39 phase diagram degrees of freedom
PDF Chapter 19. The Phase Rule - Weebly The composition of both the phase can, therefore, be expressed in terms of the same chemical individual NH 4Cl. Phase Components Solid = NH4Cl Gaseous = x NH3 + x HCl or x NH4Cl Thus dissociation of ammonium chloride is a one-component system. DEGREES OF FREEDOM The term Degree of Freedom represented by F in the phase Rule equation (F = C - P ... Degrees of Freedom - University at Buffalo Degrees of Freedom Phase Diagrams Best, Chapter 14 Gibbs Phase Rule F = 2 + C -ϕ F = degrees of freedom (P-T-X) C= components ϕ= phases Degrees of Freedom •Rule applies to a phase or assemblage •Divariant indicates two degrees of freedom •Univariant means one degree of freedom •Invariant means there are no degrees of freedom Petrogenetic Grid
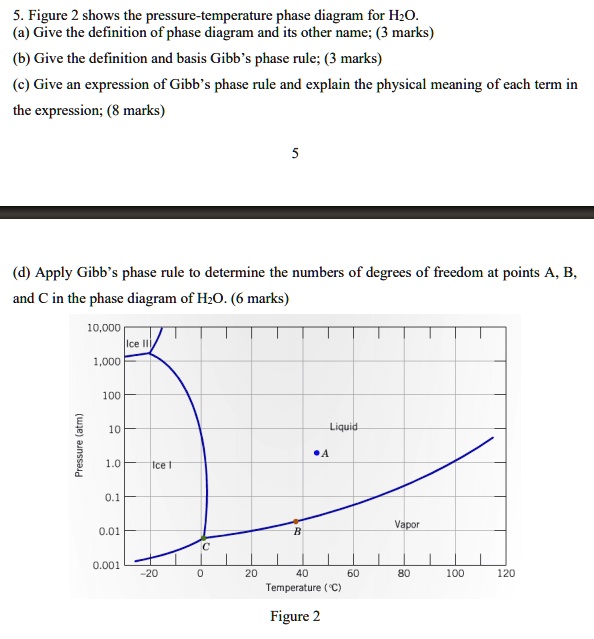
What are the degrees of freedom (from Gibbs phase rule ... The Gibbs Phase rule can be applied to a P-T thermodynamic diagrams for pure substances. On any such of diagram, each point represents a state of the material. Once the point has been located, all other thermodynamic properties can be read off. For a single phase, the required point can fall anywhere on the region of the plane representing this ...

Phase diagram degrees of freedom
Eutectic Point - Soft-Matter - Harvard University According to Gibbs Phase Rule, at this phase transition, we know that the number of degrees of freedom is F=\left( C+2-P \right)=2+2-3=1 . There is only one degree of freedom, so if we assume constant pressure (a typical choice), then all three phases can only be in equilibrium at an invariant point--- the eutectic point! This ... PDF Archived Lecture Notes #10 - Phase Equilibria and Phase ... The phase rule, also known as the Gibbs phase rule, relates the number of components and the number of degrees of freedom in a system at equilibrium by the formula F = C - P + 2 [1] where F equals the number of degrees of freedom or the number of independent variables, C equals the number of components in a system in equilibrium and P equals Phase diagrams - Florida International University One of these two remaining degrees of freedom is the pressure and the other is the composition (expressed by the mole fraction of one component. One form of the phase diagram – a map of pressures and compositions at which each phase is stable and the other – a map of temperatures and compositions. Relevant to geology
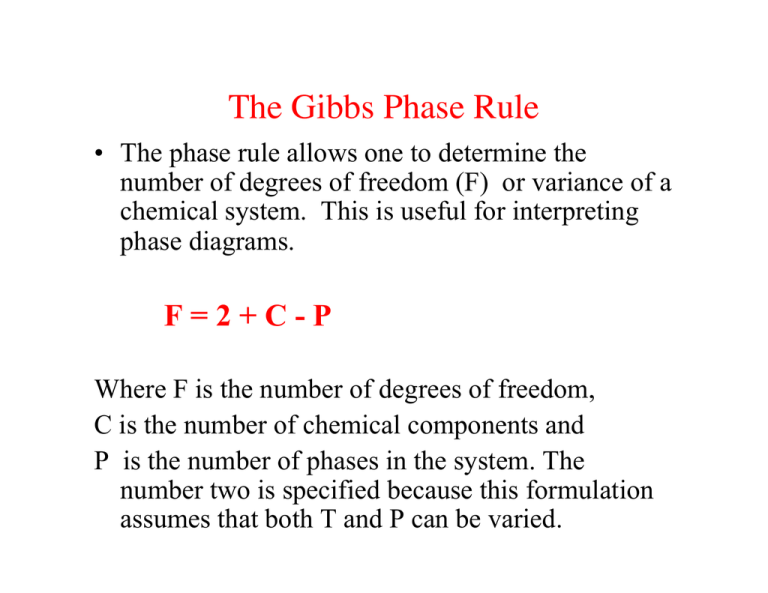
Phase diagram degrees of freedom. CHAPTER 6 LECTURE NOTES Degrees of Freedom as the phase rule: f = c – p + 2, (6.2) where f is the no. of degrees of freedom, p is the number of phases present and the “2” represents the two variables temperature and pressure. Applying this rule to a one-component phase diagram such as that of water, we see that in the interior of the solid, liquid or vapor regions, where only one Phase Diagrams | PDF | Phase (Matter) | Phase Diagram Important points about phase diagrams (Revision + extra points) * will be defined later The GIBBS PHASE RULE F = C P + 2 For a system in equilibrium F C + P = 2 or F Degrees of Freedom C Number of Components P Number of Phases The Phase rule is best understood by considering examples from actual phase diagrams as shown in some of the coming ... Chapter 8 Phase Diagrams - University of Western Ontario Phase diagram and “degrees of freedom” A phase diagramsis a type of graph used to show the equilibriumconditions between the thermodynamically-distinct phases; or to show what phases are present in the material system at various T, p, and compositions PDF Phase Diagram for Two Completely ... - Dalal Institute Before we discuss the phase diagram for two completely miscible components systems, it is better to recall the Gibbs phase rule which states that = − +2 (110) Where F is the number of degrees of freedom, C represents the number of components and P simply gives the total number of phases.
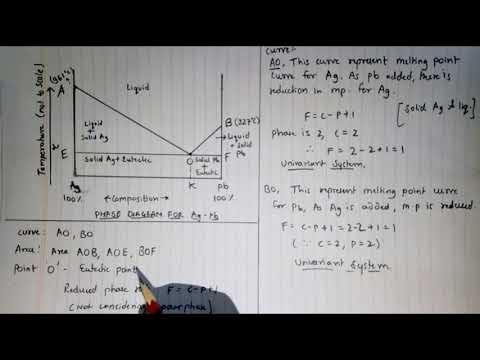
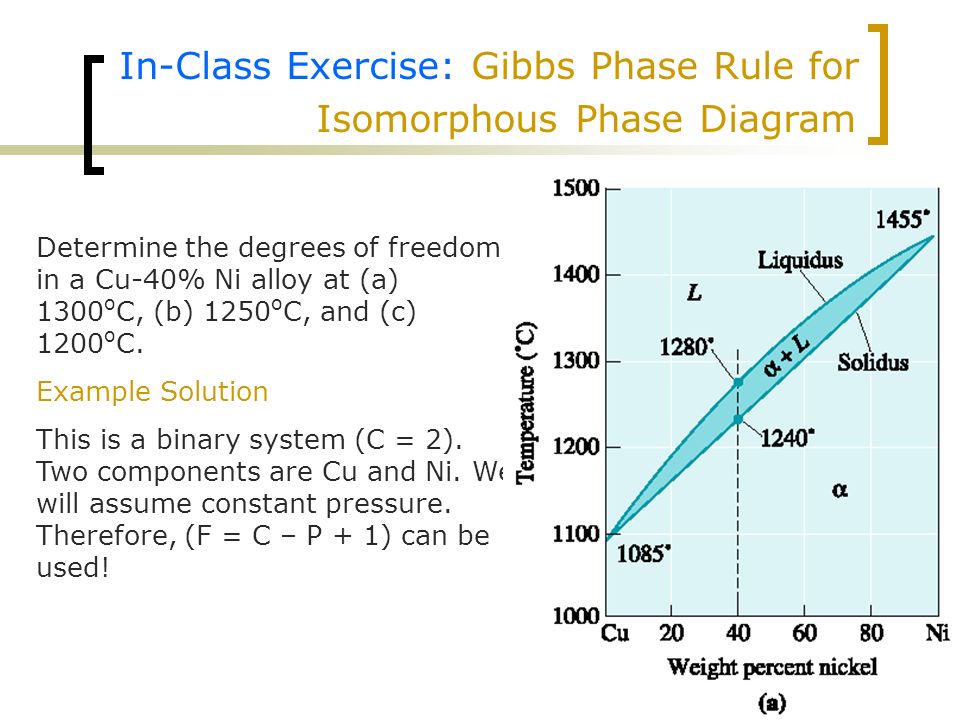
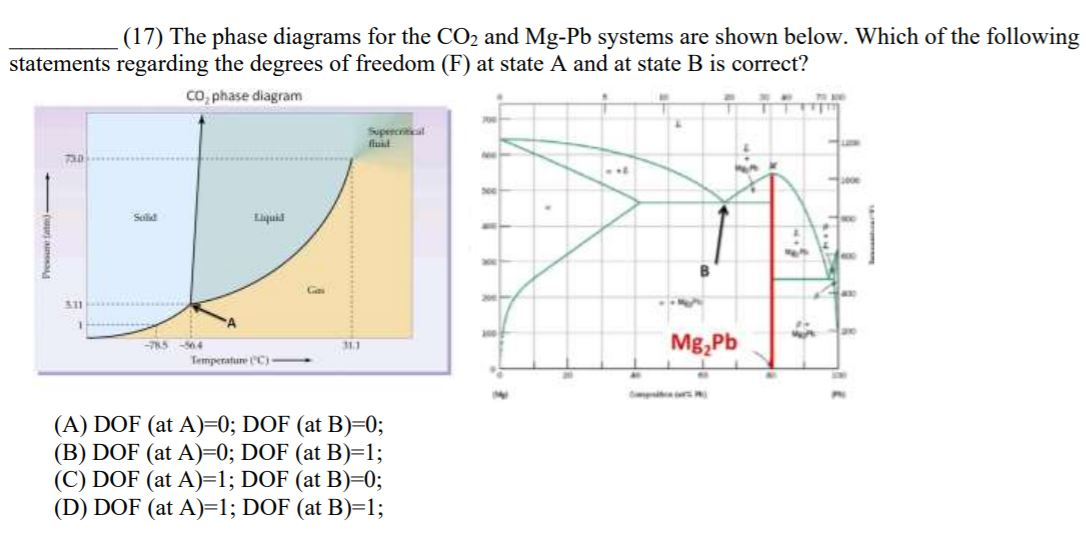
PDF Binary Phase Diagrams - University of South Alabama Phase Rule • dF = C -P + 2 • C = no. of chemical components = 1 for this example (Al 2 SiO 5 ) • P = no. of phases • dF = degrees of freedom Temp. (Deg. C) P (kbar) Kyanite Andalusite Sillimanite dF=1-1+2=2 divariant dF=1-2+2=1 univariant dF=1-3+2=0 invariant Igneous Phase Rule for Binary Systems Degrees of Freedom - MIT Degrees of Freedom. ... This shows qualitatively a very simple phase diagram for a given material. The liquid, solid, and gas phases are separated by curves in the T,P parameter space. On these curves, both phases are represented to some degree simultaneously. PDF 6. PHASE EQUILIBRIA - Louisiana Tech University PHASE EQUILIBRIA nNumber of Components and Degrees of Freedom 6.1. The region marked orthorhombic is a single-phase region. Since this is the phase diagram for pure sulfur, there is only one component. From the phase rule f = c - p + 2, with c = 1 and p = 1, the value of f is: f = 1 - 1 + 2 = 2. PDF I. Task: Analysis of cooling curves of different Sn ... - ELTE Phases, components, degrees of freedom For the description of multicomponent equilibrium system there is a general connection between the degrees of freedom (F), the number of the components (C) and the number of the phases (P) called Gibb's phase rule: P + F = C + 2. (6.1.) Expressing the degrees of freedom F = 2 + C - P .
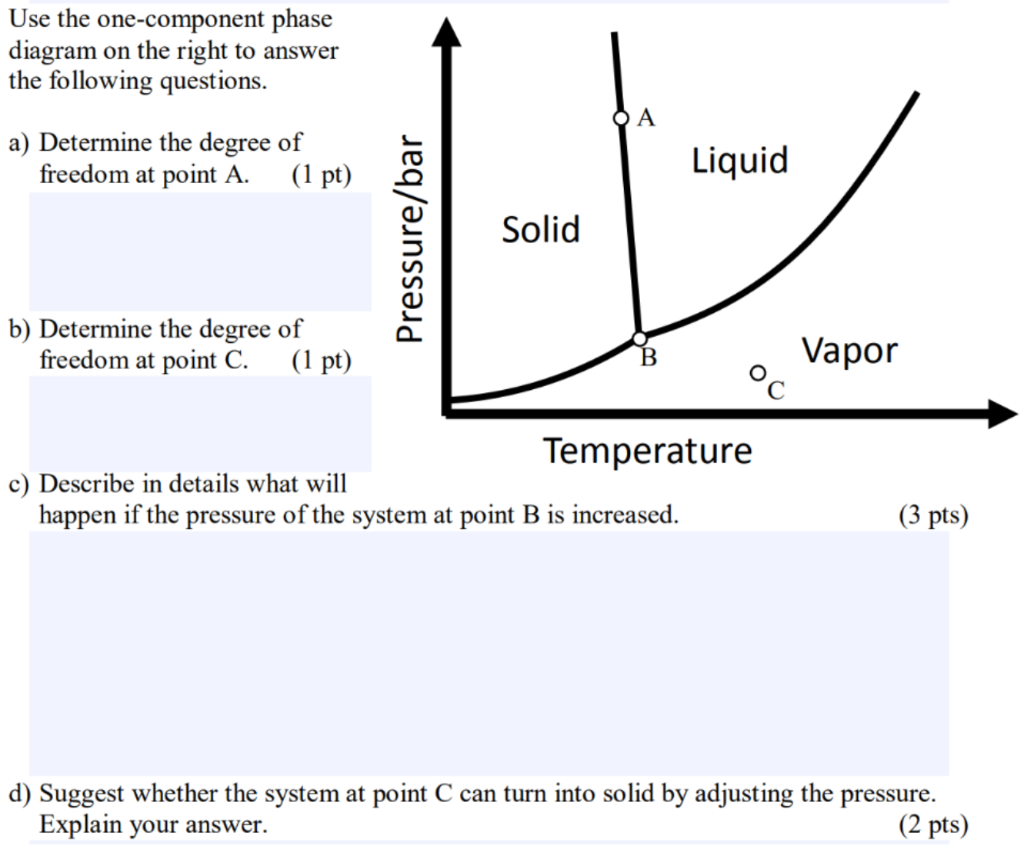
How Do You Calculate Degrees Of Freedom In A Phase Diagram ... Oct 20, 2021 · What is degree of freedom for single phase on the phase diagram? Phase diagrams For example, a single component existing as a vapor and a liquid has one degree of freedom. If the temperature is specified, then there are zero degrees of freedom—the pressure is fixed. This pressure is called the vapor pressure. phase rule | Definition, Formula, & Facts | Britannica The phase rule states that F = C − P + 2. Thus, for a one-component system with one phase, the number of degrees of freedom is two, and any temperature and pressure, within limits, can be attained. With one component and two phases—liquid and vapour, for example—only one degree of freedom exists, and there is one pressure for each temperature. Answered: Determine the degrees of freedom at… | bartleby Transcribed Image Text: Determine the degrees of freedom at each indicated point on the phase diagram. (b) Temperature Pressure. Expert Solution. Why Does an Area in Phase Diagram Considered as Having ... The Gibbs phase rule is f = c − p + 2, where f is the degrees of freedom, c is the number of components, and p is the number of phases. Your diagram says P = c s t, which I interpret to mean that pressure is constant. That specification lowers the number of degrees of freedom by one, so f = c − p + 1.
Gibbs Phase Rule - an overview | ScienceDirect Topics For a binary phase diagram plotted at 1 bar, where composition is displayed on the abscissa and temperature on the ordinate, the number of components c equals two, and the Gibbs phase rule is then f=3−ϕ.In a single-phase region, the number of degree of freedom equals 2, meaning that the two state variables temperature and composition may be varied independently.
Phase Rule - an overview | ScienceDirect Topics The phase rule, first devised by J Willard Gibbs, relates the number of degrees of freedom in a system, f, to the number of phases, p, and number of chemical components, c.Thus far, only single-component (i.e., pure, c = 1) systems have been considered, but many materials are composed of more than one component.The number of degrees of freedom is given by:
(Get Answer) - PHASE EQUILIBRIA PROBLEMS Liquid 5). The ... PHASE EQUILIBRIA PROBLEMS Liquid 5). The above figure represents the phase diagram of the one-component system, CO . i) In the area marked "solid, state how many degrees of freedom fare needed to define a state of CO, by applying the Gibbs Phase Rnle to this region You can assume no fixed pressure constraints exist.
Triangular (Three-component) Phase Diagram A three-component phase diagram has four degrees of freedom: F = 3 − 1 + 2 = 4. In this case, temperature and pressure are two of the conditions and the concentrations of two of the three components make up the rest. Only two concentrations are required because the third will be the difference between 100% and the sum of the other two components.
250+ TOP MCQs on Phase Diagram and Answers Clarification: A unary phase diagram has a single component thus, at triple point, the number of degrees of freedom, according to Gibbs phase rule F = 1 - 3 + 2 = 0. 3. The invariant reaction involving, a liquid phase decomposing into two different solids on cooling is known as _________
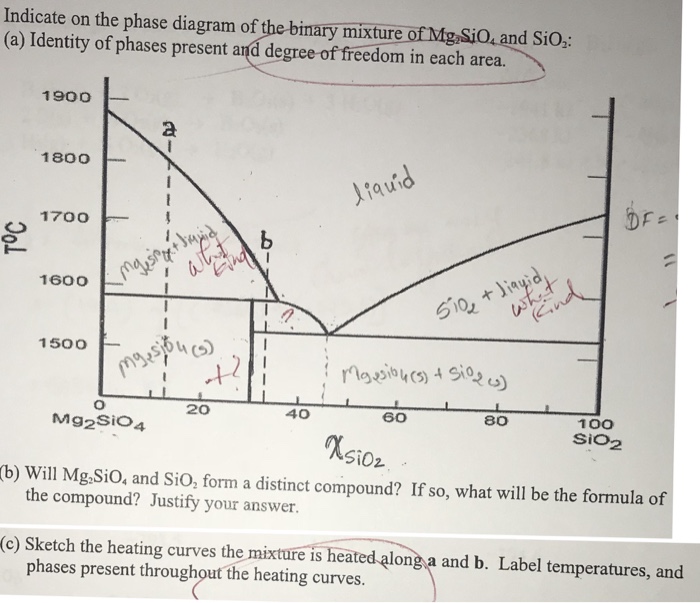
Degree of Freedom on liquidus line - ResearchGate In other words degrees of freedom 1 means you either change temperature or change component fraction composition should not change. ... I would like to draw a phase diagram for SiO2-Al2O3-(CaO+MgO ...
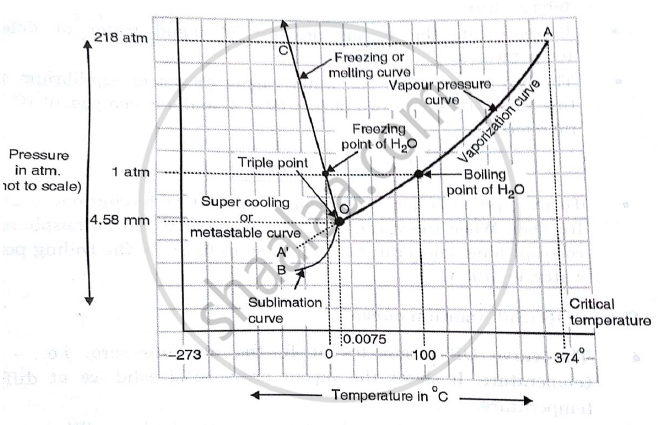
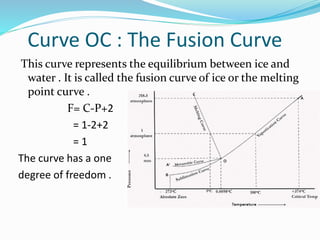
Phase diagram for Water System - Educational Portal The phase diagramcomprises : (a) Three areas, BOC, AOC and AOB. (b) Three curves, OB, OA and OC. (c) One triple point, O. For anyone component system, the maximum degree of freedom is two. Therefore, such a system can be represented completely by a two-dimensional diagram. The most convenient variables are pressure and temperature.
2.7: The Gibbs Phase Rule | PNG 301: Introduction to ... In other words, two degrees of freedom represent two-dimensional regions (areas) on the Phase Diagram in which a single phase exists. Now, let's consider the occurrence of two phases coexisting simultaneously (P = 2) in equilibrium. From Equation 2.04 with P = 2, we have one degree of freedom (F = 1).
PDF Phase Rule CHAPTER-6 PHASE RULE - Chaudhary Charan Singh ... Phase rule states that " If the equilibrium between any number of phases is not influenced by gravity, or electrical, or magnetic forces, or by surface action but are influenced only by temperature, pressure and concentration , then the number of degrees of freedom (F) of the system is related to the number of
Phase Rule - Soft-Matter - Harvard University Apr 21, 2012 · At B there are three possible phases (gas, liquid, and solid) and consequently the degrees of freedom of the system is 0 (ie B is a critical point). Similarly we can find at C the degrees of freedom to be one because there are two possible phases (fluid or solid) as indicated by the red line drawn through C.
Phase Rule - Teaching Phase Equilibria There are three solid phases shown in this diagram: the polymorphs of Al 2 SiO 5 andalusite, kyanite and sillimanite. There is only one unique place on this diagram where all three phases can coexist in equilibrium--the invariant point at 3.8 Kb and 500 o C; at this point there are zero degrees of freedom.
Determine the degrees of freedom at each indicated | Chegg.com Determine the degrees of freedom at each indicated point on the phase diagram. Show transcribed image text. Expert Answer. Who are the experts? Experts are tested by Chegg as specialists in their subject area. We review their content and use your feedback to keep the quality high. Transcribed image text: Pressure Pressure a b (a) Temperature (b ...
How do you calculate degrees of freedom in a phase diagram? Apr 11, 2020 · Likewise, what is degree of freedom in phase diagram? The 'degrees of freedom' of the system (at chemical equilibrium) refer to the number of conditions or variables that can be altered, independent of each other, without effecting the number of phases in the system. Similarly, what is phase rule equation?
Phase diagrams - Florida International University One of these two remaining degrees of freedom is the pressure and the other is the composition (expressed by the mole fraction of one component. One form of the phase diagram – a map of pressures and compositions at which each phase is stable and the other – a map of temperatures and compositions. Relevant to geology
PDF Archived Lecture Notes #10 - Phase Equilibria and Phase ... The phase rule, also known as the Gibbs phase rule, relates the number of components and the number of degrees of freedom in a system at equilibrium by the formula F = C - P + 2 [1] where F equals the number of degrees of freedom or the number of independent variables, C equals the number of components in a system in equilibrium and P equals
Eutectic Point - Soft-Matter - Harvard University According to Gibbs Phase Rule, at this phase transition, we know that the number of degrees of freedom is F=\left( C+2-P \right)=2+2-3=1 . There is only one degree of freedom, so if we assume constant pressure (a typical choice), then all three phases can only be in equilibrium at an invariant point--- the eutectic point! This ...
















![SOLVED] As per Gibb's phase rule, the number of degree of ...](https://storage.googleapis.com/tb-img/production/20/04/F1_M.J_Madhu_17.04.20_D9.png)





0 Response to "39 phase diagram degrees of freedom"
Post a Comment