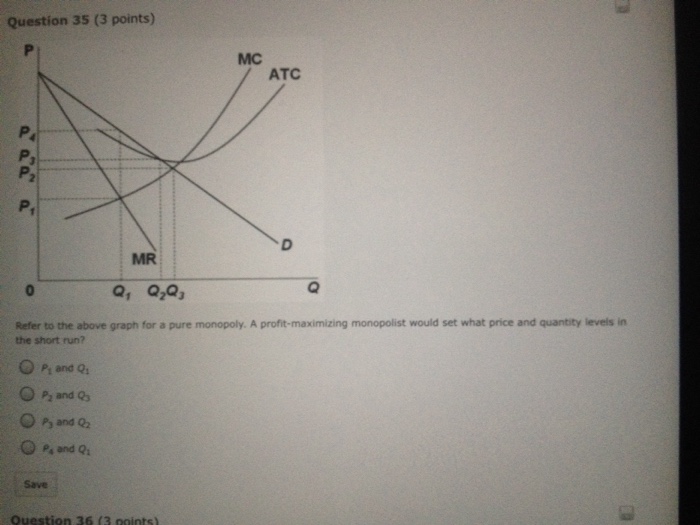
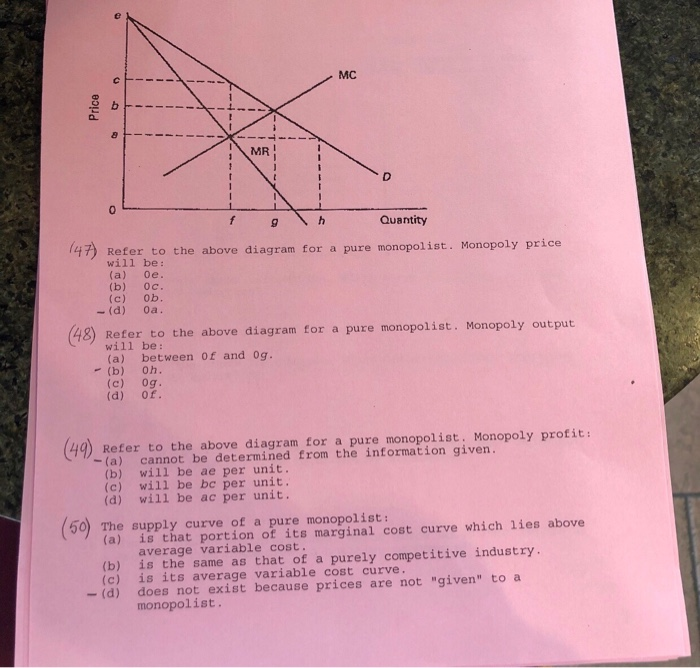
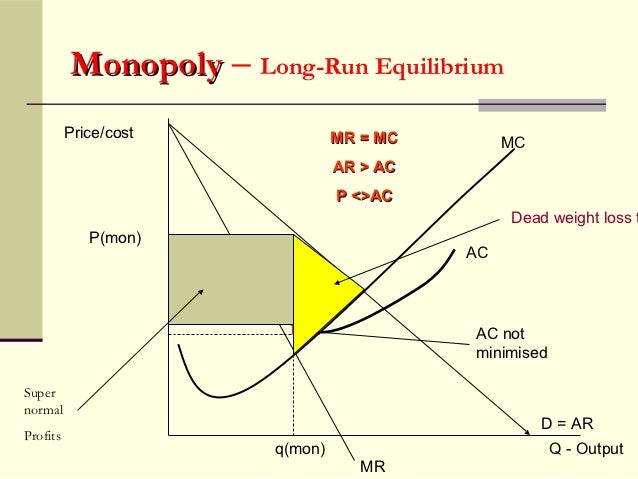
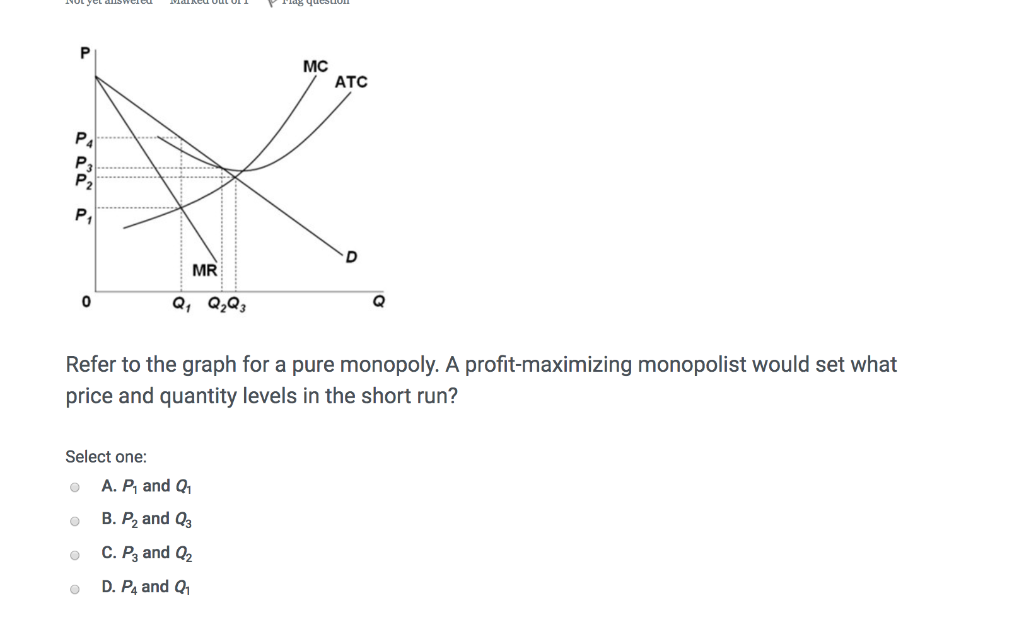
39 refer to the diagram for a pure monopolist. monopoly price will be
August 10, 2015 - ADVERTISEMENTS: A comparative analysis of monopoly and monopolistic competition has been made on the following aspects: 1. Nature of Product: Under monopoly, product produced may or may not be homogeneous. But under monopolistic competition, there is always product differentiation. Start studying Chapter 12- Monopolies. Learn vocabulary, terms, and more with flashcards, games, and other study tools.
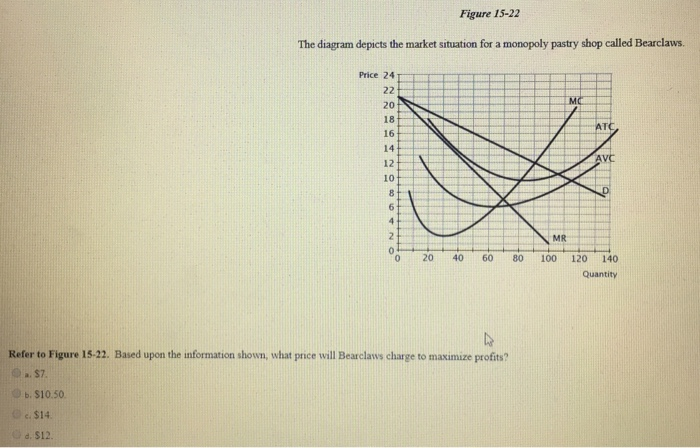
The table shows the demand schedule facing Nina, a monopolist selling baskets. What is the change in total revenue if she lowers the price from $20 to $18? Price Number of Baskets Sold $ 20 18 16 14 10 12 15 10 30 - $30 3 5 7. 15. Refer to the diagrams, which pertain to monopolistically competitive ...

Refer to the diagram for a pure monopolist. monopoly price will be
64. Refer to the above diagram for a nondiscriminating monopolist. At output Q average variable cost is QJ. True False 65. Refer to the above diagrams. Both firms are selling their products in purely competitive markets. True False 66. Refer to the above diagrams. [pc build](https://pcpartpicker.com/guide/LTgXsY/excellent-intel-gamingstreaming-build) Get the detailed answer: Refer to the diagram for a pure monopolist. Monopoly output will be: A. f B. g C. h D. between f and g
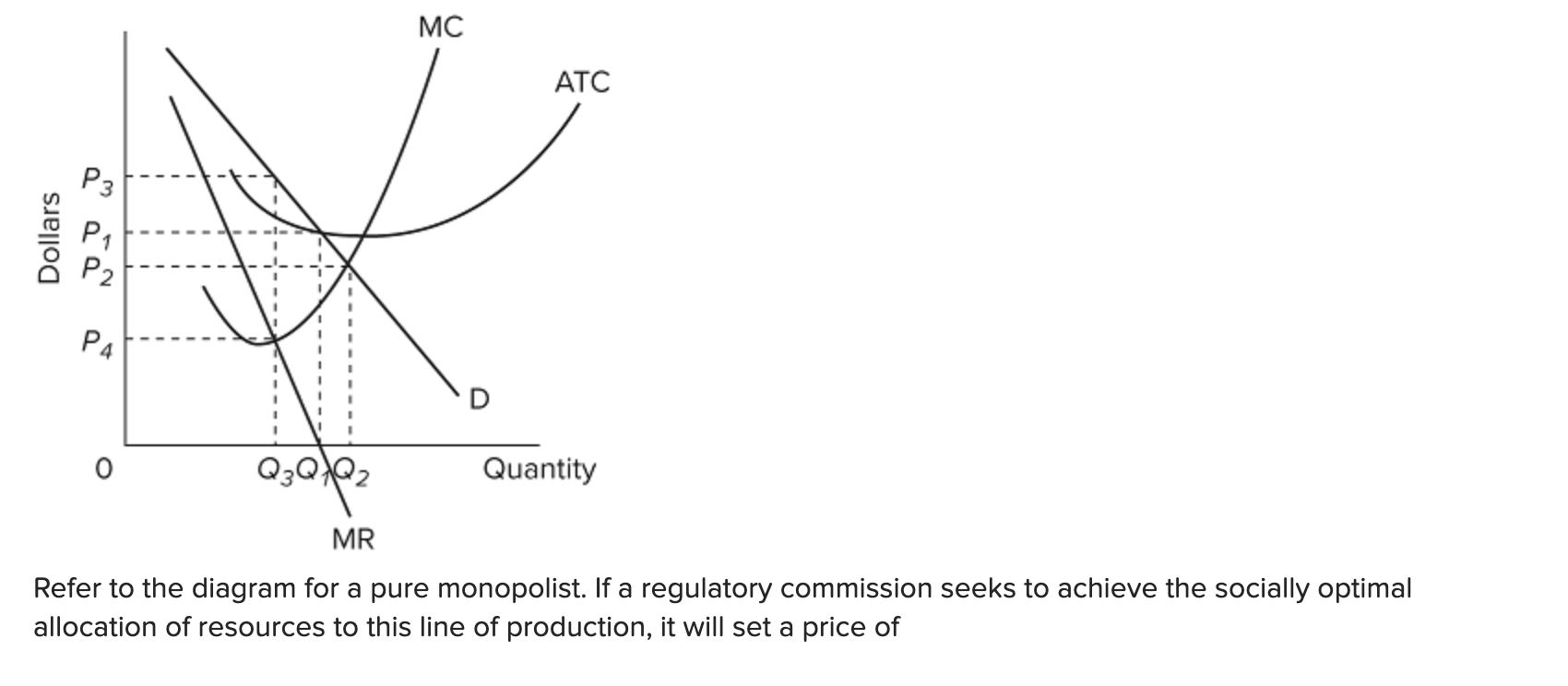
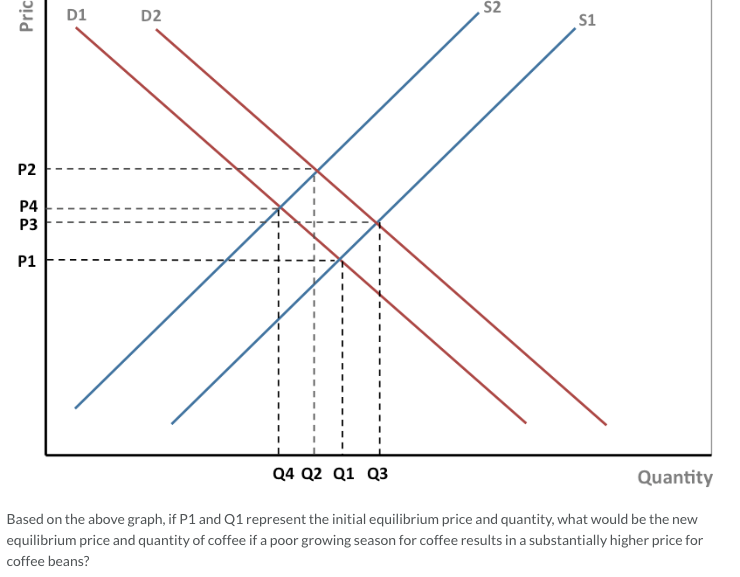
Refer to the diagram for a pure monopolist. monopoly price will be. I need this info to study for a test. Start studying ECON CH 12. Learn vocabulary, terms, and more with flashcards, games, and other study tools. Refer to the above diagram for a pure monopolist. If the monopolist is unregulated, it will maximize profits by charging: A. a price above P3 and selling a quantity less than Q3.. B. price P3 and producing output Q3.. C. price P2 and producing output Q2.. D. price P1 and producing output Q1.. February 10, 2021 - A monopoly is a market with a single seller (called the monopolist) but with many buyers. In a perfectly competitive market, which comprises
Brief video covering the basics of graphing a monopoly. I have a major microeconomics exam coming up later this week and even after watching like 30 minutes of youtube videos on the topic, I'm still not 100% clear. Thanks in advance! Monopoly vs Monopolistic Competition: Find out the top 6 Difference Between Monopoly and Monopolistic Competition. Price D f g h Quantity MR Refer to the diagram for a pure monopolist. Monopoly price will be A) a. B). Ce. D) b. Price o f g h Quantity MR Refer to the diagram for a pure monopolist. Monopoly output will be A . B) g. Ch. D) between fand g. 28) When a pure monopolist is producing its ...
Donate your notes with us. Refer to the diagram for a pure monopolist. If the monopolist is unregulated, it will maximize profits by charging: askedAug 17, 2018in Economicsby Zoeye. A. a price above P 3 and selling a quantity less than Q 3 . B. price P 3 and producing output Q 3 . Start studying Micro Chapter 24. Learn vocabulary, terms, and more with flashcards, games, and other study tools. Refer to the above diagram for a pure monopolist. Monopoly profit: A. cannot be determined from the information given. B. will be ae per unit sold. C. will be bc per unit sold. D. will be ac per unit sold. 73. In the short run a pure monopolist's profit: A. will be maximized where price equals ... Refer to the diagram for a pure monopolist. Monopoly price will be A) c. B) a. C) e. D) b. A. Refer to the diagram for a pure monopolist. Monopoly output will be A) f. C) g. B) between f and g. D) h. A. A pure monopolist is generally viewed as A) both productively and allocatively inefficient.
December 10, 2020 - There are four basic types of market ... monopolistic competition, oligopoly and monopoly. A monopoly is a structure in which a single supplier produces and sells a given product or service. If there is a single seller in a certain market and there are no close substitutes for the product, then the market structure is that of a "pure ...
Refer to the diagram for a pure monopolist. Monopoly price will be. c. Refer to the diagram for a pure monopolist. Monopoly output will be. f. Refer to the diagram for a pure monopolist. Monopoly profit. cannot be determined from the information given. In the short run, a monopolist's economic ...
Learn about how to represent a monopoly market graphically in this video. Topics covered include the profit-maximizing quantity, pricing decisions, and deadweight loss associated with monopolies.
View Homework Help - ECONHW13Sols31.pdf from ECON 4103 at University of New South Wales. 89. Award: 1.00 point Refer to the diagram for a pure monopolist. Monopoly price will be e. c. b.
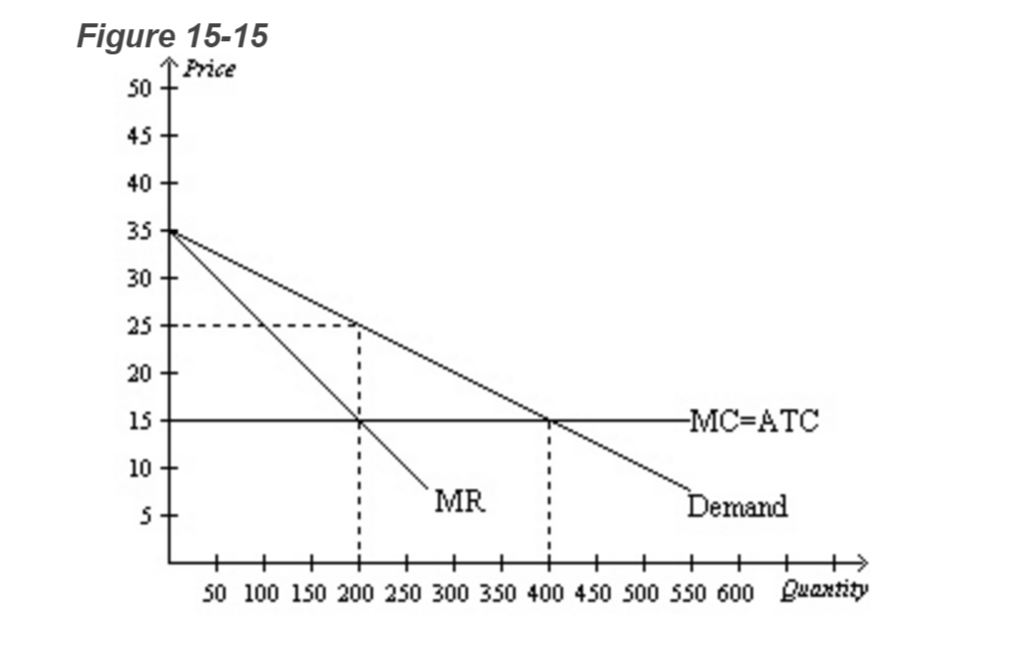
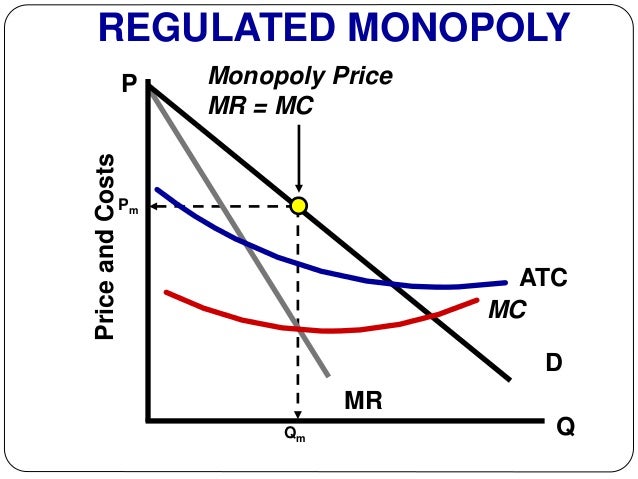
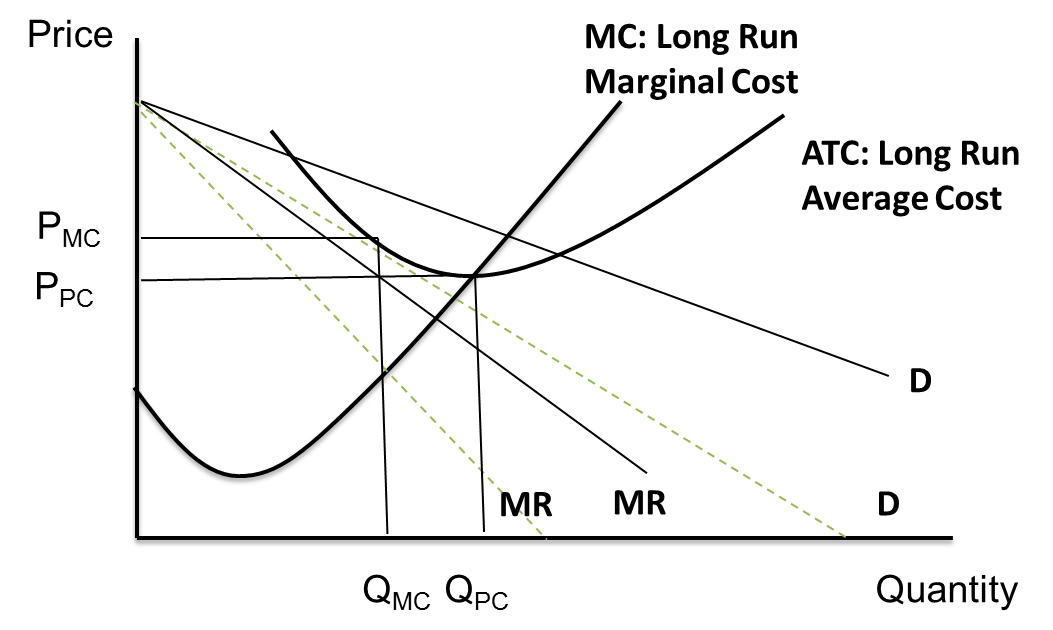
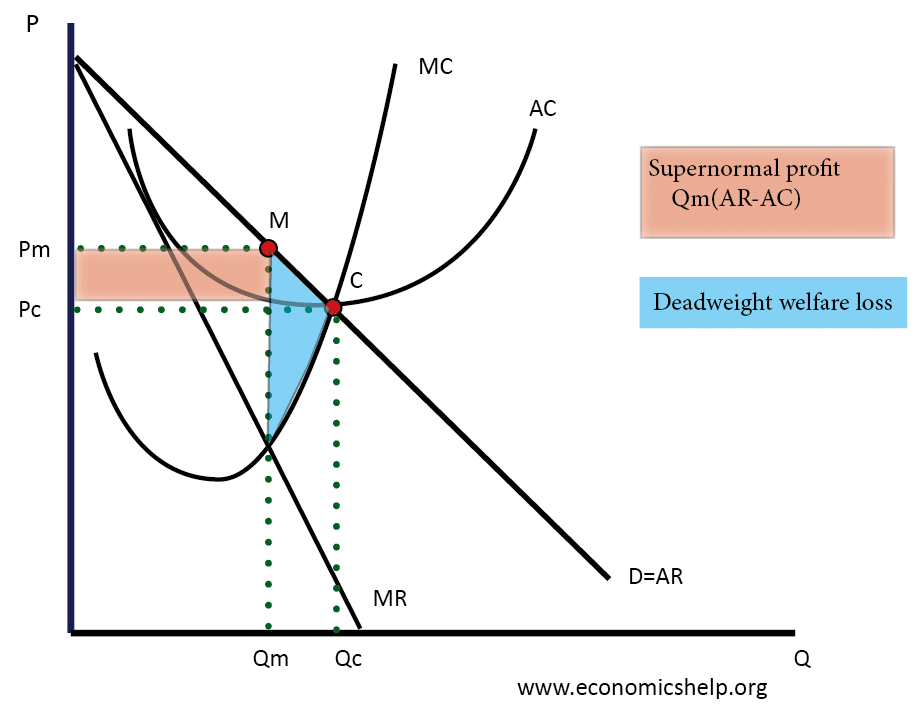
Therefore, monopolists produce less but charge more than a firm in a competitive market. Monopoly Production: Monopolies produce at the point where marginal revenue equals marginal costs, but charge the price expressed on the market demand curve for that quantity of production.
What am I?
Get the detailed answer: Refer to the diagram for a pure monopolist. Monopoly output will be: A. f B. g C. h D. between f and g
[pc build](https://pcpartpicker.com/guide/LTgXsY/excellent-intel-gamingstreaming-build)
64. Refer to the above diagram for a nondiscriminating monopolist. At output Q average variable cost is QJ. True False 65. Refer to the above diagrams. Both firms are selling their products in purely competitive markets. True False 66. Refer to the above diagrams.















0 Response to "39 refer to the diagram for a pure monopolist. monopoly price will be"
Post a Comment