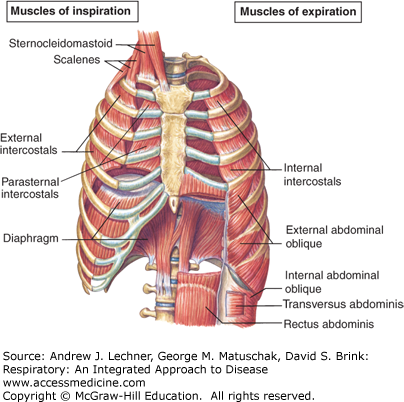
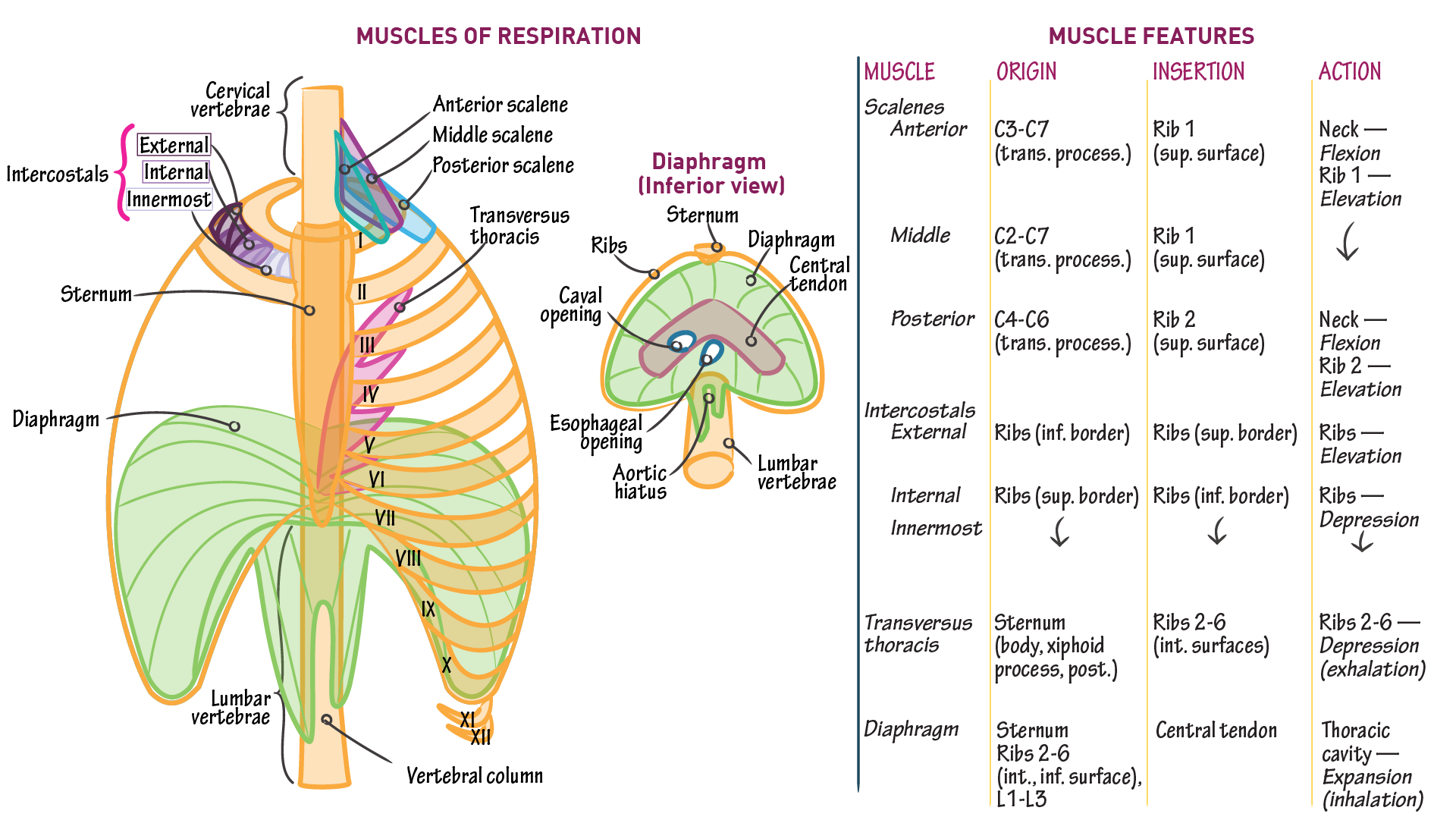
muscles of respiration diagram
Yoga Muscles. Shiatsu. Lower Back Muscles. Muscle Anatomy. 10 of the Best Workouts for Weight Loss. If your aim is to lose weight, these 10 workouts are all excellent places to start. Find out how to exercise (and eat, and other things) to reach your goals. hebaguma8022. H. Jul 29, 2020 · The diaphragm is a dome-shaped sheet of muscle located below the lungs. It separates the chest from the abdomen. The diaphragm operates as the major muscle of respiration and aids breathing .
Bird respiratory system organs diagram. I have already shown you the important labelled diagram from the bird respiratory system. Here, I tried to show you the detailed anatomical facts of most organs from a bird (chicken). If you want to get a more detailed diagram and high-quality image, make sure you join with anatomy learner on social media.

Muscles of respiration diagram
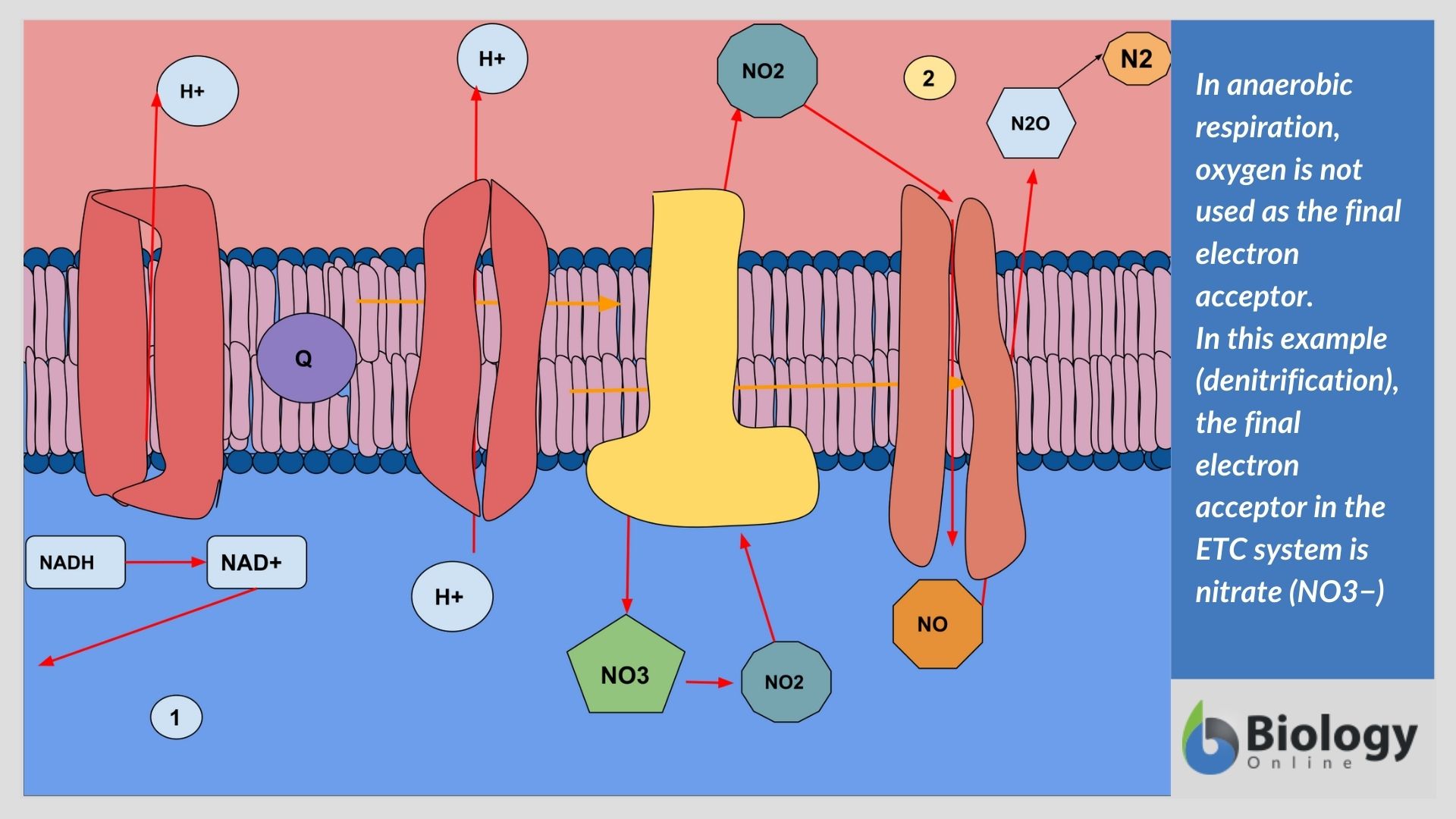
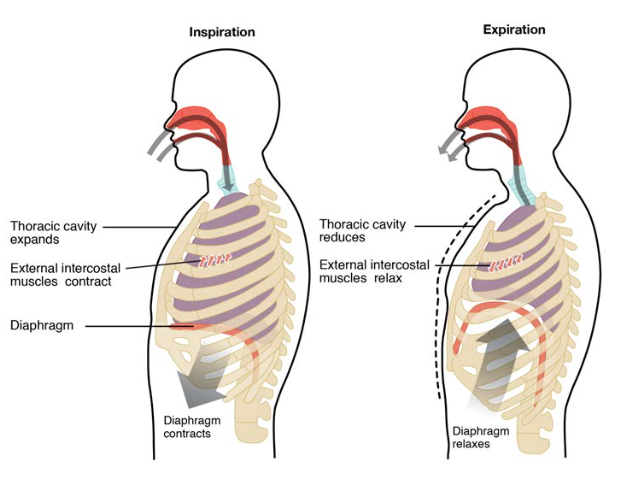
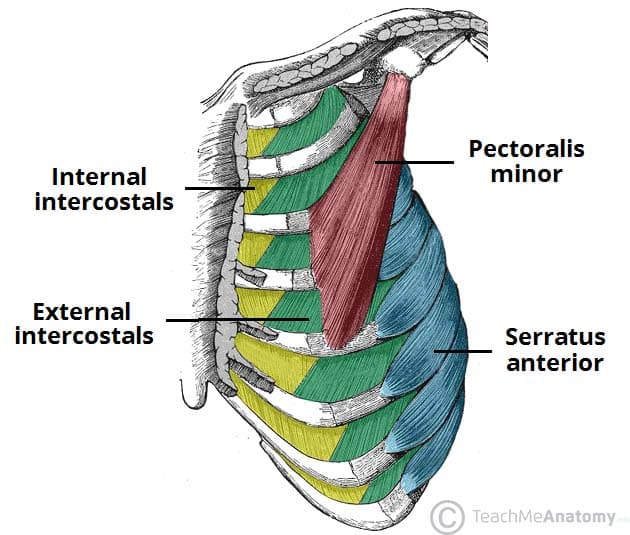
Inspiration is the phase of ventilation in which air enters the lungs. It is initiated by contraction of the inspiratory muscles: Diaphragm - flattens, extending the superior/inferior dimension of the thoracic cavity. External intercostal muscles - elevates the ribs and sternum, extending the anterior/posterior dimension of the thoracic cavity. apart from the above neck muscles, the following muscles have also been observed contributing to respiration: serratus anterior, pectoralis major and pectoralis minor, trapezius, latissimus dorsi, erector spinae, iliocostalis, quadratus lumborum, serratus posterior superior, serratus posterior inferior, levatores costarum, transversus thoracis, … Anaerobic Respiration (With Diagram) Anaerobic respiration is an alternate mode of energy generation in which an exogenous electron acceptor other than O 2 is used in electron transport chain leading to a proton motive force. In contrast to aerobic respiration where O 2 is used as electron acceptor, the electron acceptors used in anaerobic ...
Muscles of respiration diagram. The respiratory tract in humans is made up of the following parts: External nostrils - For the intake of air.; Nasal chamber - which is lined with hair and mucus to filter the air from dust and dirt.; Pharynx - It is a passage behind the nasal chamber and serves as the common passageway for both air and food.; Larynx - Known as the soundbox as it houses the vocal chords, which are ... Innermost intercostal muscles: Origin: from the costal groove of the rib above and. Insertion: the superior border of rib below. Nerve supply: all the intercostal muscles are supplied by their respective intercostal nerves. Blood supply: all three muscles receive blood supply from anterior and ... Trace the respiratory process from inspiration (how it works) and air moving from the mouth/nose down to the alveoli, and expiration. The four stages of respiration are ventilation, distribution, perfusion, and diffusion. Ventilation is the process when air enters thru the conductive respiratory pathways. Respiratory System Diagram Muscles of the Respiratory System. The diaphragm is a dome-shaped muscle that curves upwards towards the lungs. When it contracts, it becomes flattened and therefore increases the volume of the thoracic cavity.
Start studying Muscles of Respiration: Diagram. Learn vocabulary, terms, and more with flashcards, games, and other study tools. The diaphragm is the primary muscle used in respiration, which is the process of breathing. This dome-shaped muscle is located just below the lungs and heart. It contracts continually as you ... Respiratory system (anatomy diagram) So far, you have seen how the thoracic cage is a frame that encloses the respiratory system and allows breathing to take place. Several muscles that span several regions of the body, such as the thoracic wall itself, neck, shoulder girdle and abdomen , act upon this structure. Muscle Charts of the Human Body For your reference value these charts show the major superficial and deep muscles of the human body. Superficial and deep anterior muscles of upper body
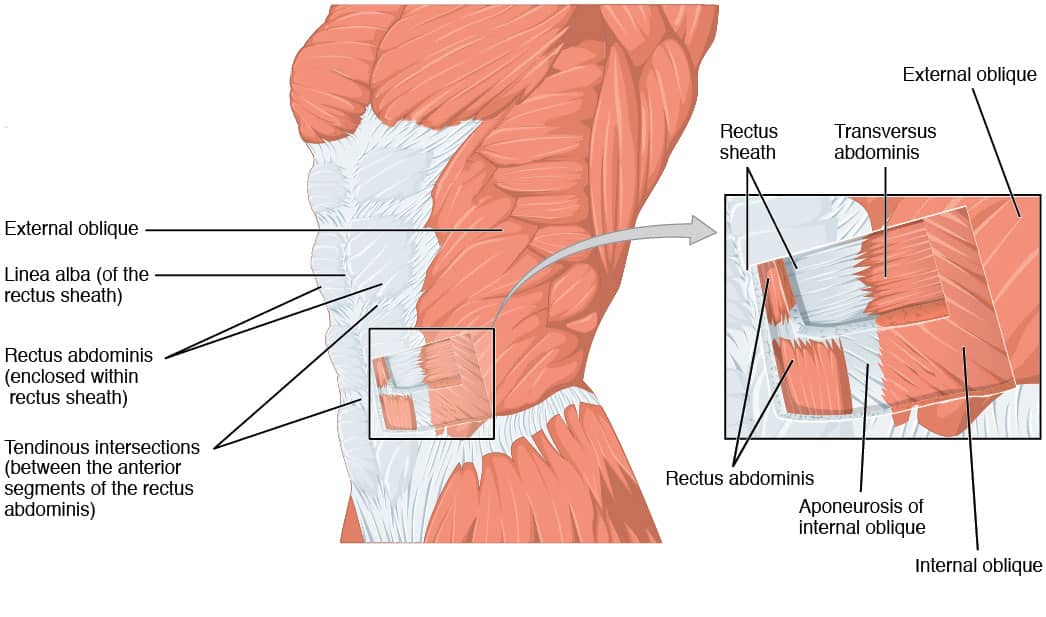
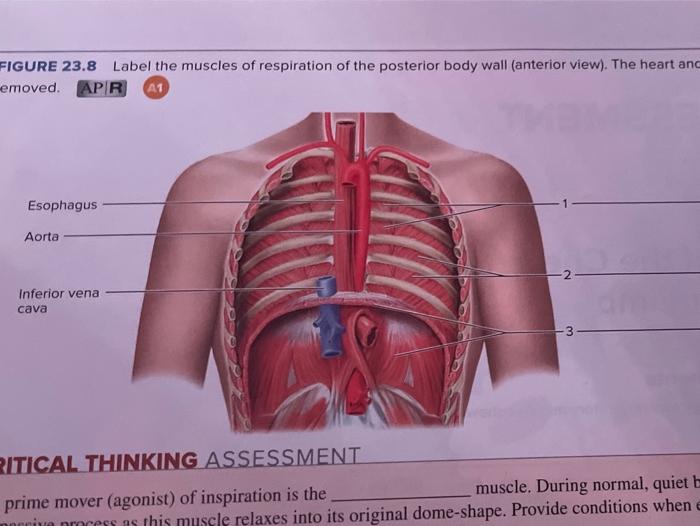
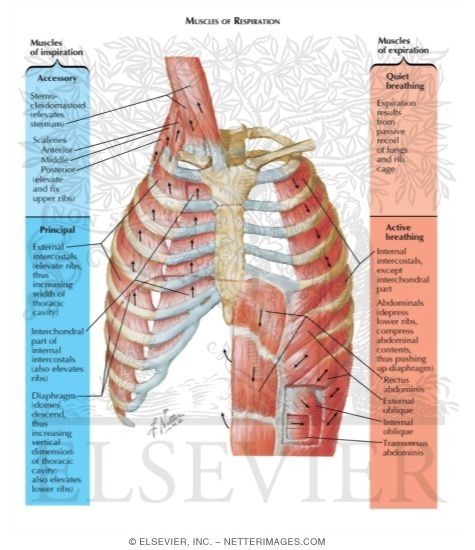
Muscles of Respiration During quiet breathing, the predominant muscle of respiration is the diaphragm. As it contracts, pleural pressure drops, which lowers the alveolar pressure, and draws air in down the pressure gradient from mouth to alveoli. Muscles get their energy from different sources depending on the situation that the muscle is working in. Muscles use aerobic respiration when we call on them to produce a low to moderate level of force. Aerobic respiration requires oxygen to produce about 36-38 ATP molecules from a molecule of glucose. The muscles of the thorax include both the diaphragm as well as the muscles of the thoracic cage. The diaphragm can be located below the lungs and consists of a sheet of skeletal muscle which displays a double-domed structure. The diaphragm is important as it separates the thoracic cavity from the abdominal cavity and therefore requires 3 openings that act as channels for structures to pass ... Respiratory Quotient (RQ): Respiratory quotient is the ratio of the volume of carbon dioxide produced to the volume or oxygen consumed over a period of time in respiration. RQ = Volume of CO 2 evolved/Volume of O 2 absorbed . Respiratory quotient varies with different foods utilized in respiration.
The respiratory pause continues for 0.5 to 1.5 s during swallowing, and respiration usually resumes with expiration. 32-34 This resumption is regarded as one of the mechanisms that prevents inhalation of food remaining in the pharynx after swallowing. 35 When performing sequential swallows while drinking from a cup, respiration can resume with ...
these muscles play a role in lifting up upper part of rib cage, have a small role in respiration scalenus muscle anterior, middle, and posterior muscles of the neck that elevate the first and second ribs accessory muscles of inspiration; support head scalenus muscles sternomastoid muscles these muscles will move when you have a shortage of breathe
Factors regulating the nervous signal going to the spiracle muscles 1.High levels of carbon dioxide and low levels of oxygen in tissues 2.This causes a reduction in the action potential frequency of the nerves going to the spiracle muscles. 3.This causes relaxation of the closure muscles and spiracles open 4.Water balance can also affect this.
Start studying Respiratory--Anatomy, Muscles of respiration. Learn vocabulary, terms, and more with flashcards, games, and other study tools.
Title: MUSCLES INVOLVED IN RESPIRATION Author: Dr. Zeenat Zaidi Last modified by: 3422 Created Date: 1/27/2010 8:25:16 AM Document presentation format - A free PowerPoint PPT presentation (displayed as a Flash slide show) on PowerShow.com - id: 780459-ZmRkM
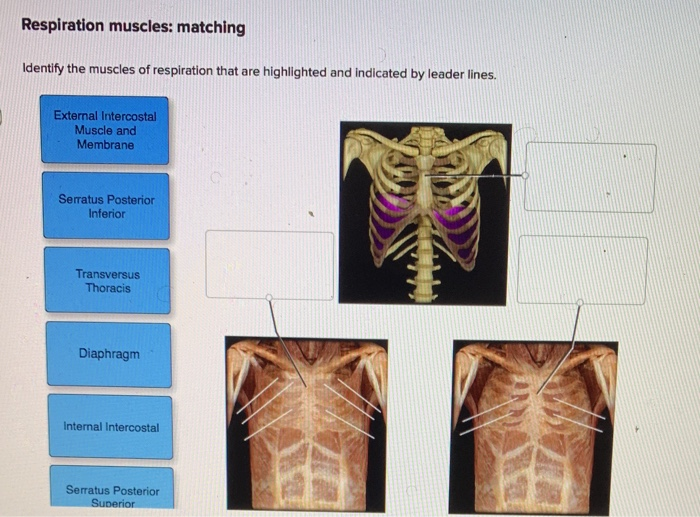
Start studying Quiz 2 - Internal & External Intercostal Muscles of Respiration. Learn vocabulary, terms, and more with flashcards, games, and other study tools.
During forced inspiration and expiration many other muscles besides the diaphragm and intercostal muscles come into play to assist respiration. Most important of this group are the scalene and sternocleidomastoids of the anterior neck muscles which stabilise the first ribs and upper sternum during forced inspiration.
The main muscle that aids in respiration is the diaphragm, which is the long muscle that separates the thoracic and abdominal cavities. The intercostal muscles are the muscles between the ribs.
Inspiration or inhalation is the process of bringing air from outside the body into the lungs. It is carried out by creating a pressure gradient between the lungs and the atmosphere. When air enters the lungs, the diaphragm contracts toward the abdominal. cavity, thereby increasing the space in the thoracic cavity for accommodating the inhaled air.
Smooth muscle: Smooth muscle makes up the walls of hollow organs, respiratory passageways, and blood vessels. Its wavelike movements propel things through the bodily system, such as food through ...
Anaerobic Respiration (With Diagram) Anaerobic respiration is an alternate mode of energy generation in which an exogenous electron acceptor other than O 2 is used in electron transport chain leading to a proton motive force. In contrast to aerobic respiration where O 2 is used as electron acceptor, the electron acceptors used in anaerobic ...
apart from the above neck muscles, the following muscles have also been observed contributing to respiration: serratus anterior, pectoralis major and pectoralis minor, trapezius, latissimus dorsi, erector spinae, iliocostalis, quadratus lumborum, serratus posterior superior, serratus posterior inferior, levatores costarum, transversus thoracis, …
Inspiration is the phase of ventilation in which air enters the lungs. It is initiated by contraction of the inspiratory muscles: Diaphragm - flattens, extending the superior/inferior dimension of the thoracic cavity. External intercostal muscles - elevates the ribs and sternum, extending the anterior/posterior dimension of the thoracic cavity.




:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/2313_The_Lung_Pleurea-6c90e267b8c9452289ab976ce32d1b83.jpg)




:background_color(FFFFFF):format(jpeg)/images/library/12404/anatomy-of-respiratory-system_english.jpg)



/respiration-58b9a1d93df78c353c0e3e0f.jpg)









:watermark(/images/watermark_only.png,0,0,0):watermark(/images/logo_url.png,-10,-10,0):format(jpeg)/images/anatomy_term/external-intercostal-muscles/KgvHVds4KmLjMc2yGFCnw_Musculi_intercostales_externi_2.png)




0 Response to " muscles of respiration diagram"
Post a Comment