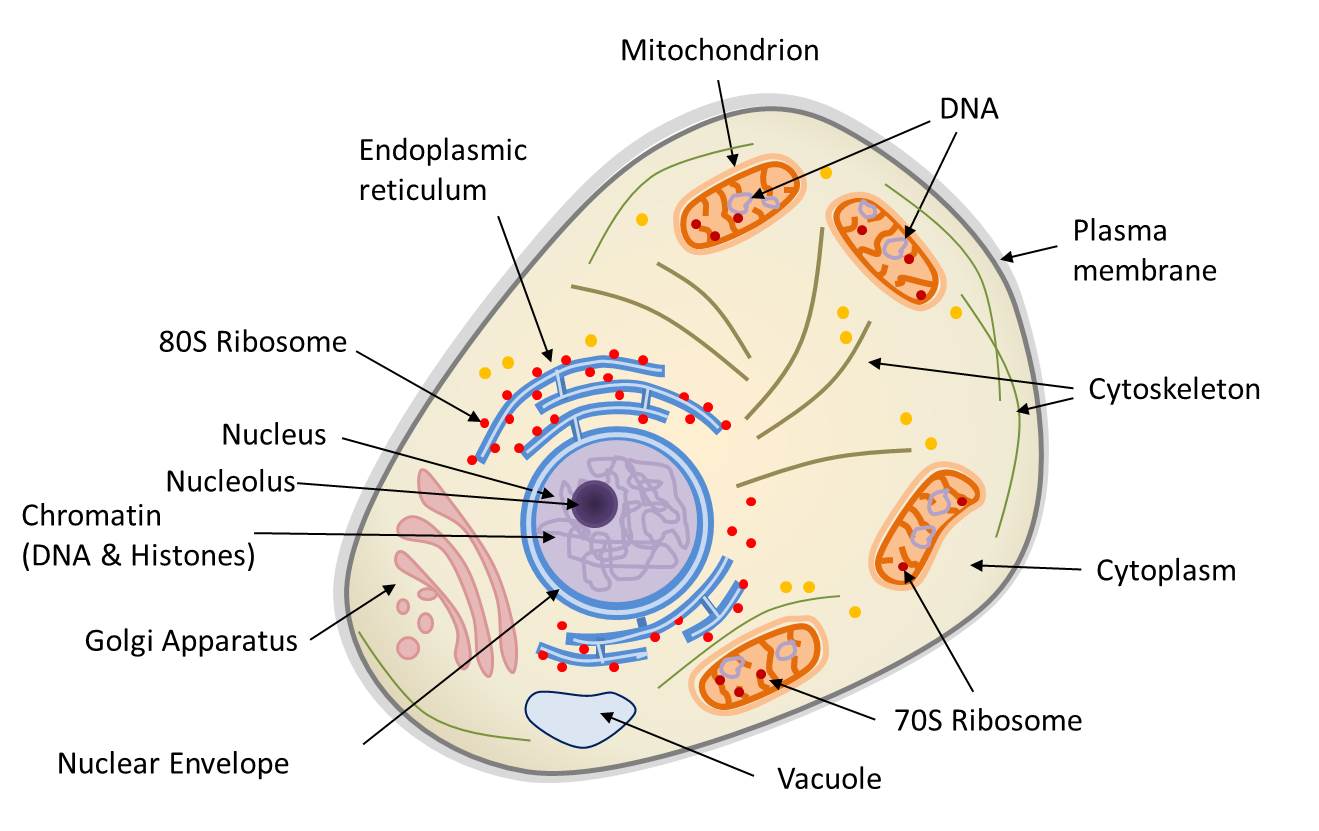
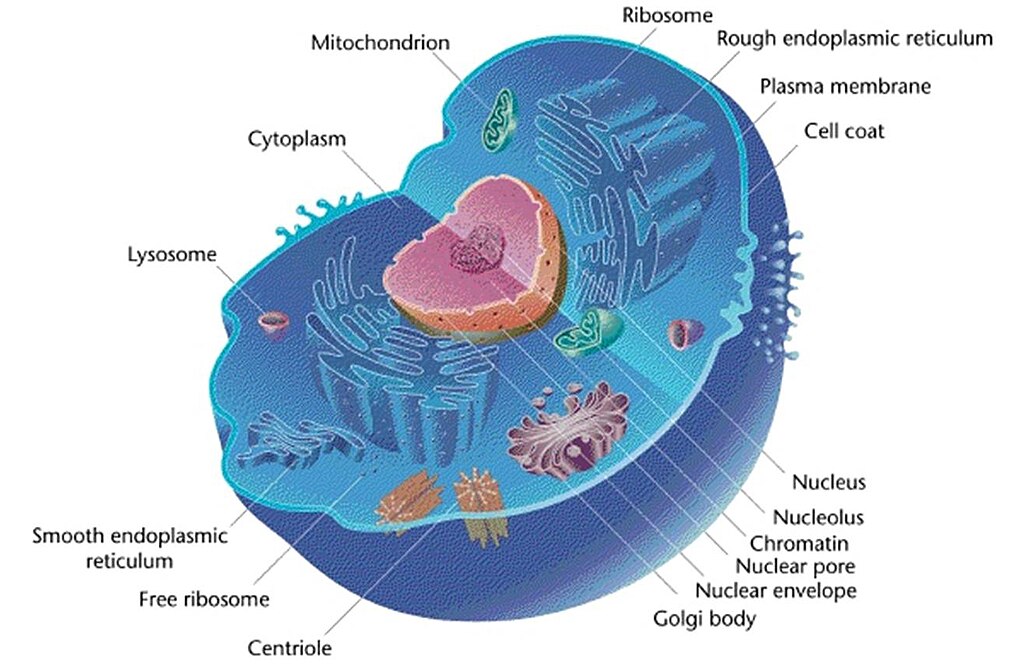
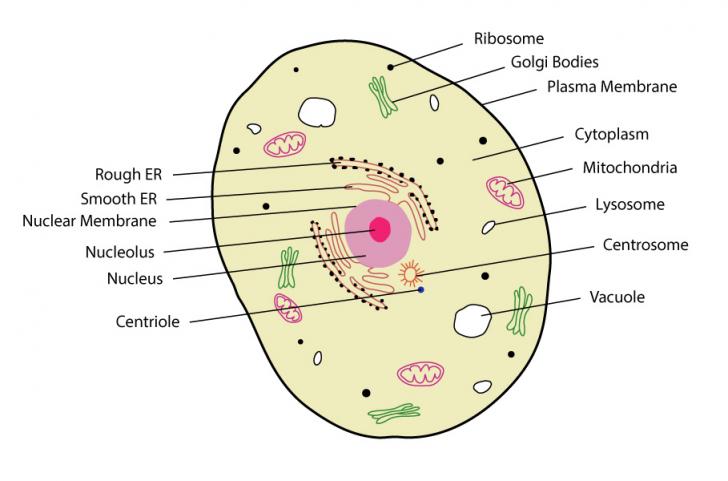
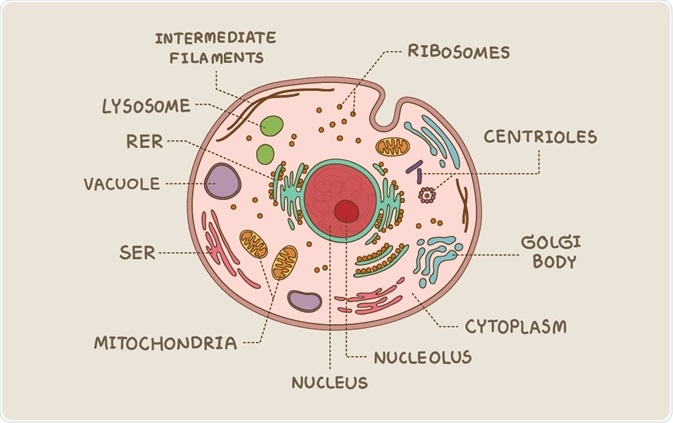
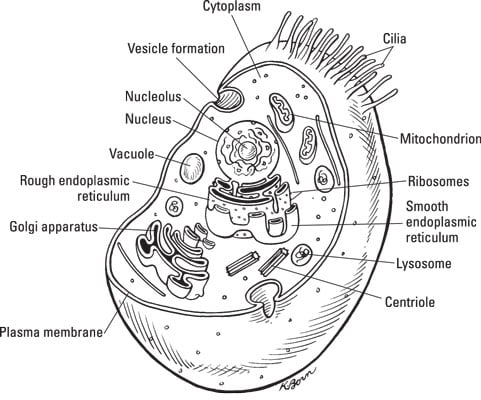
41 diagram of eukaryote cell
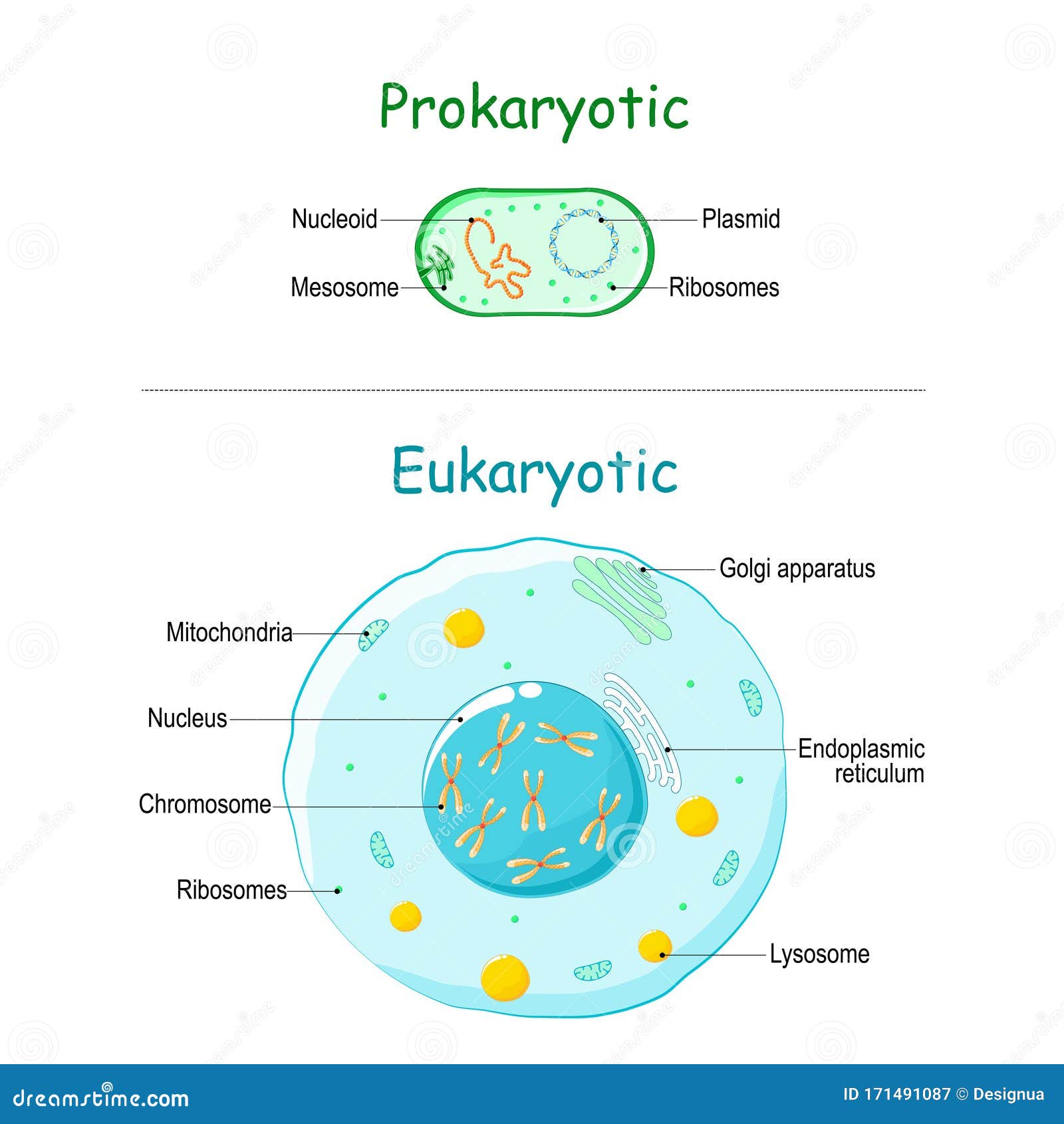
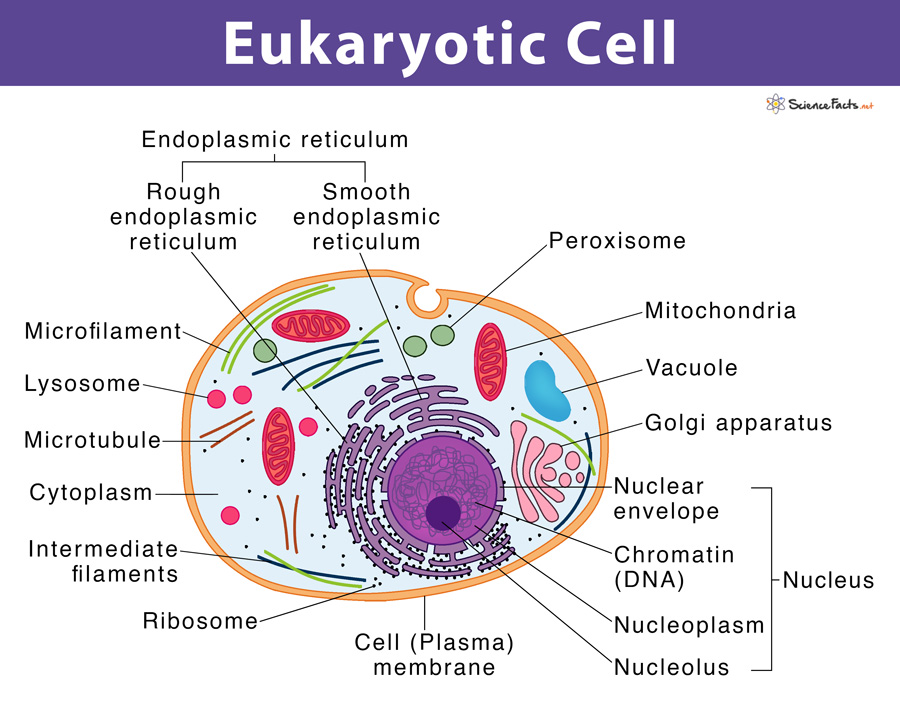
Unlike prokaryotic cells, eukaryotic cells have: 1) a membrane-bound nucleus; 2) numerous membrane-bound organelles such as the endoplasmic reticulum, ...
Bacteria lack the relatively stable poly(A) tails found on eukaryotic mRNA. Until very recently, isolating mRNA from bacteria has been virtually impossible. The Invitrogen MICROB Express Bacterial mRNA Isolation Kit employs a novel technology to remove >95% of the 16S and 23S rRNA from total RNA of E. coli and other bacterial species.
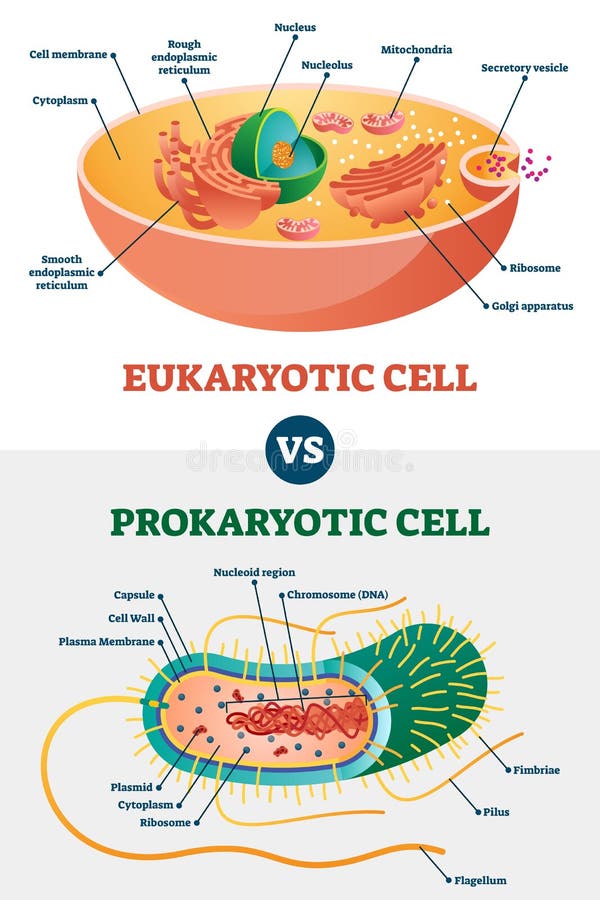
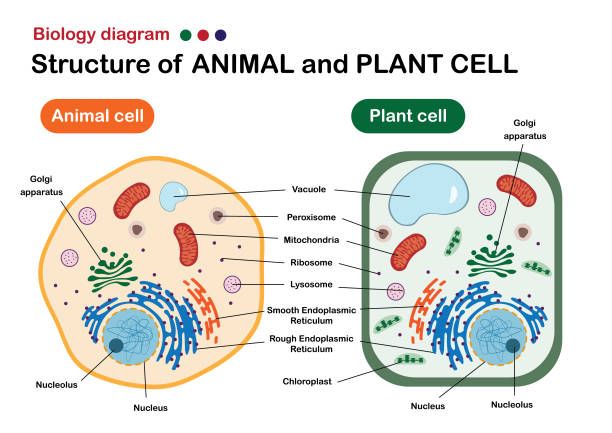
Answers: Eukaryotic cells have a true nucleus and membrane-bound organelles like mitochondria, Golgi complex, etc. The cell organelles and nucleus is embedded ...The main site of lipid synthesis: Site of protein ...Smooth due to lack of ribosomes: Rough due to ...Smooth Endoplasmic Reticulum (SER): Rough ...Describe the characteristics of eukaryotic cells.Unlike eukaryotic cells, prokaryotic cells A. Lack in plasma membrane B. Do not have a nucleus C. Have RNA not DNA D. All of above

Diagram of eukaryote cell
Oct 20, 2021 — A eukaryotic cell can be defined as a cell that has a membrane-bound nucleus and other membrane-bound structures located in the cytoplasm called ...
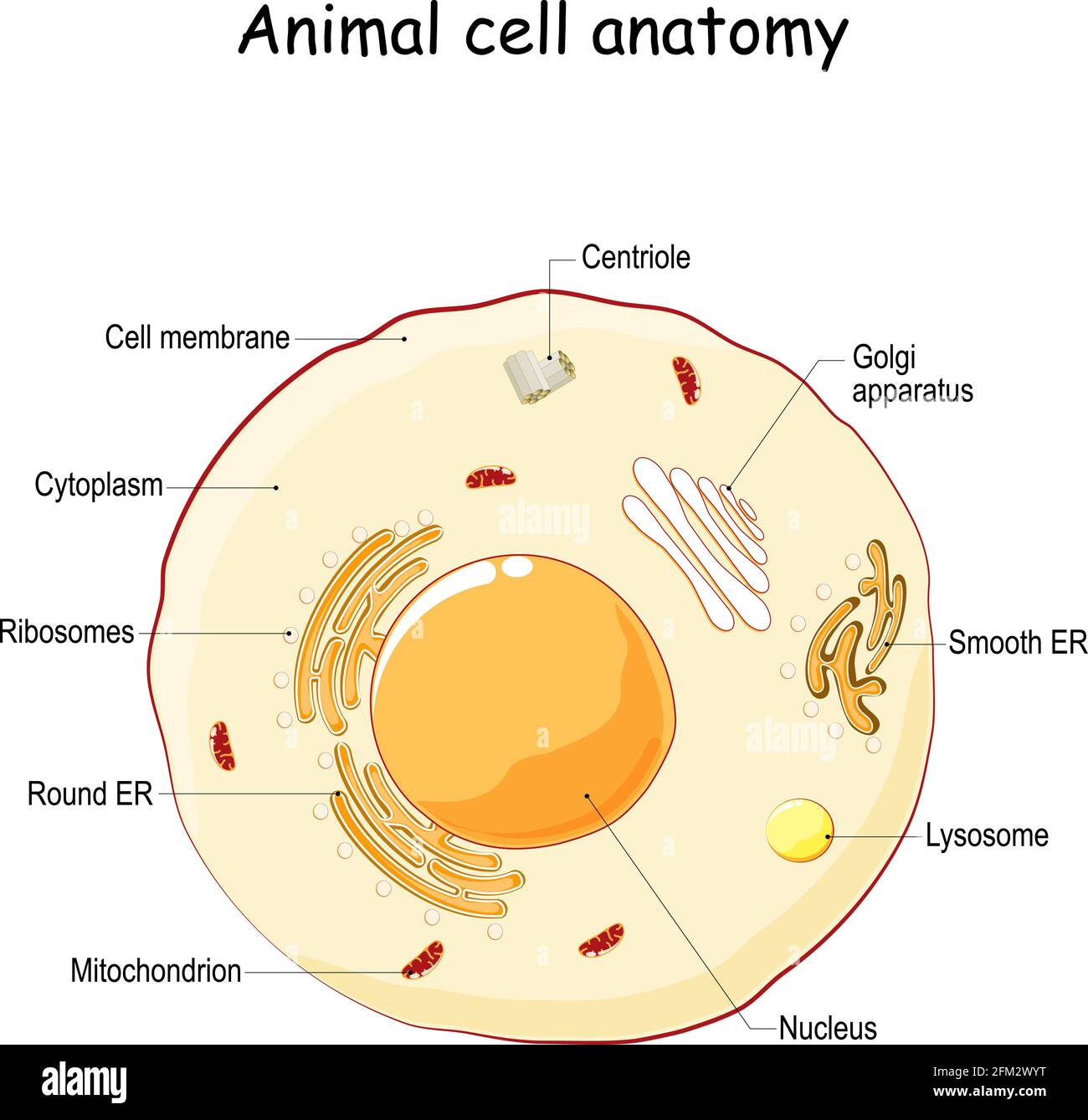
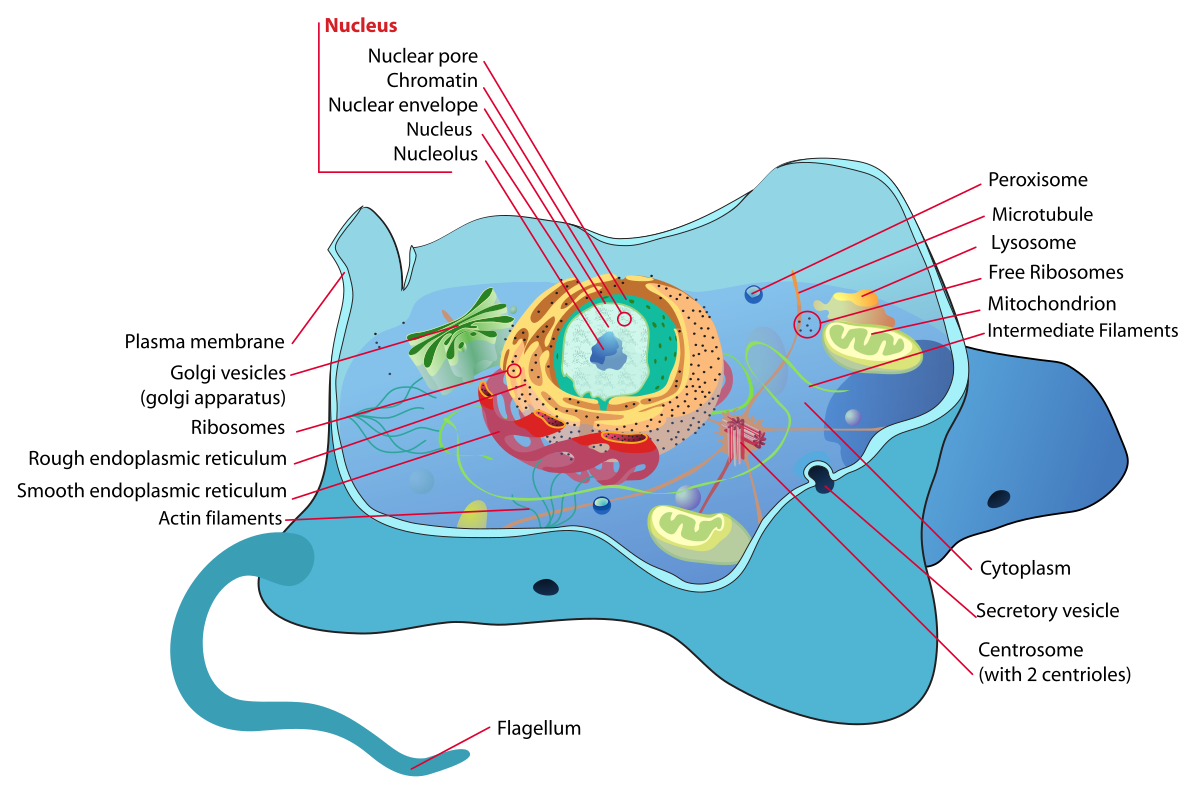
A Labeled Diagram of the Animal Cell and its Organelles. There are two types of cells - Prokaryotic and Eucaryotic. Eukaryotic cells are larger, more complex, ...
The mitochondrial DNA is located inside the mitochondria, which are cellular organelles within eukaryotic cells that convert chemical energy from food into a form that cells can use. The mitochondrial DNA is passed down directly from the mother and the genes are specific to the mother's lineage.
Diagram of eukaryote cell.
Cell Structure and Function:CellTypes andTransportLABREPORTASSISTANTThisdocumentisnotmeanttobeasubstituteforaformallaboratoryreport.TheLabReport ...
The diagram was popularised in the 1880s by John Venn, an English logician during the 1880s. Similar diagrams were designed in the 1700s through Leonard Euler, a Swiss mathematician. He referred to them as Eulerian circles.
Then, they move on to another fresh host cell and the cycle continues. 2. Lysogenic Cycle. Viruses that take more time to multiply use this cycle for reproduction - this is the case for viruses like the herpes virus and the HIV virus. During this cycle, the nucleic acid of the virus takes time to develop complete hold on the host cell.
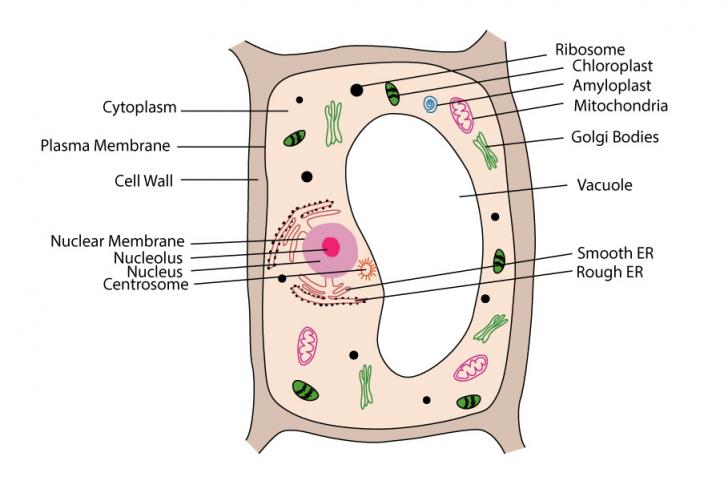
Eukaryotes have a compartmentalised cell structure. ... Click on the diagram to show / hide labels. Typical Structure of a Plant Cell. plant-labelled.
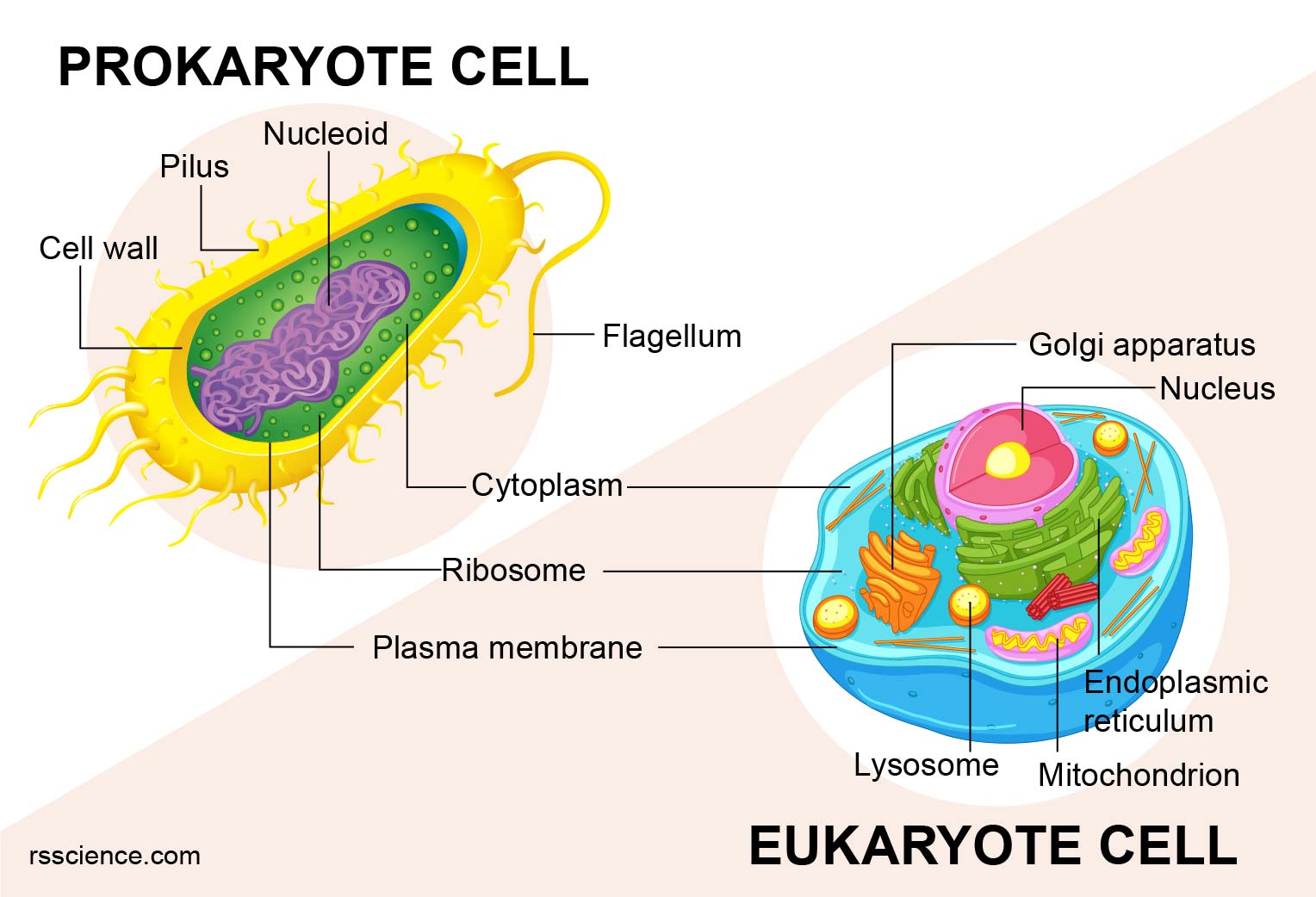
Today, we classify prokaryotes and eukaryotes based on differences in their cellular contents (Figure 5). A diagram of a prokaryotic cell is shown beside a ...
[PMC free article] Krishna TS, Kong XP, Gary S, Burgers PM, Kuriyan J. Crystal structure of the eukaryotic DNA polymerase processivity factor PCNA. There is a membrane present throughout the nucleus in case of Eukaryotic cells whereas there is no such thing as a such factor as a membrane found inside the Prokaryotic cells.
You should use diagrams and/or comparison tables to support your commentary where appropriate. • Discuss the selected characteristics of living cells. • Compare and contrast prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells, and explain the impact that viruses have on them. • Discuss eukaryotic sub-cellular structure and organelles. SECTION 2
Cells are small compartments that hold the biological equipment necessary to keep an organism alive and successful. Living things may be single-celled or they may be very complex such as a human being. Unit: Structure of a cell. Legend (Opens a modal). Eukaryotic cell structures Get 3 of 4 questions to level up! Extracellular structures and ...
Eukaryote prokaryote reproduction or animal plant cell energy. To do this print or copy this page on a blank paper and underline or circle the answer. Animal cells come in all kinds of shapes and sizes with their size ranging from a few millimeters to micrometers.
At its most simple, the ribosomes of bacteria are smaller, made of different subunits than those of eukaryotic cells. As such, antibiotics can be designed to target prokaryotic ribosomes whilst leaving the eukaryotic cells (e.g. our cells or the cells of animals) unharmed. With no functioning ribosomes, the cell cannot complete protein synthesis.
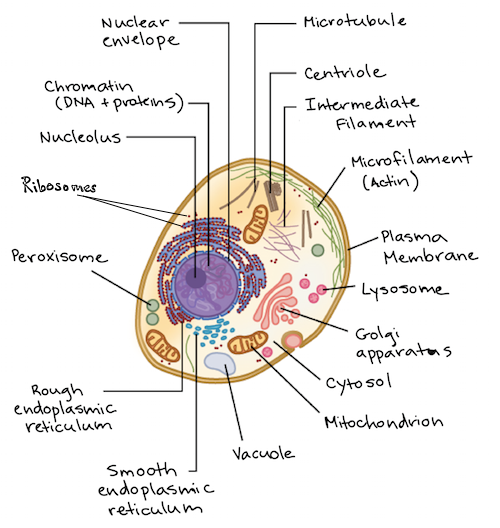
Plant cells are eukaryotic cells present in green plants, photosynthetic eukaryotes of the kingdom Plantae. Their distinctive features include primary cell walls containing cellulose, hemicelluloses and pectin, the presence of plastids with the capability to perform photosynthesis and store starch, a large vacuole that regulates turgor pressure, the absence of flagella or centrioles, except in ...
Objective: To understand isolation of RNA, the most critical step in performing most of the molecular biology experiments. Principle: RNA (Ribonucleic acid) is a polymeric substance present in living cells and many viruses, consisting of a long single-stranded chain of phosphate and ribose units with the nitrogen bases adenine, guanine, cytosine, and uracil, which are bonded to the ribose ...
Eukaryotic cells have defined nucleus along with other membrane bound cell organelles such as mitochondria, ribosome, lysosome, Golgi bodies, endoplasmic ...
Tremellomycetes. Pucciniomycotina p. p. Microbotryomycetes. Yeasts are eukaryotic, single-celled microorganisms classified as members of the fungus kingdom. The first yeast originated hundreds of millions of years ago, and at least 1,500 species are currently recognized. They are estimated to constitute 1% of all described fungal species.
RBSE Solutions for Class 11 Biology Chapter 6 The Cell. Rajasthan Board RBSE Class 11 Biology Chapter 6 The Cell RBSE Class 11 Biology Chapter 6 Multiple Choice Objective Questions. Question 1. Study of cell structure and composition is called as - (a) Biology (b) Morphology (c) Cell Biology (d ) Genetics. Question 2. Living cell was first ...
1)Both plant and animal cells are eukaryotic, which means they have a defined nucleus which contains chromosomes. 2)Animal and plant cells have a cell membrane that surrounds the cell. 3) Both cells have complex structures. 4)Both plant and animal cells have plasma membranes. CELL STRUCTURE AND FUNCTIONS.
Prokaryotic cells, differences between prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells and lastly we started the discussion about the structure of eukaryotic cells. In continuation to previous. Prokaryotes and Eukaryotes Dr. Lamees A.Razzak. Eukaryotic cell membrane contain sterols, whereas no prokaryotes. In its membrane. All animals are eukaryotes.
Prokaryote cell structure & function. ... Time: 1h Mitosis is a miraculous process. In the making of the three trillion cell s of our bodies it manages to ... Just a r and om help cell structure and process es practice worksheet fill out the chart about cell s with a or a prokaryotic eukaryotic cell membrane yes yes.
Eukaryote, any cell or organism that possesses a clearly defined nucleus. The eukaryotic cell has a nuclear membrane that surrounds the nucleus, ...
The diagram on the left above shows a proposed model of microbial distribution, ... The endosymbiotic theory suggests that photosynthetic bacteria were acquired (by endocytosis) by early eukaryotic cells to form the first plant cells. Therefore, chloroplasts may be photosynthetic bacteria that adapted to life inside plant cells.
The eukaryotic cells have ER. The ER membrane synthesizes all of the transmembrane proteins and lipids necessary for most of the cells' organelles. They have several functions in the cell like protein synthesis, production of steroids, sequestration of calcium, and also storage and production of glycogen.
The Oxidative Stress and Cell Cycle Research Group at UPF has discovered a mechanism whereby cells under stress conditions stop their polarized growth. The study, published in the journal Cell ...























0 Response to "41 diagram of eukaryote cell"
Post a Comment