and some other criteria like airflow) r = air density. W = weight of the falling object. A = cross sectional area of the object falling.
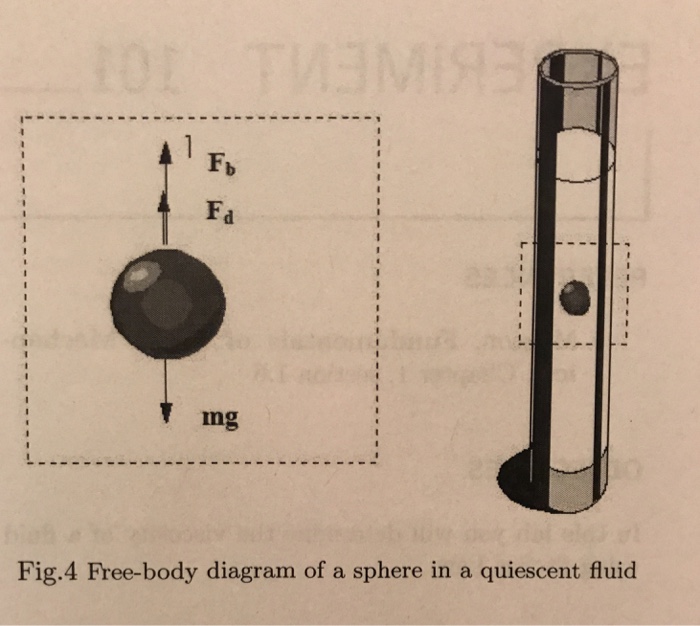
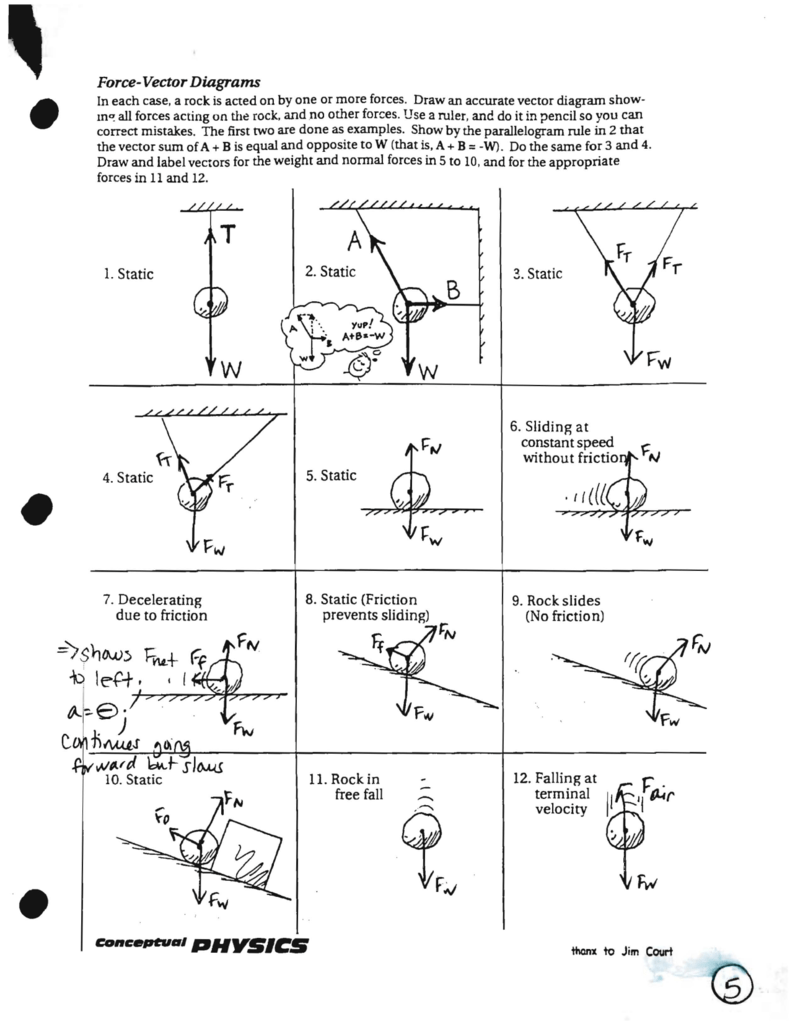
Free-Body Exercises: Circular Motion Draw free-body diagrams showing forces acting on the rock, and in each case, indicate the centripetal force. Please note that the rock is not in equilibljum if it is moving in a circle. The centripetal force depends on angular velocity and there may not be any indication of exactly how big that force should ... velocity of the sphere relative to the fluid, and d is the diameter of the sphere. Using this equation, along with other well-known principle of physics, we can write an expression that describes the rate at which the sphere falls through a quiescent, viscous fluid. To be begin we must draw a free body diagram (FBD) of the sphere. That is we must A free body diagram with 2 forces: the first pointing downward labeled F Subscript g Baseline 20 N and the second pointing upward labeled F Subscript air Baseline 20 N. Explanation: This is because at terminal velocity, the ball stops accelerating and the net force on the ball is zero. Drawing Free-Body Diagrams. Free-body diagrams are diagrams used to show the relative magnitude and direction of all forces acting upon an object in a given situation. A free-body diagram is a special example of the vector diagrams that were discussed in an earlier unit. These diagrams will be used throughout our study of physics.
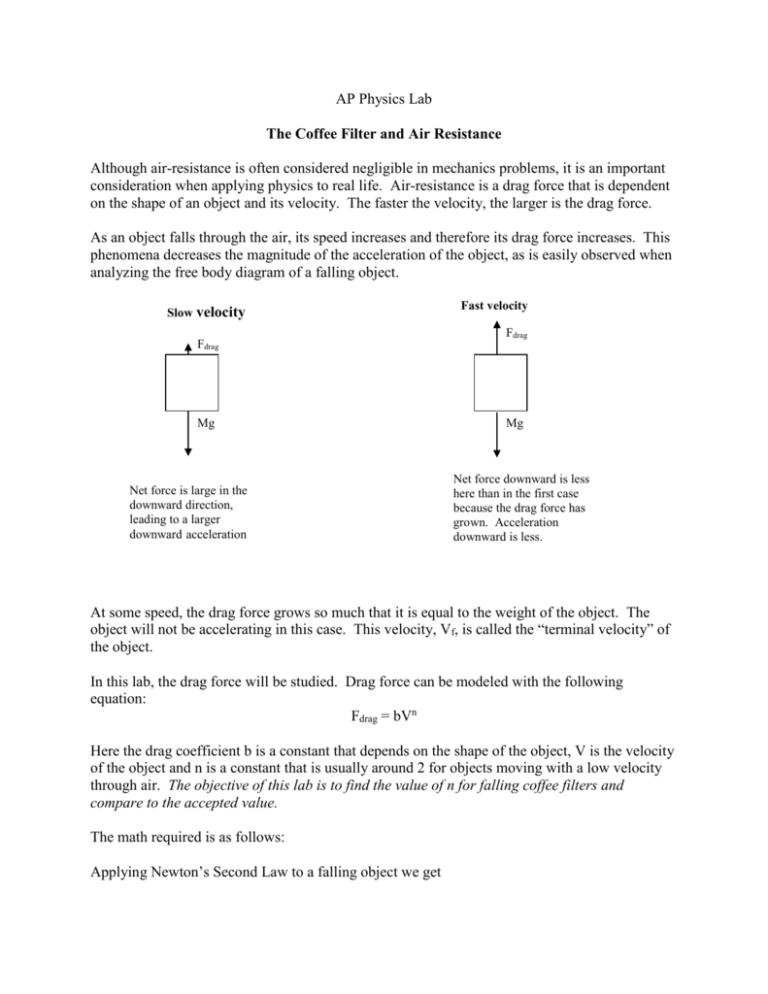
10. A parachuter that weighs 760 N is falling to Earth at terminal velocity. Recall that terminal velocity means that the freely-falling object has a constant velocity. 11. An apple that weighs 5 N at its start of a fall to Earth and is experiencing 1 N of air resistance (i.e., terminal velocity has not been reached). 12. Free body diagram showing a mass in free fall ... At this point, the object is at terminal velocity. It is no longer accelerating. Since acceleration is not constant, ... For the first free-body diagram, at the instant where the cof fee filter has just been released, the . only force acting on the coffe e filter is the force due to gravity, or mg. A fter the coffee filter has . reached terminal velocity, the mg will equal the drag force. For this reason, the arrows in the free. body diagram for mg and drag force ... Terminal velocity and free fall are two related concepts that tend to get confusing because they depend on whether or not a body is in empty space or in a fluid (e.g., an atmosphere or even water). Take a look at the definitions and equations of the terms, how they are related, and how fast a body falls in free fall or at terminal velocity under different conditions.
She has reached TERMINAL VELOCITY (air resistance =gravity) :acceleration and force Physics 12/16/04 * In order to understand this motion, we need to use a free body diagram 12/16/04 * Terminal Velocity of a human~180mph 12/16/04 :acceleration and force Physics 12/16/04 * In order to understand this motion, we need to use a free body diagram 12 ...

Physics And Astronomy Outreach Program At The University Of British Columbia Physics And Astronomy Outreach Program At The University Of British Columbia Ppt Download
Draw Free Body Diagram (FBD) for the falling object: (Note: don't forget to label all forces exerted on the object) a) Neglect air resistance b) Do not neglect air resistance Q2: In general, what is the direction of acceleration? (Recall: Newton's Second Law) Q3: What does is mean that an object is falling with is terminal velocity? Explain.
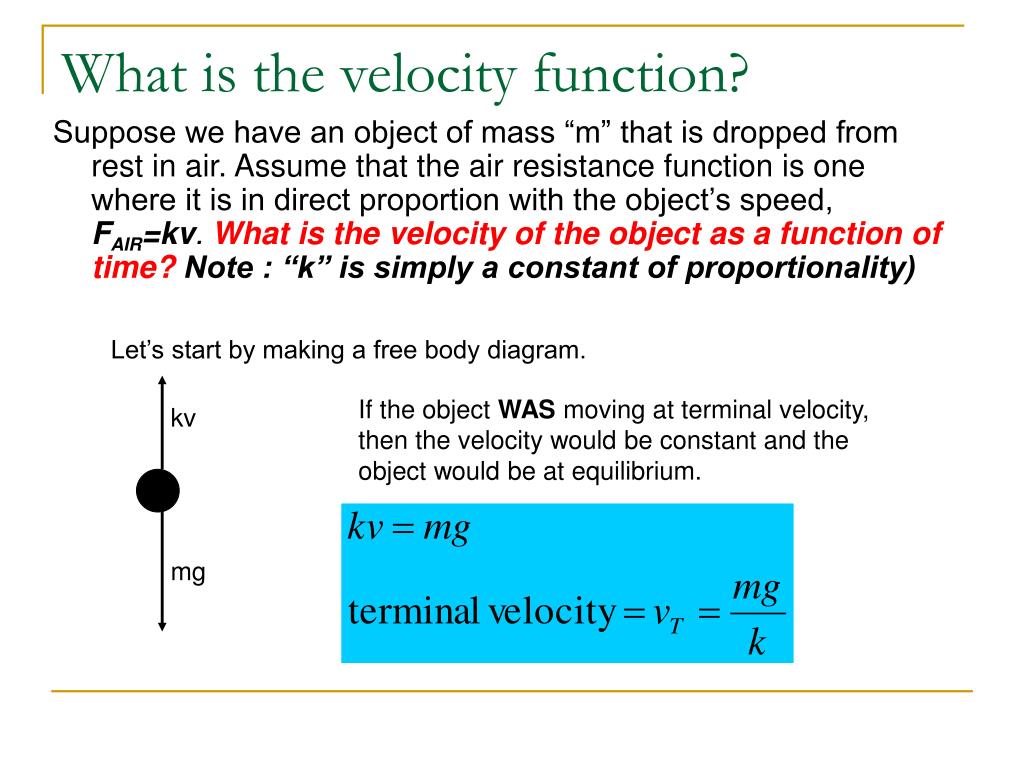
net downward force and acceleration become zero and the velocity becomes constant. This is known as the terminal velocity vT. Therefore, by de nition, when the terminal velocity is achieved the net force on the sphere is zero, the three forces balance each other out. Looking at the free-body diagram this means W= FB + FD (2) Substituting (1)
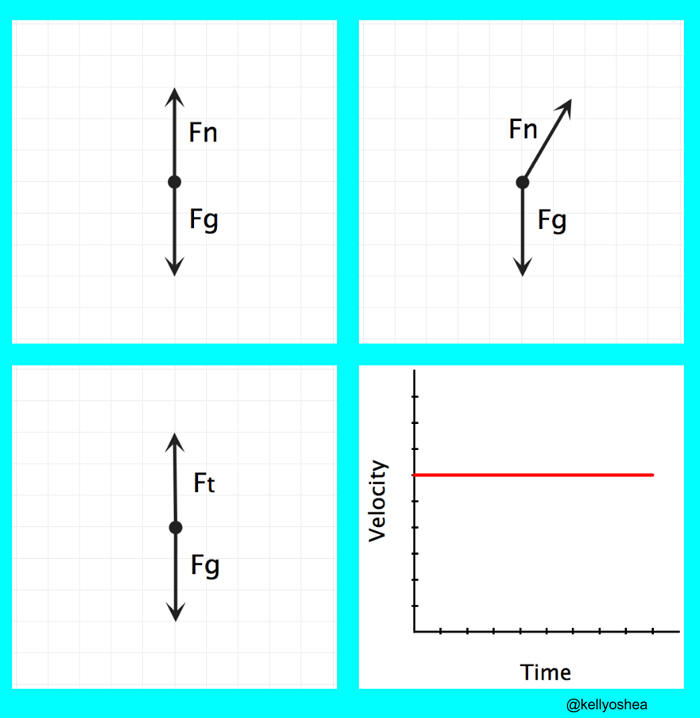
The diagrams below represent the free-body diagrams for different skydivers at various moments during their fall. What is the acceleration of each skydiver and which Skydiver has reached terminal velocity? 1. Skydiver B 2: A) a=-1.6 B) a=0 C) a=1.26 D) a=.89.
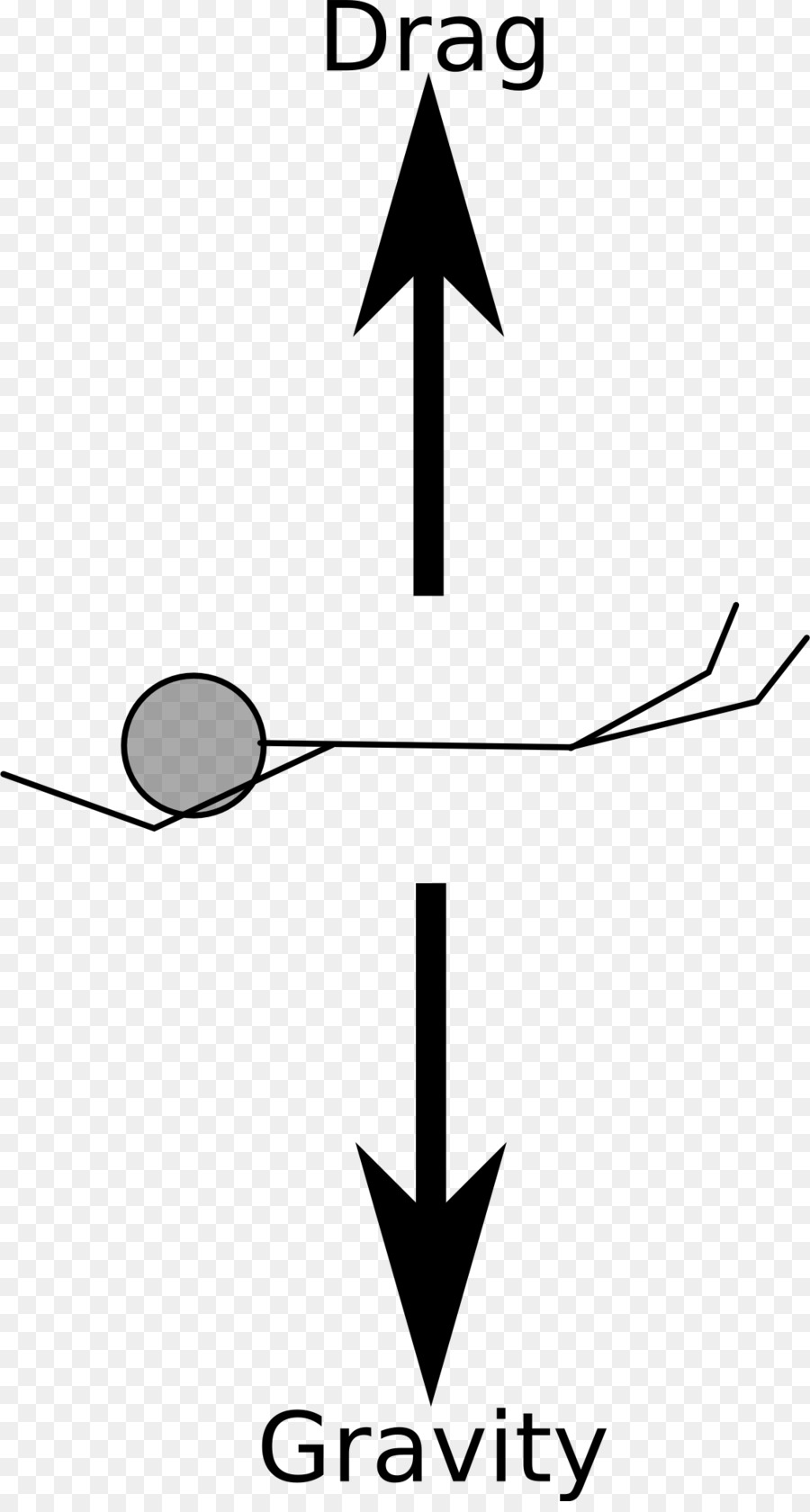
Draw a free body diagram of a meteor that is falling towards earth at terminal velocity. F air F gravity Net Force = 0 N The meteor is falling down, but its net force is 0 N! There is no acceleration!
Which free body diagram shows the ball falling at terminal velocity? A free body diagram with one force pointing downward labeled F Subscript g Baseline 20 N. A free body diagram with 2 forces: the first pointing downward labeled F Subscript g Baseline 20 N and the second pointing upward labeled F Subscript air Baseline 20 N.
Answer: 1 📌📌📌 question A ball is falling at terminal velocity. Terminal velocity occurs when the ball is in equilibrium and the forces are balanced. Which free body diagram shows the ball falling at terminal velocity? - the answers to estudyassistant.com

You Throw A Baseball Straight Upward The Drag Force Is Proportional To V 2 In Terms Of G What Is The Y Component Of The Ball S Acceleration When The Ball S Speed Is Half Its
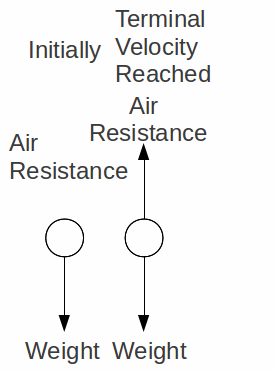
The free-body diagrams are shown below for the instant in time in which they have reached terminal velocity. As learned above , the amount of air resistance depends upon the speed of the object. A falling object will continue to accelerate to higher speeds until they encounter an amount of air resistance that is equal to their weight.
"The terminal velocity of a falling human being with arms and legs outstretched is about 120 miles per hour (192 km per hour) — slower than a lead balloon, but a good deal faster than a feather!" 53 m/s: The terminal velocity of a falling body occurs during free fall when a falling body experiences zero acceleration. This is because of the ...
This diagram shows a few of the snapshots, but they are out of order. Place them in order, from the instant it jumps out of the plane and begins free-fall until the time it attains terminal velocity. Assume that the parachute has not deployed yet. If any of the diagrams depict a situation not physically possible, omit it from the ordering. a. L ...
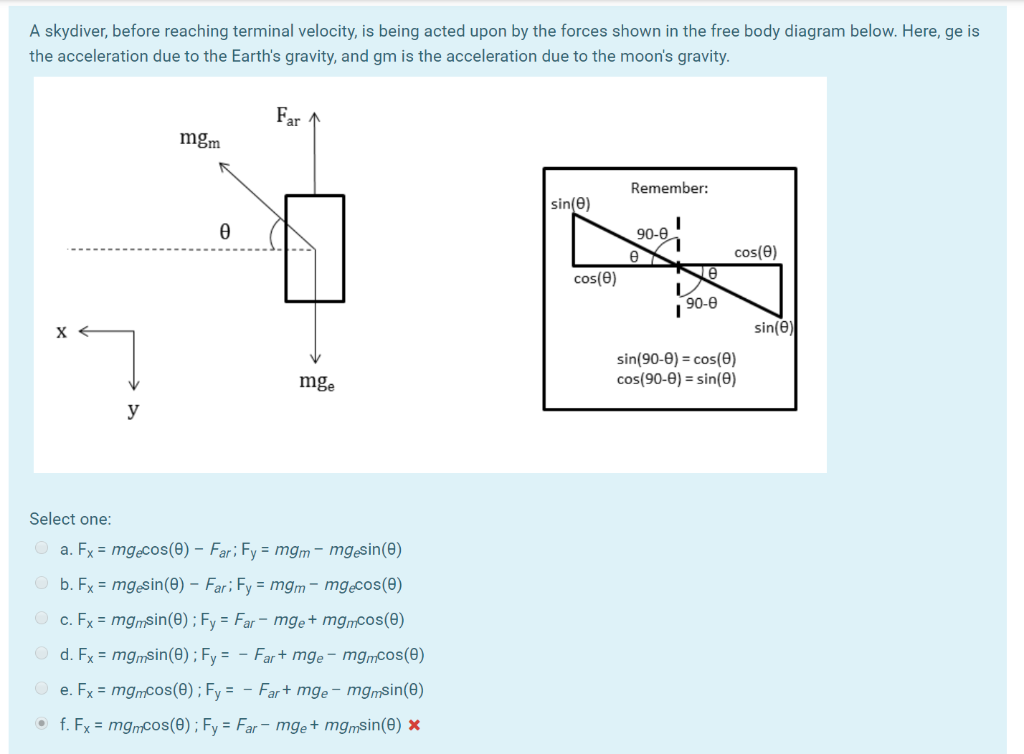
Draw a free-body diagram of the forces to see what the angle [latex]\theta[/latex] should be.) A car of mass 1000.0 kg is traveling along a level road at 100.0 km/h when its brakes are applied. Calculate the stopping distance if the coefficient of kinetic friction of the tires is 0.500.
Figure 5.32 (a) The free-body diagram for isolated object A. (b) The free-body diagram for isolated object B. Comparing the two drawings, we see that friction acts in the opposite direction in the two figures. Because object A experiences a force that tends to pull it to the right, friction must act to the left. Because object B experiences a component of its weight that pulls it to the left ...
Terminal velocity Falling objects. There are two main forces which affect a falling object at different stages of its fall: The weight of the object - this is a force acting downwards, caused by ...
Terminal velocity is the maximum speed achieved by an object freely falling through a gas or liquid. At terminal velocity, the forces acting on the object are balanced so it is no longer accelerating.
Solved Explain The Notion Of Free Fall And Terminal Velocity You Are Floating In Space And Caught By The Gravitational Field Of Mercury It Applie Course Hero

Ben Sudjaitham On Twitter Dualcoding Free Body Diagrams Newton S 1st Amp 2nd Law Teacher Guided Explanations Terminal Velocity For Horizontal And Vertical Motions Big Q Why Does Object That Encounters Air

Terminal Velocity Arizona State University Ranked 1 Velocity Acirc Euro Cent The Object Acirc Euro Trade S Velocity Kinematics Kinetics Linear Angular Linear Angular Positioin Free Body Pdf Document















0 Response to "40 terminal velocity free body diagram"
Post a Comment