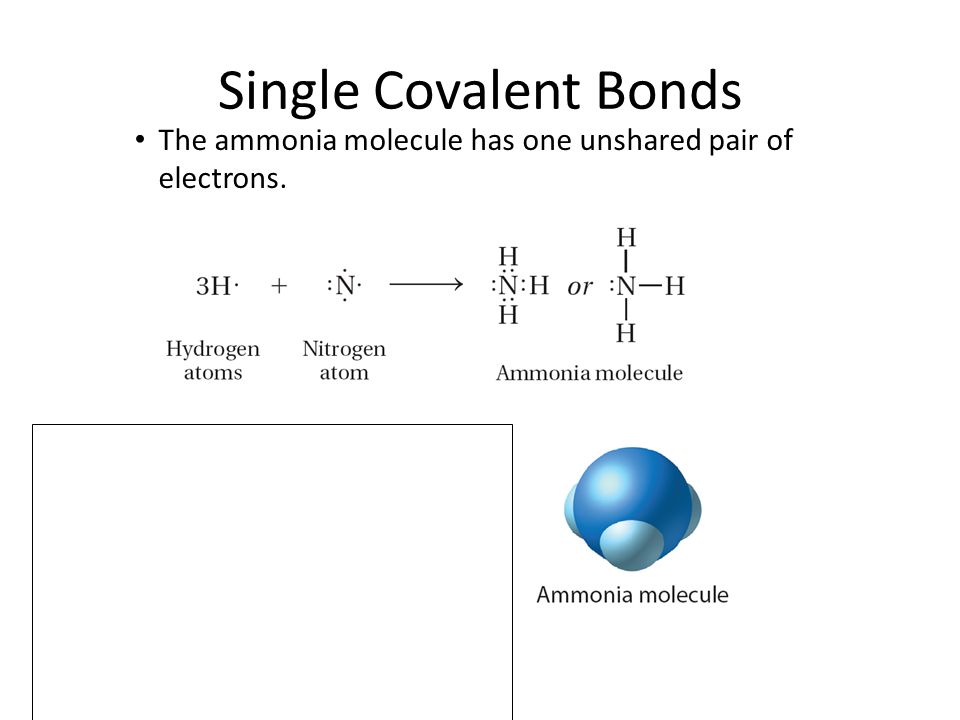
40 the ammonia molecule in the diagram has the observed bond orientation because ...
A method for determining geometry of binary compounds.. Given a binary compound #AX_n# where A is the central element, X the attached substrate element and n the number of substrate elements attached. If the structure has non-bonded electron pairs, then the objective is #AX_nE_n# where #E_n# is the number of non-bonded electron pairs.. Needed is the number of 'Bonded electron pairs' (BPrs) and... Feb 07, 2016 · The ammonia molecule in the diagram has the observed bond orientation because. The ammonia molecule in the diagram has the observed bond orientation because. N has four pairs of electrons in the valence shellb. Electrons repel one another c. Rotation can occur around single bonds. All of the above e. N has 7 protons in its nucleus.
View full document. The ammonia molecule in the diagram has the observed bond orientation because…. All of the above (N has 7 protons in its nucleus, electrons repel one another, N has four pairs of electrons in the valence shell) The discovery of which of the following led to a drastic change in deep sea mining?
The ammonia molecule in the diagram has the observed bond orientation because ...
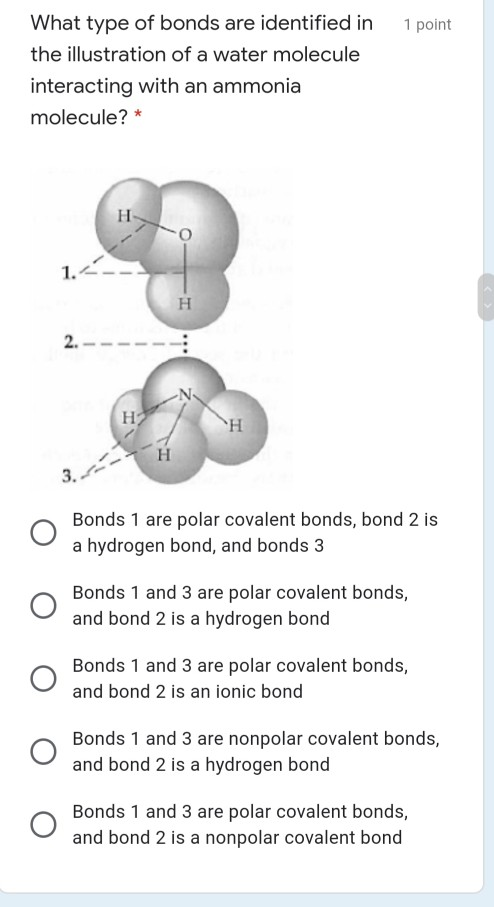
Molecular geometry. The theory of valency which we have been developing is known as valence bond theory.One further feature of this theory is that it may be used to predict (or in some cases, rationalize) the observed geometries of molecules By the geometry of a molecule we mean the relative arrangement of the nuclei in three-dimensional space. The ammonia molecule (NH3) in the diagram has the observed bond orientation because...a. N has four pairs of electrons in the valence shell. b. N has 7 protons in its nucleus. c. electrons repel one another. d. All of the above. e. None of the above. Part (b)(i) did not earn the point for an incorrect electron-dot diagram for the wrong molecule shown in the box, but part (b)(ii) earned 1 point for showing the orientation for the formation of a hydrogen bond even though the molecule shown is still wrong. Part (c)(ii) did not earn the point because the solid phase is discussed.
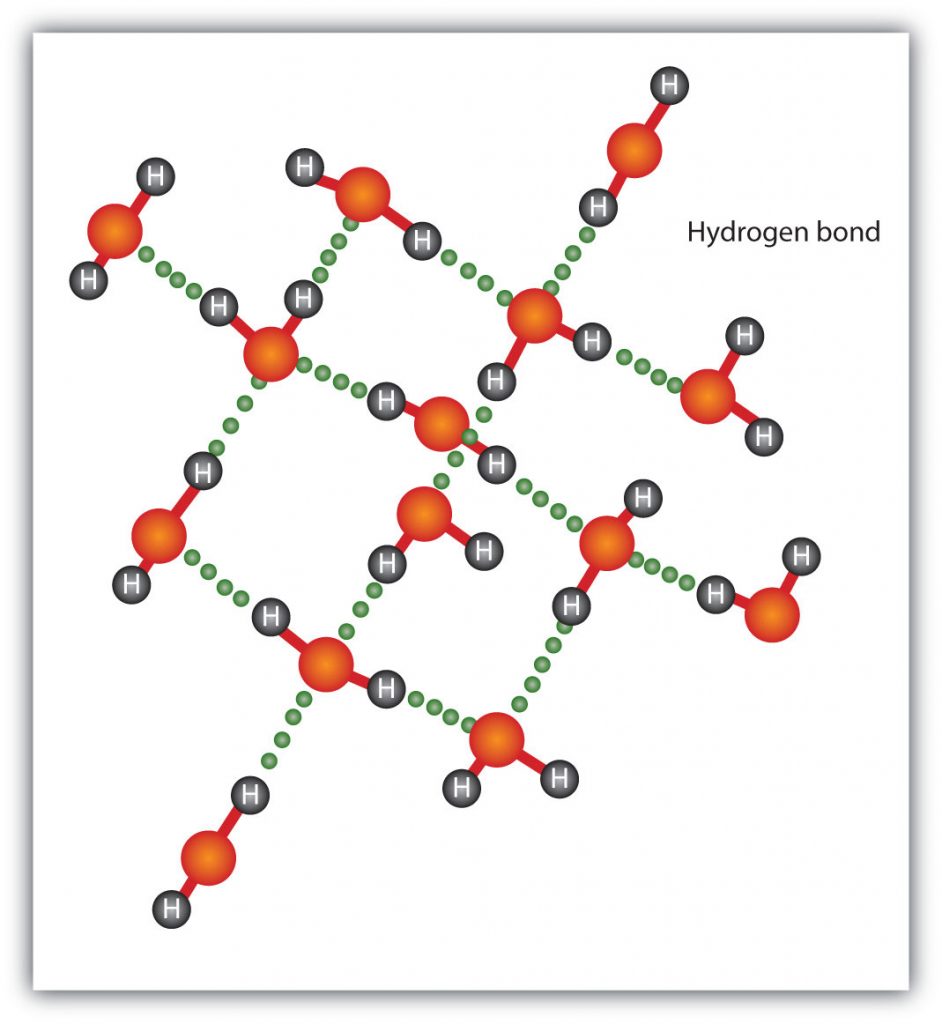
The ammonia molecule in the diagram has the observed bond orientation because .... The ammonia molecule in the diagram has the observed bond orientation because 30 more tips 1994 ford ranger fuse box diagram 30 even more tips troy bilt pony parts diagram 50 more step and image. Chap 2 Chemical Bond Chemical Polarity None of the above. The ammonia molecule in the diagram has the observed bond orientation because. Each pair of... The ammonia molecule in the diagram has the observed bond orientation because...A. N has four pairs of electrons in the valence shell. B. electrons repel one another. C. N has 7 protons in its nucleus. D. All of the above. E. None of the above. Bacteria found in the intestines can produce ammonia. Ammonia is a colorless gas with a very distinct odor. This odor is familiar to many people because ammonia is used in smelling salts, many household and industrial cleaners, and window-cleaning products. Ammonia gas can be dissolved in water. This kind of ammonia is called liquid ammonia or... Figure 27 illustrates the hydrogen bonding as observed in crystalline ammonia. The hydrogen bonds are longer than those in ice and are non-linear. Although each ammonia molecule forms hydrogen bonds with six neighbors in the crystal, only two ammonia molecules are shown here.
The Ammonia Molecule In The Diagram Has The Observed Bond Orientation Because The electrons form 3 bonds and 1 lone pair of electrons. N has four pairs of electrons in the valence shell b. If a molecule contains only two atoms, those two atoms are in a straight line and thus form a linear molecule. Some three-atom molecules also have straight-line geometry. For example: Notice that, in the Lewis structure of these molecules, the central atom(s) bonds with only two other atoms and has no unshared electrons. The ammonia molecule in the diagram has the observed bond orientation because...There is a ball-and-stick model of ammonia, NH3. Three hydrogen atoms are attached to nitrogen. N has 7 protons in its nucleus. N has four pairs of electrons in the valence shell. All of the above. None of the above. Since lone pairs occupy more space than bonding pairs, structures that contain lone pairs have bond angles slightly distorted from the ideal. Perfect tetrahedra have angles of 109.5°, but the observed angles in ammonia (107.3°) and water (104.5°) are slightly smaller. Other examples of sp 3 hybridization include CCl 4, PCl 3, and NCl 3.
Chem 302. The Molecular Orbitals of Ammonia. Determing the electronic structure of ammonia will introduce the new ideas of degenerate orbitals and degenerate axes. It is important to understand these concepts because of the large number of molecules that have point groups such as C 3v or D 3h. To determine the MO's of ammonia. Dec 25, 2018 · The ammonia molecule in the diagram has the observed bond orientation because a. (c) The electrostatic potential diagram of the water molecule. The polarity of the NOH bonds occurs because nitrogen has a greater electronegativity than hydrogen. (b) The dipole moment of the ammonia molecule oriented in an electric field. The ammonia molecule in the diagram has the observed bond orientation because... a) electrons repel one another b) N has four pairs of electrons in the valence shell c) N has 7 protons in its nucleus d) all of the above e) none of the above Construct SALCs and the molecular orbital diagram for NH\(_3\). This is the first example so far that has more than two pendant atoms and the first example in which the molecule has atoms that lie in three dimensions (ie it is not flat). Ammonia is a trigonal pyramidal molecule, with three pendant hydrogen atoms.
1. By making two covalent bonds, an O atom with 8 protons fills its valence shell. why does the atoms charge stay close to zero?a. The atom lost electrons from other; Question: 1. By making two covalent bonds, an O atom with 8 protons fills its valence shell. why does the atoms charge stay close to zero?a. The atom lost electrons from other
The ammonia molecule in the diagram has the observed bond orientation because...A. N has four pairs of electrons in the valence shell. B. electrons repel one another. C. N has 7 protons in its nucleus. D. All of the above. E. None of the above.
Thus far, we have used two-dimensional Lewis structures to represent molecules. However, molecular structure is actually three-dimensional, and it is important to be able to describe molecular bonds in terms of their distances, angles, and relative arrangements in space ().A bond angle is the angle between any two bonds that include a common atom, usually measured in degrees.
Dec 17, 2019 · Ammonia, , is a molecule which contains three N-H bonds, as well as one lone pair on nitrogen. According to the VSEPR theory, molecules try to acquire a shape which would minimize the repulsion exhibited by the electron clouds present, that is, between the bonding (shared in a bond) and non-bonding (lone pair) electrons.
molecular nitrogen, so this is additional evidence for the dissociative mechanism. formed as a result of ammonia decomposition, has also been observed by secondary ion mass spectrometry. ^ ^ There is also evidence for atomic nitrogen on iron surfaces. On doubly promoted industrial catalysts little or no molecular nitrogen is
The Ammonia Molecule In The Diagram Has The Observed Bond Orientation Because The electrons form 3 bonds and 1 lone pair of electrons. N has four pairs of electrons in the valence shell b.
Covalent Bonds hold atoms together because they....an atoms atomic number is 7. Its valence is most likely. 3. By making two covalent bonds, an O atom (w/ 8 protons) fills its valence shell...In a double covalent bond, a carbon atom shares.. electrons in two orbitals. The ammonia molecule in the diagram has the observed bond orientation...
Molecular oxygen makes up nearly 21% of the atmosphere. The simple electron dot diagram indicates that O 2 has a double bond (one sigma bond and one pi bond) between the two oxygen atoms. Each oxygen also has 2 non-bonding pairs of electrons. When we count the shared electrons and the non-bonding electrons for each oxygen atom, we get 8 electrons.
The ammonia molecule in the diagram has the observed bond orientation because. N has four pairs of electrons in the valence shell b. The electrons form 3 bonds and 1 lone pair of electrons. All of the above. The ammonia molecule in the diagram has the observed bond orientation because. Electrons repel one another c. N has 7 protons in its nucleus.
Dec 16, 2019 · Nitrogen has a total of 7 protons (its atomic number is 7) in its nucleus. Explanation: The shape and the bond orientation of molecules and ions are both explained by the valences shell electron pair repulsion theory (VSEPR). Ammonia, , is a molecule which contains three N-H bonds, as well as one lone pair on nitrogen. According to the VSEPR ...
Figure 9.2. 1: The two isolated hydrogen atoms at the top have one electron in their 1s orbital, and so they are free radicals. When they form a bond, each of the hydrogen donates one electron. This bond is called a σ bond because there is overlap along the internuclear axis. In valence bond theory we will often visualize bonds being formed...
Part (b)(i) did not earn the point for an incorrect electron-dot diagram for the wrong molecule shown in the box, but part (b)(ii) earned 1 point for showing the orientation for the formation of a hydrogen bond even though the molecule shown is still wrong. Part (c)(ii) did not earn the point because the solid phase is discussed.
The ammonia molecule (NH3) in the diagram has the observed bond orientation because...a. N has four pairs of electrons in the valence shell. b. N has 7 protons in its nucleus. c. electrons repel one another. d. All of the above. e. None of the above.
Molecular geometry. The theory of valency which we have been developing is known as valence bond theory.One further feature of this theory is that it may be used to predict (or in some cases, rationalize) the observed geometries of molecules By the geometry of a molecule we mean the relative arrangement of the nuclei in three-dimensional space.










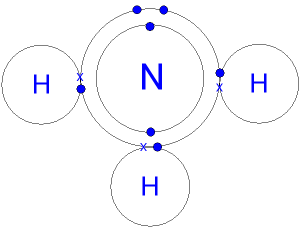







0 Response to "40 the ammonia molecule in the diagram has the observed bond orientation because ..."
Post a Comment