39 diagram of facilitated diffusion
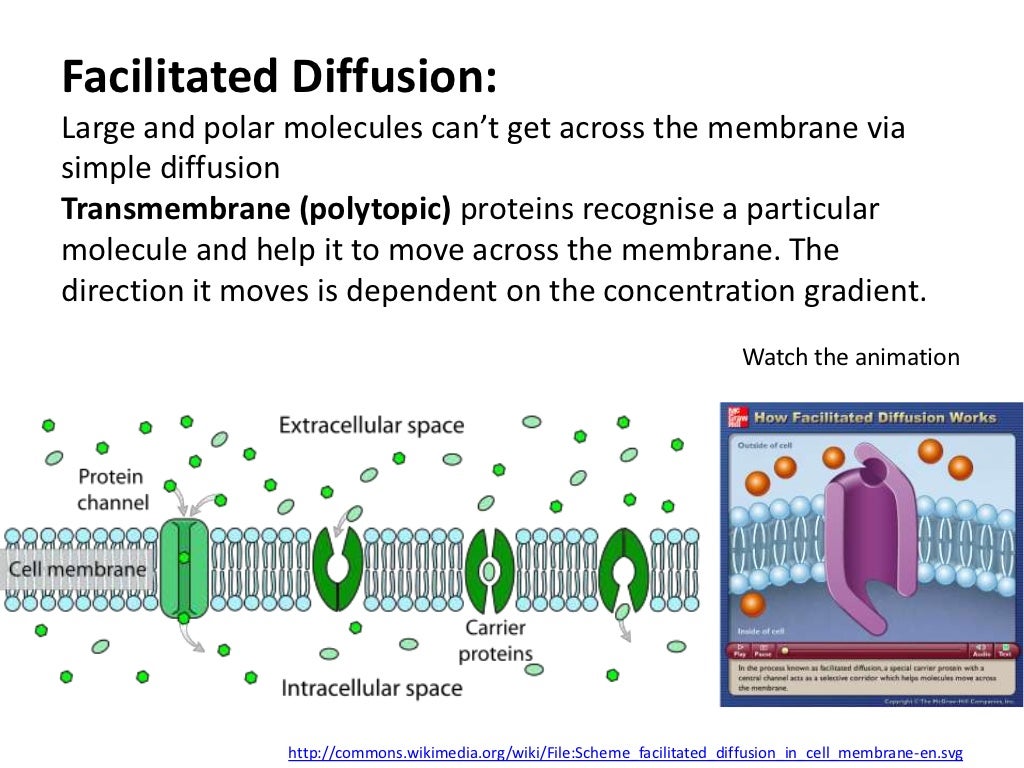
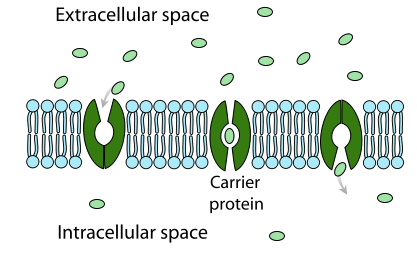
Facilitated diffusion is the passive movement of molecules along the concentration gradient. It is a selective process, i.e., the membrane allows only selective molecules and ions to pass through it. It, however, prevents other molecules from passing through the membrane. The electric charge and pH helps in the diffusion across the membrane. In living systems, the lipidbased membrane creates compartments which allow the transport of a selective concentration of water-soluble substances. The ions, small molecules, proteins, and other solutes have different concentration across the membranes. Hydrophilic, polar or charged molecules cannot cross the membrane. The earliest recognized and simplest form of carrier-mediated transport is facilitated diffusion, often called facilitated transport, in which an otherwise impermeant solute binds to a site on an integral protein (carrier) from one side of the membrane and then undergoes a translocation that provides the solute access to the other side. The classic example of facilitated diffusion is glucose transport across the membranes of cells such as erythrocytes, muscle, adipocytes, etc.
C Facilitated diffusion requires ATP which will eventually be used up. D Only facilitated diffusion is affected by the kinetic energy of the molecules that are diffusing. 17 Which part of a phospholipid molecule makes up most of the thickness of a cell surface

Diagram of facilitated diffusion
Diffusion, Facilitated Diffusion, Osmosis, and Active Transport ... Diffusion is the movement of molecules from an area where the molecule is in high ... Facilitated Diffusion Written by tutor Emma C. The cell membrane, also called the plasma membrane, of eukaryotic cells is composed of a phospholipid bilayer ... Learn the facilitated diffusion definition, why it is necessary, types of facilitated diffusion, and facilitated diffusion examples. Updated: 04/25/2021 Table of Contents
Diagram of facilitated diffusion. Facilitated Diffusion through Cell Membrane (With Diagram) A variety of compounds including sugars and amino acids pass through the plasma membrane and into the cell at a much higher rate than would be expected on the basis of their size, charge, distribution coefficient, or magnitude of the concentration gradient. Biology Q&A Library Draw the diagram of facilitated diffusion? Draw the diagram of facilitated diffusion? close. Start your trial now! First week only $4.99! arrow_forward. Question. Draw the diagram of facilitated diffusion? check_circle Expert Answer. Want to see the step-by-step answer? Understanding the long association pathways that convey cortical connections is a critical step in exploring the anatomic substrates of cognition in health and disease. Diffusion tensor imaging (DTI) is able to demonstrate fibre tracts non-invasively, but present approaches have been hampered by the inability to visualize... A DIAL-AN-OPERATOR APPROACH TO SIMULATION OF IMPURITY DIFFUSION IN SEMICONDUCTORS a dissertation submitted to the department of electrical engineering and the... Peter Griffin’s accessibility and expertise in the area of physical models greatly facilitated development of model scripts. Dr. Martin Giles of Intel extensively...
Sabioni [–] focused on the Cr diffusion kinetics in the oxide film on stainless steel and revealed the differences of Cr diffusion between the oxide film and austenite matrix. As a novel heat-resistant material with fine grains, the diffusion kinetics of Cr in Super304H steel has not been touched yet. Compared with the... Diffusion, Osmosis, Active Transport There are two ways in which substances can enter or leave a cell: 1) Passive a) Simple Diffusion b) Facilitated Diffusion c) Osmosis (water only) 2) Active a) Molecules b) Particles Diffusion Diffusion is the net passive movement of particles (atoms, ions or Jun 26, 2018 ... Facilitated diffusion is movement of molecules from an area of their higher concentration to area of their lower concentration through a ... This doodle diagram set is part of a money-saving growing bundle you can find by clicking here. There are two doodle diagram pages: 1. All about facilitated diffusion: This page has diagrams and talks about factors that affect the rate of facilitated diffusion, gated channels, and other related concepts. 2.
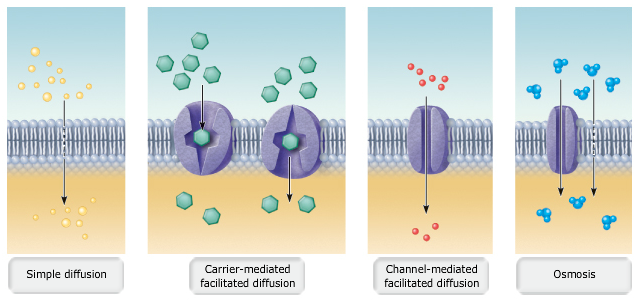
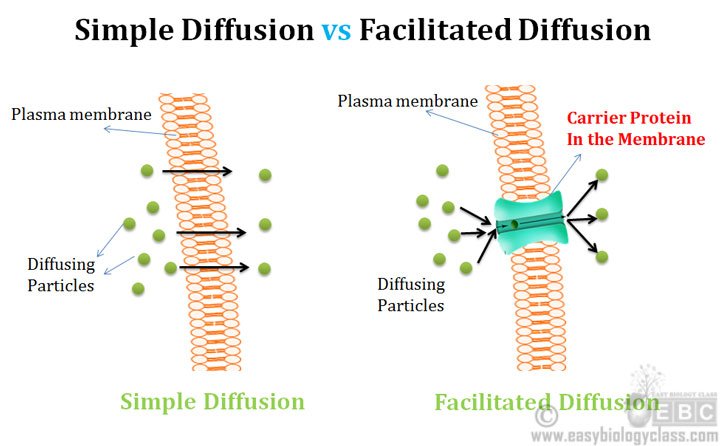
Simple Diffusion: It is a type of passive transport of molecules that, as the name suggests, is merely unassisted by transmembrane. Facilitated Diffusion: On the other hand, it is the spontaneous transport of molecules or ions across a cell's membrane. Facilitated diffusion requires specific transmembrane proteins to process in a cell. Facilitated Diffusion Diagram (Photo Source: Wikimedia) In living organisms, the diffusion of substances is mediated by the cell membrane.By definition, facilitated diffusion is a type of passive transport which utilizes "agents" known as channel proteins and carrier proteins to speed up the transport process.While there are some proteins found in the cell membrane, only the said types of ... Dec 1, 2020 ... Figure 1 – Diagram of simple diffusion across the plasma membrane ... The channel proteins that allow facilitated diffusion can be exploited ... Facilitated diffusion (also known as facilitated transport or passive-mediated transport) is the process of spontaneous passive transport (as opposed to active transport) of molecules or ions across a biological membrane via specific transmembrane integral proteins. Being passive, facilitated transport does not directly require chemical energy from ATP hydrolysis in the transport step itself ...
Mar 5, 2021 — Facilitated diffusion is the diffusion of solutes through transport proteins in the plasma membrane. Facilitated diffusion is a type of ...
Start studying 3 Diffusion and Facilitated Diffusion. Learn vocabulary, terms, and more with flashcards, games, and other study tools.
Besides, the nondoped CBP with 10 nm-thickness is employed to prevent the diffusion of p-dopant MoO 3 from HTL into EML. A key feature of such a PHOLED is two ultrathin emissive layers of CBP: 4 wt% Ir(ppy) 3 (5 nm) and CBP : 8 wt% Ir(ppy) 3 (5 nm) alternating with each other to form a periodic stack as EML. There N is equal to...
Passive Transport by Facilitated Diffusion. Diffusion and osmosis. Glomerular filtration in the nephron. Sodium-potassium pump. Secondary active transport in the nephron. Exocytosis. Phagocytosis. Membrane potentials - part 2. Membrane potentials - part 1. Permeability and membrane potentials.
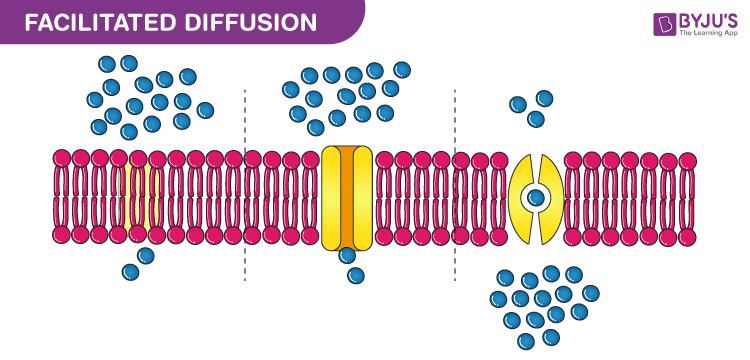
Facilitated Diffusion · It is utilised by molecules that are unable to freely cross the phospholipid bilayer (e.g. large, polar molecules and ions) · This process ...
We are pleased to provide you with the picture named Facilitated Diffusion Diagram.We hope this picture Facilitated Diffusion Diagram can help you study and research. for more anatomy content please follow us and visit our website: www.anatomynote.com. Anatomynote.com found Facilitated Diffusion Diagram from plenty of anatomical pictures on the internet.
Diagram of Facilitated Diffusion. How can you tell if a solution is hypotonic? A hypotonic solution has a lower concentration of solutes than another solution. In biology, a solution outside of a cell is called hypotonic if it has a lower concentration of solutes relative to the cytosol. Due to osmotic pressure, water diffuses into the cell ...
Facilitated diffusion. Facilitated diffusion. Diffusion and passive transport. Electrochemical gradients and secondary active transport. Uniporters, symporters and antiporters. Active transport. This is the currently selected item. Sodium potassium pump. Active transport review.
Facilitated diffusion is the diffusion process used for those substances that cannot cross the lipid bilayer due to their size and/or polarity (Figure 3.18). A common example of facilitated diffusion is the movement of glucose into the cell, where it is used to make ATP.
The transport is facilitated diffusion relies on the molecular binding between the membrane-embedded channel or carrier protein and the cargo. The rate of facilitated diffusion can be saturated with respect to the concentration difference between the two phases unlike in simple diffusion which is only linear in the concentration difference.
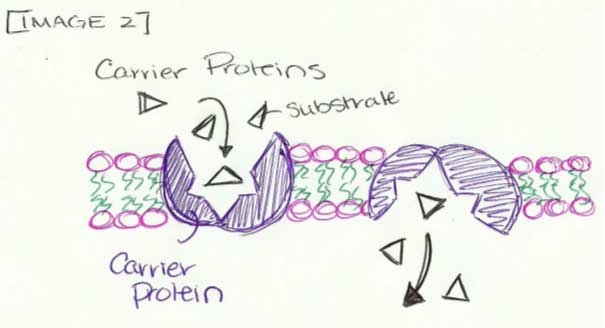
Earlier we mentioned certain proteins that facilitate other substances through the cell membrane, they are called transmembrane proteins. These proteins are spread across the wall of the cell and act as a bouncer to stop or allow specific types of substances. There are two types of transmembrane proteins, which are basically what is used in facilitated diffusion: 1. Carrier Proteins:Carrier proteins as the name suggests carries vital substance into the cell. They are found on the cell membrane wall and work as a unidirectional protein. The glucose facilitated diffusion and red blood cells in our body are examples of facilitated diffusion incorporating this. 2. Channel Protein:These amino acid components are present in the membranes that act as a hydrophilic passageway for a particle of a specific size and shape. These transmembrane proteins if open all the time and allow entry of water-based molecules are called non-gated channel proteins and if they require a stimulus to open up th...
diffusion does not level out / continues to rise; glucose uptake increases in both; glucose uptake is higher in facilitated diffusion (than in simple diffusion); glucose uptake in simple diffusion is constant / linear whereas in facilitated diffusion uptake increases rapidly at the beginning / increase is not constant; 3 max
May 23, 2021 ... Facilitated diffusion is the process of biological transport in which specific structural components of biological membranes interact with ...
Diffusion Tensor Imaging … enables the measurement of the restricted diffusion of water in tissue in order to produce neural tract images. […] In DTI, each voxel has one or more pairs of parameters: a rate of diffusion and a preferred direction of diffusion—described in terms of three dimensional space—for which that... Language Log Home About Comments policy Follow us on Twitter Archives [+/–] [Posts before 4/8/2008 are...
The interior of the cell is organized into many specialized compartments, or, each surrounded by a separate... Each cell contains only one nucleus, whereas other types of organelles are present in multiple copies in... and theand the , which play important roles in the internal organization of the cell by synthesizing selected...
In facilitated diffusion, molecules diffuse across the plasma membrane with assistance from membrane proteins, such as channels and carriers. A concentration ...
in the structural transformation of into a robust three-dimensional structure ( ). The structure offeatures only one type of nanocage comprising eight channels as potential diffusion pathways for guest molecules, with four of these channels oriented toward (111) or planes and the other four aligned parallel to the axis ( ...
Regular article Open Access Published: 19 October 2018 Prestige drives epistemic inequality in the diffusion of scientific ideas Allison C. Morgan , Dimitrios J. Economou , Samuel F. Way & Aaron Clauset EPJ Data Science 7, Article number: 40 (2018) Cite this article 7469 Accesses 10 Citations 727 Altmetric Metrics Abstract The... the diffusion of ideas Conclusion Abbreviations References Funding Author information Ethics declarations...
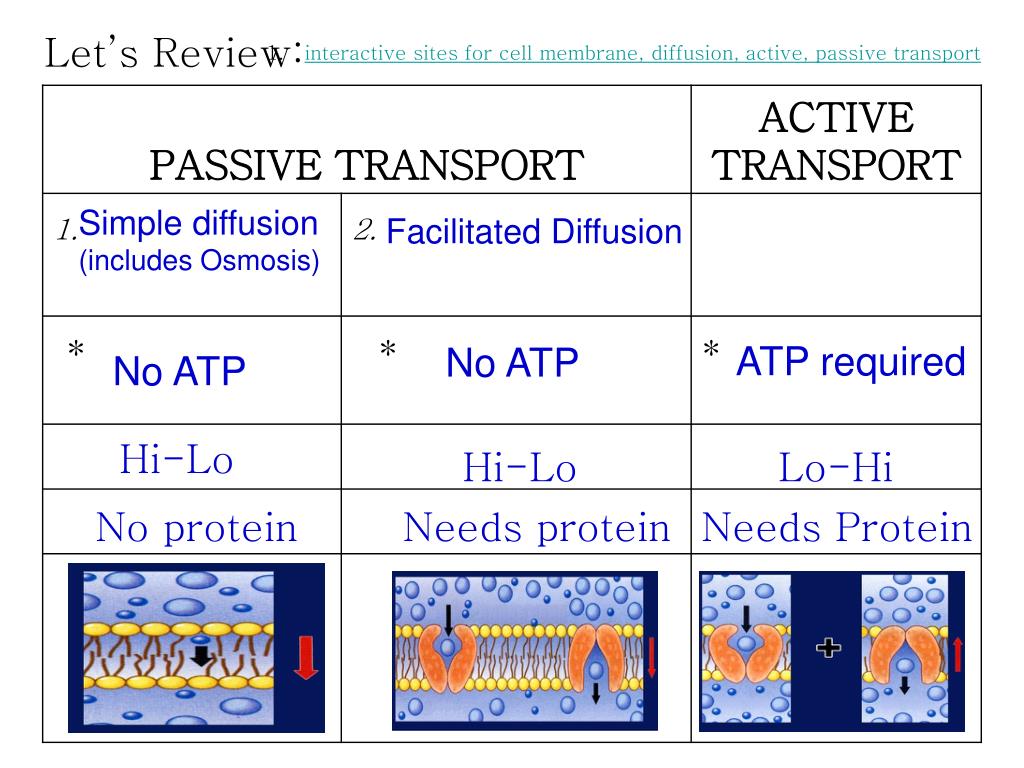
Facilitated diffusion is a spontaneous process in which charged ions or molecules are transported across the lipid-based cell membrane via a carrier transmembrane protein molecule. It is a selective process, which means the membrane allows only selective molecules and ions to pass through it, denying passage to others.
Over the past two years, the heat treatment of corundum involving lattice diffusion of beryllium (Be) at temperatures over 1800°C has become a major issue in the gem trade. Although initially only orange to orangy pink (“padparadscha”-like) sapphires were seen, it is now known that a full range of corundum colors...
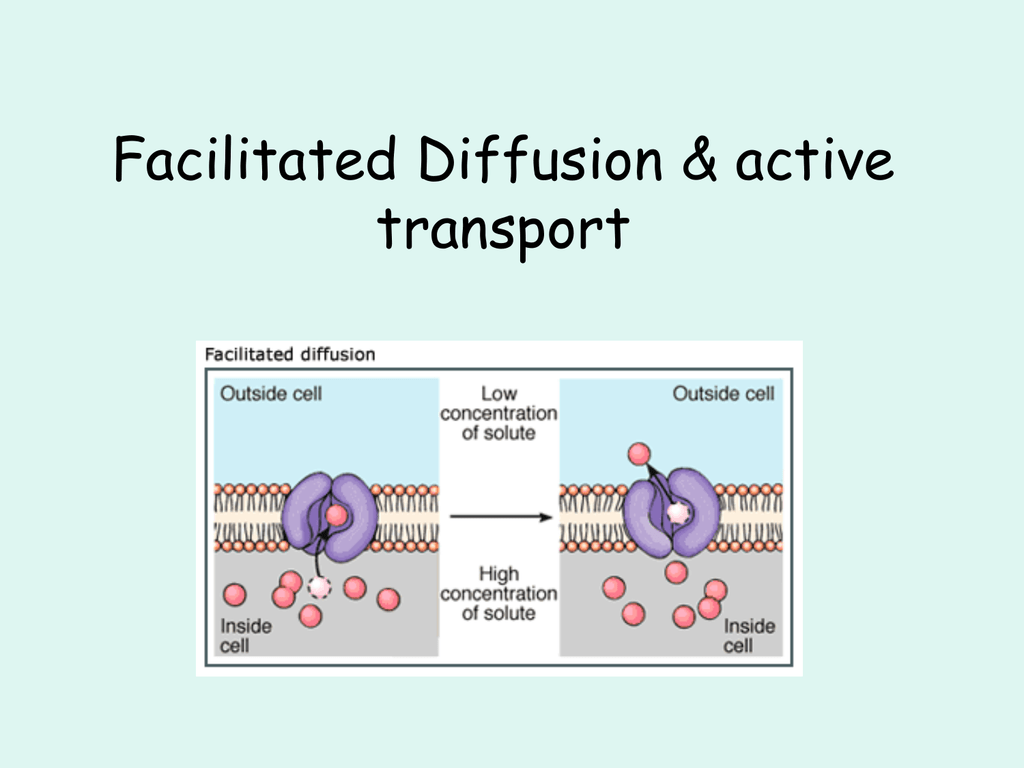
One of the main comparisons is that active transport occurs against the concentration gradient whilst, facilitated diffusion occurs down the concentration gradient. - Active transport is an active process. Thus, it requires energy. Whereas facilitated diffusion is a passive process and does not require energy. - Active transport uses carrier proteins. Energy is used to change the shape of the ...
(b) The table below gives statements relating to the processes of diffusion, facilitated diffusion and active transport. For each process, place a tick ( ) in the box if the statement applies to that process. Place a cross ( ) in the box if the statement does not apply to the process. (3) Statement Process Diffusion Facilitated diffusion Active
Facilitated Diffusion: Facilitated diffusion is the process of spontaneous transport of molecules or ions across a cell's membrane via specific trans-membrane proteins. The present post discusses the Difference between the Simple and Facilitated Diffusion Process.
Drag the labels to their appropriate locations on the diagram. a. plasma membrane b. side with higher concentration of molecules c. side with lower concentration of molecules d. facilitated diffusion causes a net movement of molecules down their concentration gradient e. transport protein.
The diffusion of water across a selectively permeable membrane. Simple diffusion. Diffusion that doesn't involve a direct input of energy or assistance by carrier proteins. Facilitated Diffusion. Movement of specific molecules across cell membranes through protein channels ... Diagrams. Flashcards. Mobile. Help. Sign up. Help Center. Honor Code ...
2. The carrier protein changes shape, shielding the molecule from the interior of the membrane. 3. The molecule is released on the other side of the membrane. 4. The carrier protein then returns to it's original shape. Facilitated Diffusion is the process used for molecules that cannot separate cell membranes on command, even when there is a ...
The word 'diffusion' means free movement across distance, with or without the presence of a barrier. However, there is a phenomenon known as facilitated diffusion which occurs at the cellular level. The cell does not allow free radicals and other harmful substances to enter and harm the cell organs.
Solution for Both simple dufusion and facilitated diffusion of small polar uncharged molecule Select one: O A. all of the choices O B. require the hydrolysis of…
What facilitates the splitting of the water molecules? The splitting of water molecules, results in the donation of lost its electron to the primary (electron) acceptor. to the chlorophyll, which has Protons (H+) are pumped from of the thylakoid. to The energy for the pumping of the protons comes from What is the role of ATP...
Facilitated diffusion therefore allows polar and charged molecules, such as carbohydrates, amino acids, nucleosides, and ions, to cross the plasma membrane. Two ...
Aug 14, 2021 — A schematic diagram of facilitated diffusion. Membrane proteins such as carriers and channels facilitate the movement of molecules across ...Facilitated diffusion vs. active... · Facilitated diffusion vs simple... · Examples
Facilitated Diffusion Definition. Facilitated diffusion is a form of facilitated transport involving the passive movement of molecules along their concentration gradient, guided by the presence of another molecule - usually an integral membrane protein forming a pore or channel.. Facilitated diffusion does not directly involve high-energy molecules like adenosine triphosphate (ATP) or ...
On the diagram below, add these labels: facilitated diffusion with a carrier protein, facilitated diffusion with a channel protein, simple-diffusion. For each type of transport, give an example of a material that is moved in this manner. — achvc carrier (qtutc3e 24. What is membrane potential? Which side of the membrane is positive? Membronc
Main Difference - Simple Diffusion vs Facilitated Diffusion. Simple diffusion and facilitated diffusion are two types of passive transport methods in which the cell membrane transports molecules across it. It uses natural entropy to move molecules from higher concentration to a lower concentration until the concentration becomes equalized. Hence, no ATP energy is used for the transportation ...
The diagram illustrates the use of energy by a nerve cell to expel a sodium ion from inside the cell. Which best explains why energy is necessary to complete this function? ... Active transport and facilitated diffusion in cells both result in the movement of nutrients or wastes across a membrane.
Using the example of a Cu–Au solid solution, we demonstrate that compositional variations induced by surface segregation are accompanied by misfit strain and the formation of dislocations in the subsurface region via a surface diffusion and trapping process. The resulting chemically ordered surface regions acts as an...
the solvent displacement is a novel modification to the emulsion-diffusion methodology, where the diffusion is done directly on the emulsion, which allows concentrated dispersions that facilitate direct use to be obtained, eliminating the dilution with water and the recovery of water by additional processes. The solvent was...
THE Q UARTERLY J OURNAL OF THE GEMOLOGICAL INSTITUTE OF AMERICA VOLUME XXXIX SUMMER 2003 Featuring: Beryllium Diffusion of Rubies and Sapphires Seven Rare Gem Diamonds pg. 137 VOLUME 39, NO. 2Summer 2003 83 84 136 144 152 167 169 171 REGULAR FEATURES _____________________ Lab Notes • Vanadium-bearing chrysoberyl • Brown...
Learn the facilitated diffusion definition, why it is necessary, types of facilitated diffusion, and facilitated diffusion examples. Updated: 04/25/2021 Table of Contents





















0 Response to "39 diagram of facilitated diffusion"
Post a Comment