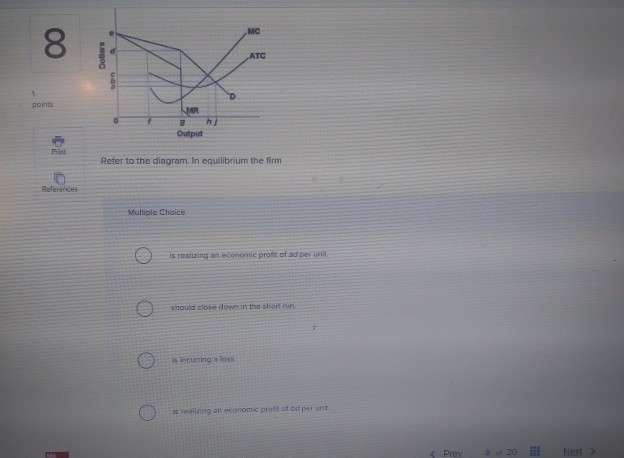
37 refer to the diagram. in equilibrium the firm
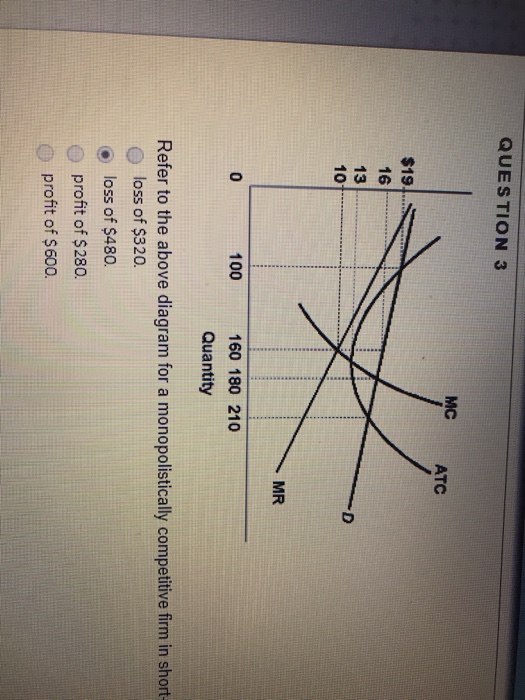
160. Refer to the above diagram for a monopolistically competitive firm in short-run equilibrium. This firm will realize an economic: profit of $480. Refer to the above diagrams, which pertain to monopolistically competitive firms. Short-run equilibrium entailing economic loss is shown by: diagram c only.
Not sure if this is the place to post this (if not I'd really appreciate if someone could point me to the appropriate subreddit) but I'm a high school student studying IBDP economics HL. As part of the IB course we're supposed to write a 4000 word extended Essay in one of our subjects and I've chosen Economics.This essay is ideally supposed to be an exploration of either an application or extension of the concepts of the chosen subject *beyond* the syllabus. So what I'm essentially looking for...
Refer to the above long-run cost diagram for a firm. If the firm produces output Q2 at an average cost of ATC 2, then the firm is: A) producing the potentially profit-maximizing output, but is failing to minimize production costs.
Refer to the diagram. in equilibrium the firm
Economics Q&A Library Refer to the diagrams, which pertain to monopolistically competitive firms. Long-run equilibrium is shown by diagram b only. diagram a only. none of these diagrams. diagram c only.
Refer to the diagram for a monopolistically competitive firm in short-run equilibrium. The profit-maximizing output for this firm will be.
2. the equilibrium position of a competitive firm in the long run. 3. a competitive firm that is realizing an economic profit. 4. the loss-minimizing position of a competitive firm in the short run. 9. Refer to the above diagram. If this competitive firm produces output Q, it will: 1. suffer an economic loss. 2. earn a normal profit.
Refer to the diagram. in equilibrium the firm.
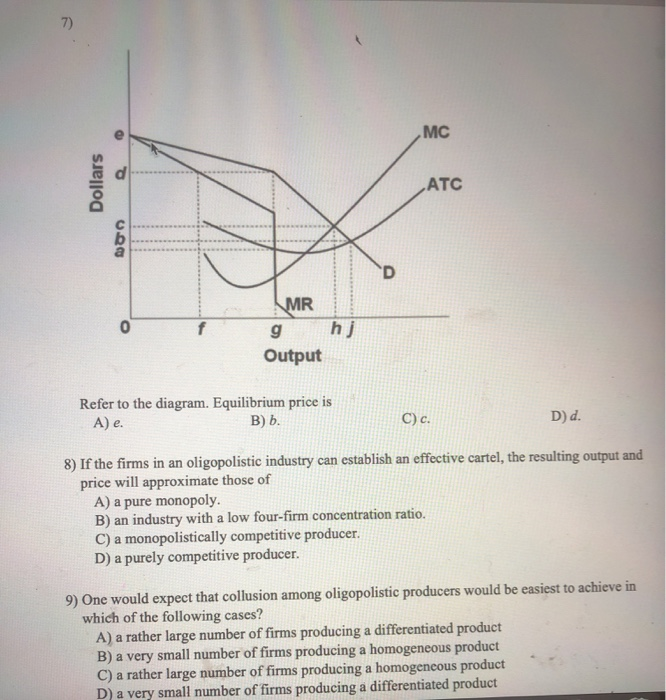
Refer to the above diagram. Equilibrium price is: A. e. B. d. C. c. D. b. E. a. 7. R-1 F26063. Refer to the above diagram. This firm's demand and marginal revenue curves are based on the assumption that: A. the firm has no immediate rivals. B. rivals will match both a price increase and a price decrease. C. rivals will match a price increase ...
Refer to the above diagram. In short-run equilibrium, the monopolistically competitive firm shown will set its price: A. below ATC. B. above ATC. C. below MC. D. below MR. 39. Refer to the above diagram. The monopolistically competitive firm shown: A. will realize allocative efficiency at its profit-maximizing output.
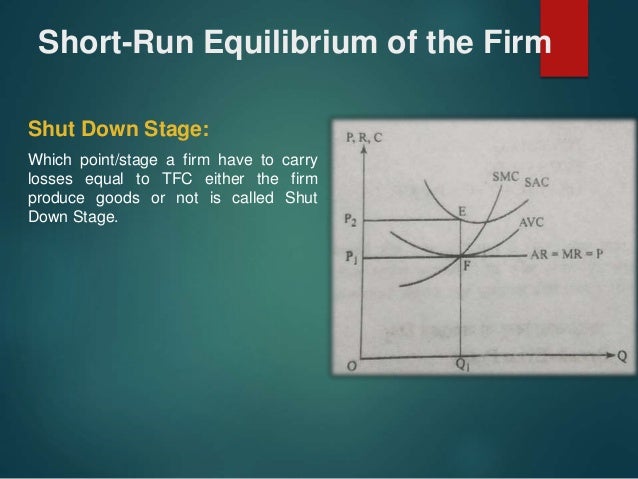
The firm in the short run is minimizing losses if the market price is smaller than average total cost but larger than average variable cost. The loss minimizing position of a price taker firm is explained with the help of a diagram. We assume in the diagram (15.5) that the market price is QP. The firm is in equilibrium at point N where MR = MC.
The diagram below shows a pharmaceutical firmʹs demand curve and marginal cost curve for a new heart medication for which the firm holds a 20-year patent on its production. FIGURE 10-5 11) Refer to Figure 10-5. Assume this pharmaceutical firm charges a single price for its drug. At its
We are approximately 3 weeks from the first Economics paper. The next 21 days are extremely crucial if you are hoping for a significant grade improvement. The positive way to look at it, is that this is a second chance to make up for all the disappointing grades throughout the last 18-odd months. And if your grades *were* disappointing, just know that it wasn't entirely your doing. It is impossible to expect peak performance when you just finished a chapter, and the test is next week, especially...
**Okay, so, I am going to break down this guide into the subjects which I took. Use Control F to read about the subjects you want because this guide is quite long.** SL: English A Language & Literature, Spanish Ab Initio, Mathematics HL: Biology, Chemistry, Economics First of all, a huge **shoutout to everyone on this sub** for all of the help they gave me during the IB, specifically all of those resources and all of the memes to keep me going. A special thanks to the mods who keep the pl...
Often, a retort used by our kind against the red menace is that they lack an understanding of, “basic economics”. In this series I hope to explain basic economic ideas with examples. I should probably start with supply and demand, but that’s boring, so I’ll contrive it to be about monopoly as well. This series is aimed at people who know absolutely NOTHING about econ, so basically half of twitter, my dog and probably me as well. A monopoly can refer to several different things, but usually ref...
Refer to the above graphs. The long-run equilibrium for a monopolistically competitive firm is represented by graph -B. 52. Refer to the diagram for a monopolistically competitive firm. If more firms were to enter the industry and product differentiation were to weaken, then -the demand curve would become more elastic. 53. Refer to the diagrams.
E) None of the above - it is not a long-run equilibrium. 33) Refer to Figure 11-2. The position of a typical firm when the industry is in long -run equilibrium with free entry and exit and product differentiation is exhibited in diagram A) A. B) B. C) C. D) D. 34) In long-run equilibrium, a monopolistically competitive industry is characterized by
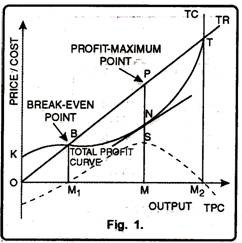
The firm at this point is in equilibrium and either ensuring maximizing profit or minimizing loss. This is shown with the help of a diagram below: Diagram (Profit Maximization): In the diagram (15.2) quantity of output is measured along OX axis and marginal cost and marginal revenue on OY axis.
62. Refer to the diagram. The monopolistically competitive firm shown A. will realize allocative efficiency at its profit-maximizing output. B. cannot operate at a loss. C. is in long-run equilibrium. D . is realizing an economic profit.
by J Hirshleifer · 1962 · Cited by 9 — The standard textbook presentation of the equilibrium of the firm is marred by an imperfect symmetry--at least in the usuLal diagrammatic.
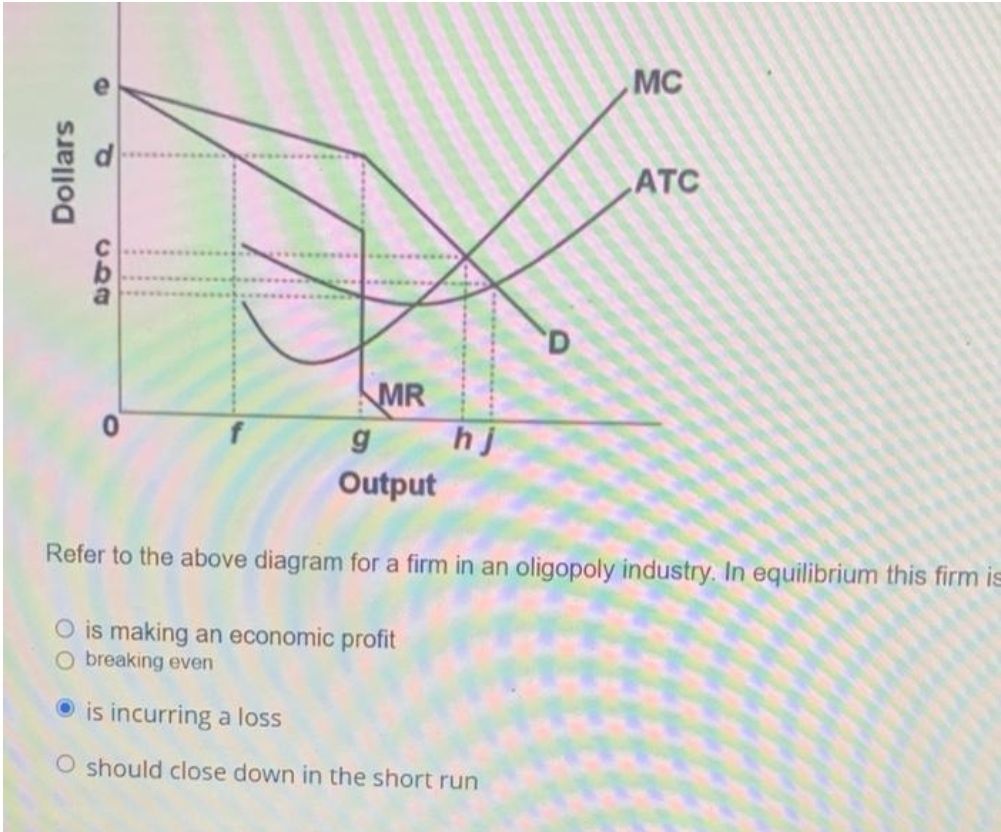
Refer to the above diagram. In equilibrium total cost will be: A. NM times 0M. B. 0AJE. C. 0CGC. D. 0BHE. 11. R-2 F24079. Refer to the above diagram. In equilibrium the firm will realize: A. an economic profit of ABHJ. B. an economic profit of ACGJ. C. a loss of GH per unit. D.
refer to the diagram. the equilibrium price and quantity in this market will be. A. $1.00 and 200. B. $1.60 and 130. C. $.50 and 130. D. $1.60 and 290.
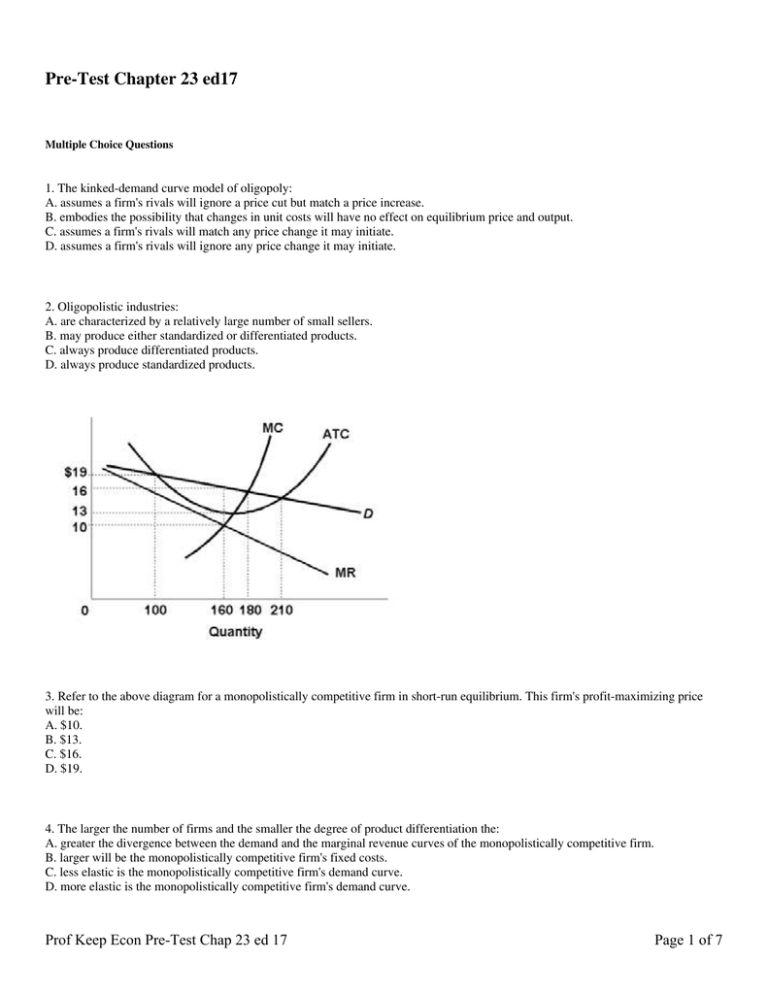
Refer to the above diagram for a monopolistically competitive firm in short-run equilibrium. This firm's profit-maximizing price will be: A. $10. B. $13. C. $16. D. $19. 5. R-1 F25030. Refer to the above diagram for a monopolistically competitive firm in short-run equilibrium. ...
The diagram shows the average total cost curve for a purely competitive firm. At the long-run equilibrium level of output, this firm's total revenue A) is $10. B) is $400. C) is $40. D) cannot be determined from the information provided.
Refer to Figure 7.4 for a perfectly competitive firm. ... to a firm's production decision, and diagram "b" shows the market demand and supply curves for the ...
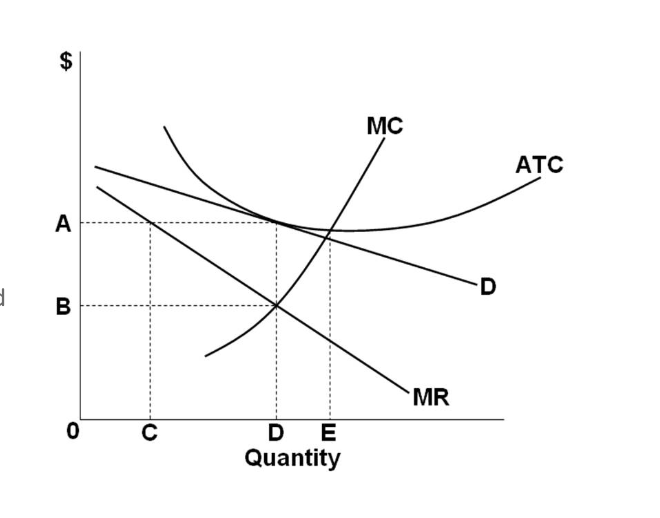
A. Consider the diagram below depicting the demand and cost conditions faced by a monopolistically competitive firm. a. Use the graph to show how price and output will vary depending upon which point the firm produces. Indicate the levels that will be produced under profit maximization, productive efficiency, and allocative efficiency.
Refer to the diagrams, which pertain to monopolistically competitive firms. Long-run equilibrium is shown by -diagram a only. 16. Refer to the graph, which shows a total revenue curve for a monopolist. The profit-maximizing firm will produce in that output level where total revenue is -Rising. 17. Refer to the data.
A firm is in equilibrium when it has no desire to change (increase or decrease) its output levels. At the equilibrium point, the firm earns maximum profits. In this article, we will talk about the equilibrium of the firm along with two approaches to the producer's equilibrium.
Refer to Figure 12-11. Suppose the prevailing price is $20 and the firm is currently producing 1,350 units. In the long-run equilibrium, the firm represented in the diagram. A) will continue to produce the same quantity. B) will reduce its output to 750 units.
Refer to the above diagram. In equilibrium the firm will realize: A) an economic profit of ABHJ . C) a loss of GH per unit. B) an economic profit of ACGJ .
24. Refer to the above diagrams which pertain to a purely competitive firm producing output q and the industry in which it operates. Which of the following is correct? A. The diagrams portray neither long-run nor short-run equilibrium. B. The diagrams portray both long-run and short-run equilibrium. C.
78. Refer to the above diagrams. Diagram (A) represents: A. equilibrium price and quantity in a purely competitive industry. B. the pure monopoly model. C. an industry in which there is productive efficiency but not allocative efficiency. D. a single firm operating in a purely competitive industry.
Equilibrium of Firm: "A firm is a unit engaged in the production for sale at a profit and with the objective of maximizing profit." -Watson. A firm is in equilibrium when it is satisfied with its existing level of output. The firm wills, in this situation produce the level of output which brings in greatest profit or smallest loss.
The diagram below shows demand and cost curves for a monopolistically competitive firm. FIGURE 11-3 16) Refer to Figure 11-3. A monopolistically competitive firm is said to be inefficient because in the long-run equilibrium A) MC is greater than LRAC B) LRAC at Q 1 is not at its minimum.. 16)
##Magick and Hermetics ###[The Kybalion](http://english.grimoar.cz/?Loc=book&Lng=2&Back=nam&UID=390) An occult classic Since its first publication in 1908, The Kybalion, Hermetic Philosophy by Three Initiates, has been in constant demand by students and investigators of the Secret Doctrines. It is a modern addition to the body of work devoted to Hermes Trismegistus, an icon of ancient teachings that reveal the path to self transformation. In this revised edition, we have correct...
41.Refer to the diagrams, which pertain to monopolistically competitive firms. : 1637282. 41. Refer to the diagrams, which pertain to monopolistically competitive firms. Short-run equilibrium entailing economic loss is shown by: A. diagram a only. B. diagram b only. C. diagram c only. D. both diagrams a and c. 42.
At the long-run equilibrium level of output, this firm's total revenue: 400 Refer to the diagram. at output level q, average fixed cost In economics, the marginal cost is the change in the total cost that arises when the quantity produced is incremented, the cost of producing additional quantity.
Refer to the diagram to the right. the equation for market demand is given by: D (p) = 950 - 10 p the equation for the supply curve of all other firms is given by: S degree (p)= -400 + 20p at the market equilibrium price of $45.00, the residual demand for a given firm is: 0 units (enter your response as an integer).
29. Refer to the above diagram. In equilibrium the firm: A. is realizing an economic profit of ad per unit. B. should close down in the short run. C. is incurring a loss. D. is realizing an economic profit of bd per unit.
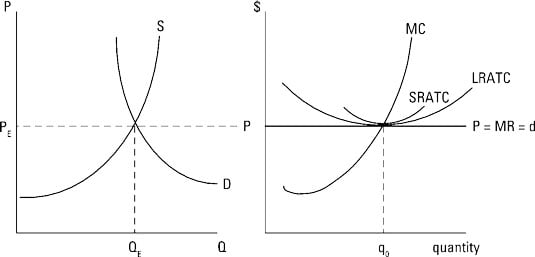
Since the industry is in long-run equilibrium, the price equals the minimum point on the representative firm's average total cost curve, so the firm produces ...
##Magick and Hermetics ###[The Kybalion](http://english.grimoar.cz/?Loc=book&Lng=2&Back=nam&UID=390) An occult classic Since its first publication in 1908, The Kybalion, Hermetic Philosophy by Three Initiates, has been in constant demand by students and investigators of the Secret Doctrines. It is a modern addition to the body of work devoted to Hermes Trismegistus, an icon of ancient teachings that reveal the path to self transformation. In this revised edition, we have correct...
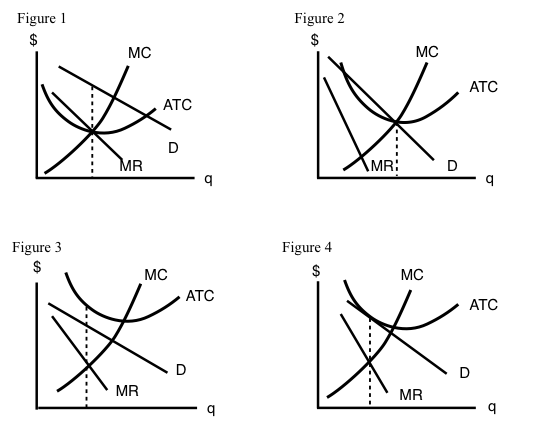
by E Hutchinson · 2017 — The following TWO questions refer to the diagram below. 3. Which of the four diagrams illustrates a long run equilibrium for a monopolistically competitive firm ...
Suppose the graph below depicts a monopolistically. chap 025 oligopoly chap 025 uploaded by matt refer to the above diagram for a monopolistically petitive firm in monopolistically petitive firms are inefficient. Question The graph below shows the short run cost revenue and perceived demand curves for all firms in t.
Note: Regarding the (now) dead links, please search https://libgen.io for these books. I will re-upload them when I have more time. ----- ##Magick and Hermetics ###[The Kybalion](http://english.grimoar.cz/?Loc=book&Lng=2&Back=nam&UID=390) An occult classic Since its first publication in 1908, The Kybalion, Hermetic Philosophy by Three Initiates, has been in constant demand by students and investigators of the Secret Doctrines. It is a modern addition to the body of work devot...










![Quiz+ | [Solved] The Diagram Below Shows Demand and Cost ...](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB5441/11ea71cb_f380_68da_91e5_a7c4098536ab_TB5441_00_TB5441_00_TB5441_00_TB5441_00_TB5441_00_TB5441_00.jpg)





0 Response to "37 refer to the diagram. in equilibrium the firm"
Post a Comment