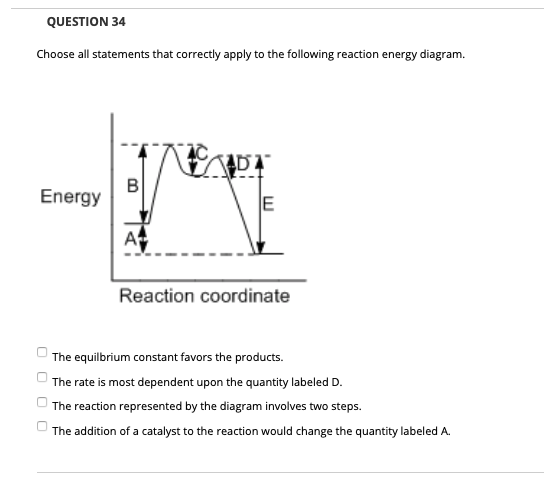
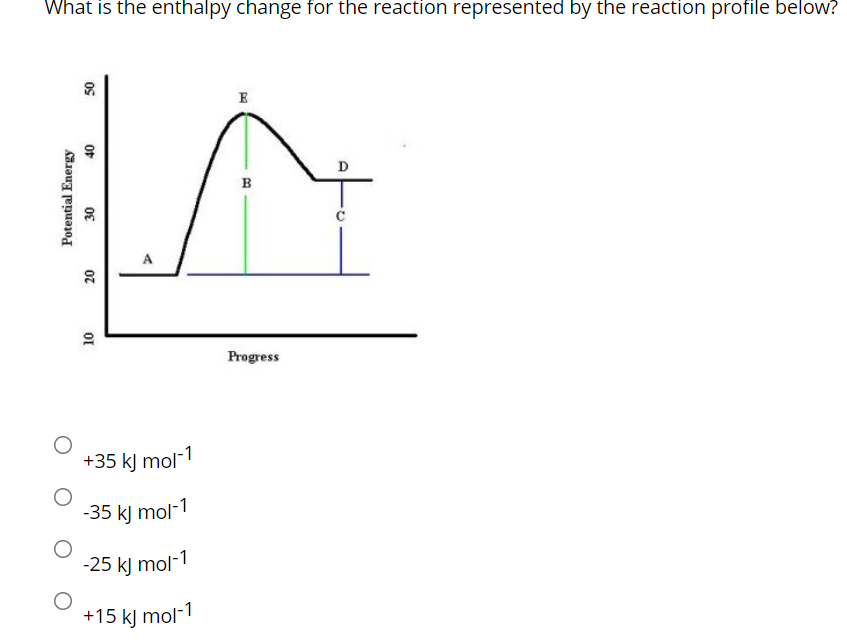
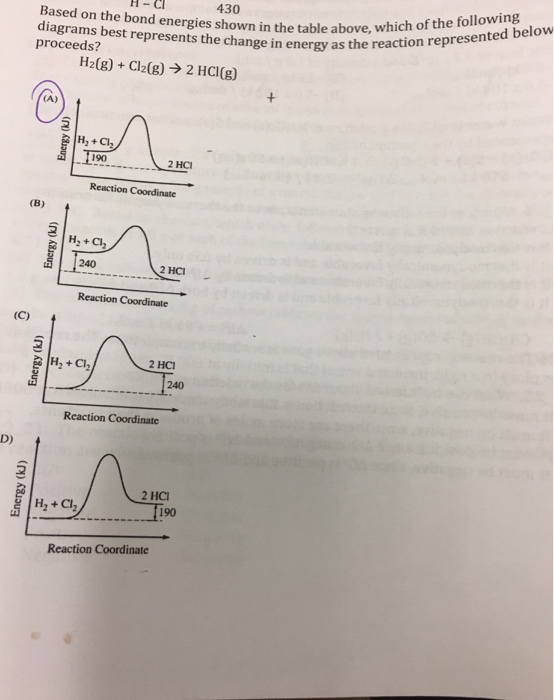
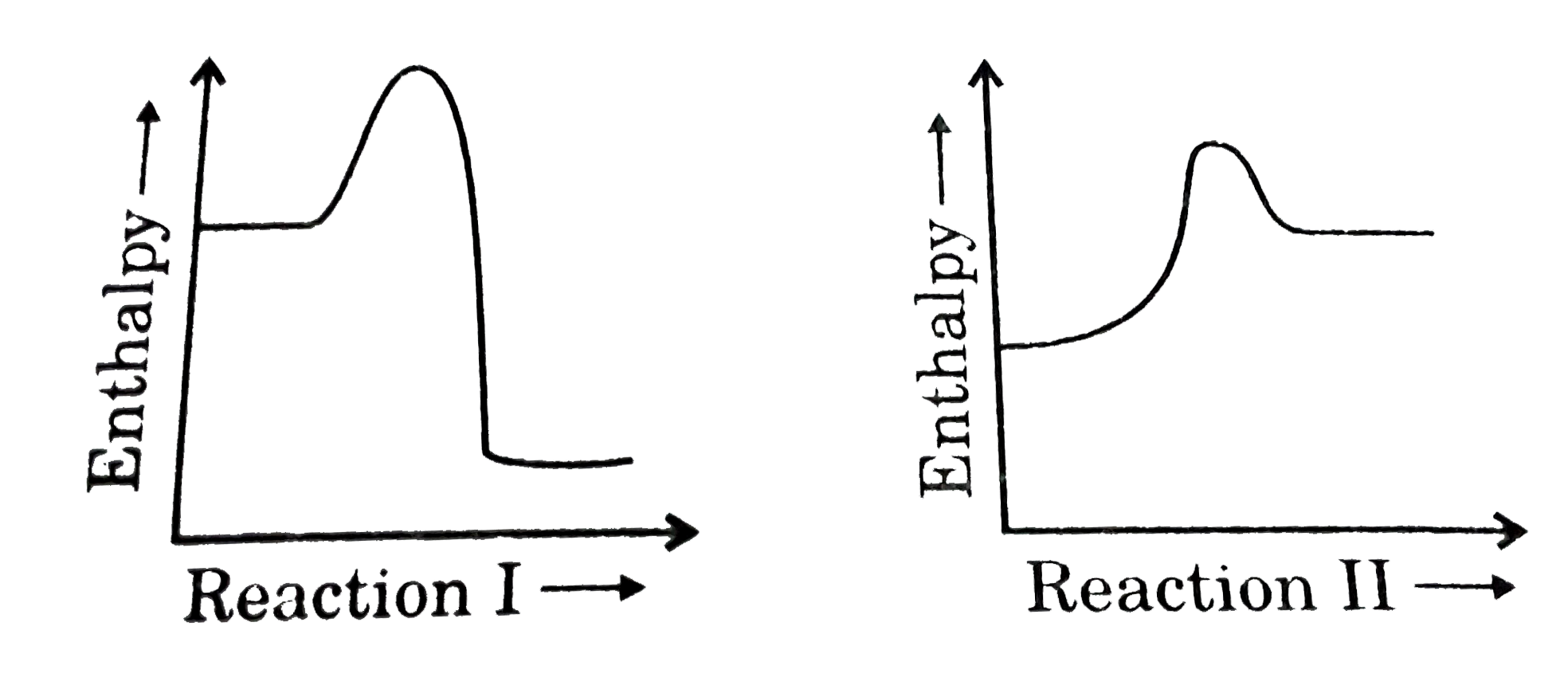
40 which of the following enthalpies of reaction would the reaction represented by the diagram have
CHM1045 Enthalpy Lecture - Department of Chemistry ... Standard Enthalpy of Reaction. The standard enthalpy of reaction (ΔH o Rxn) is the enthalpy of a reaction carried out at 1 atm. We have already learned one process by which we can calculate the Enthalpy of Reaction in Calorimetry. There are two other methods we will learn now: 1) Heat of Reaction from Standard Heats of Formation Heat of Neutralization: HCl(aq) + NaOH(aq) | Chemdemos HCl(aq) + NaOH(aq) --> NaCl(aq) + H 2 O(l) + Energy. Thermochemistry determine the heat exchanged at constant pressure, q = m c ∆T.. Calculating the limiting reactant, the change in enthalpy of the reaction, ∆H rxn, can be determined since the reaction was conducted under conditions of constant pressure ∆H rxn = q rxn / # moles of limiting reactant. This reaction is classified as an ...
Consider the following enthalpy diagram and enthalpies of ... The given statement "the overall chemical reaction is exothermic" is true regarding the enthalpy diagram and enthalpies of intermediate and overall chemical reactions.. Further explanation: Properties are categorized into two types: 1. Intensive properties: These properties depend on the nature of the substance and not on the size of the system.

Which of the following enthalpies of reaction would the reaction represented by the diagram have
ChemTeam: Hess' Law - using standard enthalpies of formation All the above values have units of kJ/mol because these are standard values. All standard enthalpies have the unit kJ/mol. As a brief reminder, here is the chemical reaction for the standard enthalpy of glucose: 6C(s, graphite) + 6H 2 (g) + 3O 2 (g) ---> C 6 H 12 O 6 (s) Each standard enthalpy value is associated with a chemical reaction. Enthalpy - Wikipedia Enthalpy / ˈ ɛ n θ əl p i / (), a property of a thermodynamic system, is the sum of the system's internal energy and the product of its pressure and volume. It is a state function used in many measurements in chemical, biological, and physical systems at a constant pressure, which is conveniently provided by the large ambient atmosphere. The pressure-volume term expresses the work ... PDF Tutorial 7 HEATS OF REACTION - Eastern Illinois University reaction performed at constant pressure is the enthalpy change for the reaction. This enthalpy change, ∆H, has units kJ/mol and is defined: (1) ∆H = H(products) - H(reactants) If energy is given off during a reaction, such as in the burning of a fuel, the products have less
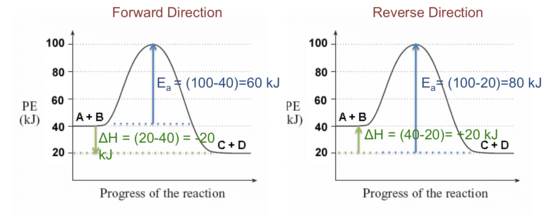
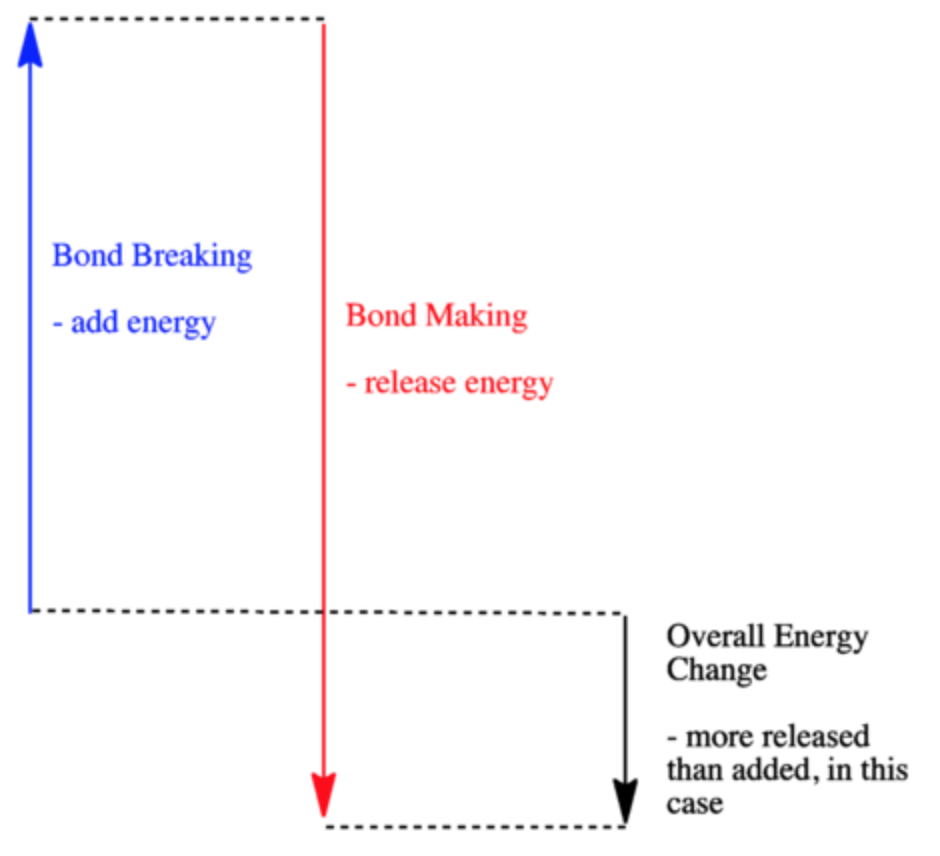
Which of the following enthalpies of reaction would the reaction represented by the diagram have. 4.09 Writing Thermochemical Equations Quiz - Quizlet NH4Cl(s)→NH +4(aq)+Cl−(aq) , ΔH= +14.8 kJ/mol. Which enthalpy of reaction would the reaction represented by the diagram have? Diagram: Chemical Reactivity - Michigan State University The covalent bond of a chlorine molecule provides a simple example of the energy changes associated with bond breaking and bond making. This bond may be broken by the introduction of heat or light energy, and it has been determined that 57.9 kcal/mol (242.3 kJ/mol) is required for bond homolysis.This is shown in the first of the following reactions; the second reaction describes the reverse ... Sample Questions - Chapter 16 - Texas A&M University Given that a reaction absorbs energy and has an activation energy of 50 kJ/mol, which of the following statements are correct? (Hint: Draw the potential energy diagram.) (1) The reverse reaction has an activation energy equal to 50 kJ/mol. (2) The reverse reaction has an activation energy less than 50 kJ/mol. What is the standard enthalpy of the reaction CO+H2O ... Explanation: We can use the standard enthalpies of formation of the reactants and products to calculate the standard enthalpy of reaction. I list their values below the corresponding formulas. Note that the substances must be in their most stable states at 298 K and 1 bar, so water is listed as a liquid. XXXXXXXXXCO(g)l +lH2O(l) → CO2(g) + H2(g)
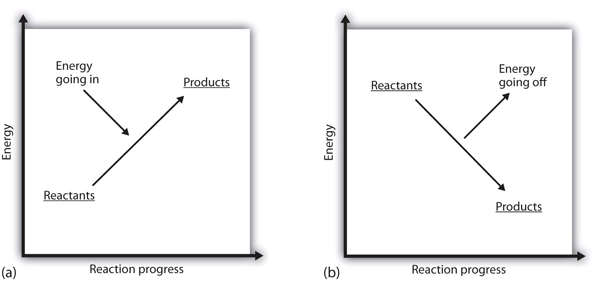
Standard Enthalpy of Formation and Reaction | Boundless ... Key Points. The standard enthalpy of reaction, ΔH⊖ rxn Δ H r x n ⊖, can be calculated by summing the standard enthalpies of formation of the reactants and subtracting the value from the sum of the standard enthalpies of formation of the products. The following equation can be used to calculate the standard enthalpy of reaction: ΔH⊖ rxn ... Enthalpy and Chemical Reactions – Introductory Chemistry A fundamental concept is that every chemical reaction occurs with a concurrent change in energy. Now we need to learn how to properly express these energy ... CHEM 245 - Enthalpy - Gonzaga University Example: Calculate the thermodynamic value ΔH° for the following reaction at 298.15 K (25.00 °C): N 2 (g) + 3 H 2 (g) → 2 NH 3 (g) Use the values for standard enthalpies of formation given in thermodynamic tables (these are usually found in an appendix of a general chemistry textbook). Enthalpy of Chemical Reactions - Nassau Community College reaction. Consider the following general type of reaction . reactant Æ products . The ∆H is defined as the difference between the enthalpies of products and the reactants. Thus . ∆H = Hproducts - Hreactants . The enthalpy of reaction can be positive or negative or zero depending upon whether the heat is gained or lost or no heat is lost or ...
which of the following enthalpies of reaction would the ... The x-axis represents the reaction progress. Chemical reactions proceed (or are read) from left to right. Therefore, looking at the potential energy diagram, ... PDF 6 g What is the standard enthalphy change ΔH Which of the following expressions is equivalent to ΔHo for the reaction represented above? A x + y B x - y C x + 2y D 5. How much heat is released or absorbed when 0.050 mol of Cl2(g) is formed from KCl(s)? 87.4 kJ is released 43.7 kJ is released 43.7 kJ is absorbed 87.4 kJ is absorbed 6. Hess' Law - Chemistry | Socratic The law states that the total enthalpy change during a reaction is the same whether the reaction is made in one step or in several steps.. In other words, if a chemical change takes place by several different routes, the overall enthalpy change is the same, regardless of the route by which the chemical change occurs (provided the initial and final condition are the same). PDF Unit 6 Review Key - Chemistry with Ms. Ye - Home 15.For the reaction represented above, the value of the equilibrium constant, Kc, is 240 at 250C. From this information, correct deductions about the reaction at 250C include which of the (B) Greater than 1.2 atm but less than 2.4 atm (D) Greater than 2.4 atm PC13(g) + C12(g) J hif-+ 6.5 following? I. The reaction is quite rapid. Il.
sem 2 chem 4.09 Flashcards | Quizlet Which of the following enthalpies of reaction would the reaction represented by the diagram have? ...
Chemistry chapter 6 smartbook Flashcards | Quizlet In the enthalpy diagram shown, the reactants are _____ in energy than the ... Which of the following reactions would have an enthalpy change equal to ΔHfo?
PDF UNIT 1 THERMOCHEMISTRY - Nova Scotia Department of Education UNIT 1 CORRESPONDENCE STUDY PROGRAM PAGE 19 INTRODUCTION TO THERMOCHEMISTRY LESSON 1 Thermochemistry is the study of the change in thermal energy (energy due to the motion of particles). It takes place during physical and chemical changes. Energy is defined as the ability to do work. Work is defined as a force exerted over a distance. There are two types of energy, kinetic
Answered: 2C(s) + 2H2O(g)→ CH4(g) + CO2(g)… | bartleby Science Chemistry Q&A Library 2C (s) + 2H2O (g)→ CH4 (g) + CO2 (g) Determine AH for this reaction using the following enthalpies of reactions: C (s) + H2O (g) → CO (g)+ H2 (g) CO (g) + H2O (g) → CO2 (g) + H2 (g) CH4 (g) + H2O (g) → 3H2 (g) + CO (g) AH = 131.3 kJ AH = - 41.2 kJ AH = 206.1 kJ.
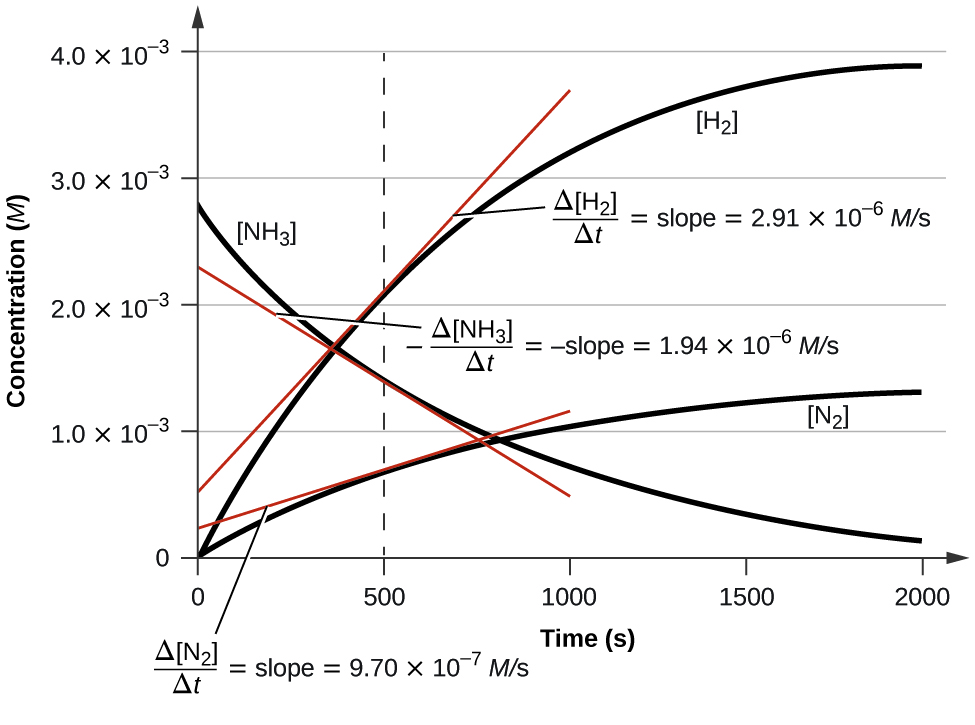
PDF Chapter 14 Chemical Kinetics - University of Pennsylvania ... In reactions, most likely, one would be interested in knowing how much reactant is left after a certain period of time. The mathematics to do this involves calculus and is quite complex. We will look at first and second order reactions as well as half-life. A. First Order Reaction For the reaction A→ products, the rate is as follows: Δ[A]
AP Chemistry Kinetics Review | Chemistry Quiz - Quizizz The rate of reaction between Zn(s) and HCl(aq) is determined by measuring the volume of H2(g) produced over time. In trial 2 of the experiment, 5.0g of powdered Zn(s) is added to 100mL of 0.10MHCl(aq). Which trial will have a faster initial rate of reaction and why?
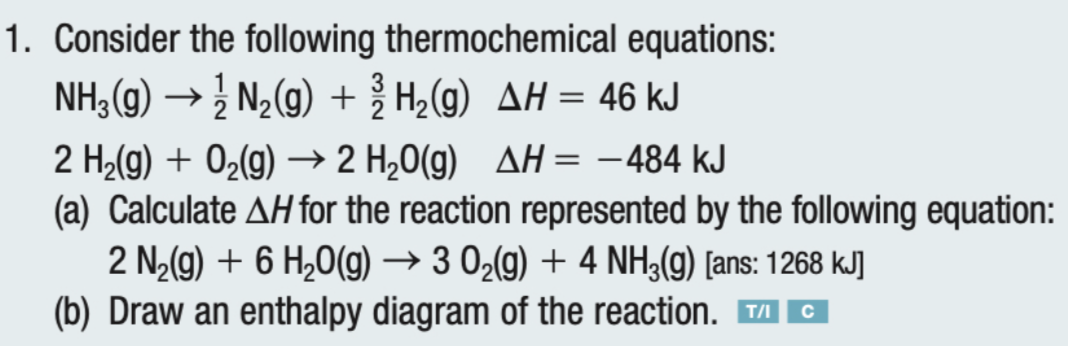
ChemTeam: Hess' Law - three equations and their enthalpies ... Calculate the enthalpy of reaction for: 2CH 4 + 3O 2---> 2CO + 4H 2 O. Solution: 1) Apply the following changes to the data equations: a) multiply by 3 b) multiply by 3 c) reverse equation, multiply by 2 The need for a 3 and 2 is because the hyrogens in equations 2 & 3 have coefficients of 2 and 3.
Answered: Determine the enthalpy of formation for… | bartleby Ethanol, C2H5OH, is used as a fuel for motor vehicles, particularly in Brazil.(a) Write the balanced equation for the combustion of ethanol to CO2(g) and H2O(g),and calculate the enthalpy of combustion of 1 mole of ethanol.(b) The density of ethanol is 0.7893 g/mL.
Enthalpies for Different Types of Reactions: Enthalpy ... Enthalpy change is the standard enthalpy of formation. We have determined it for a vast number of substances. In any given chemical reaction, the reactants undergo chemical changes and combine to form different products. For any such reaction, we represent the enthalpy change as Δ r H. We term it as the reaction enthalpy.
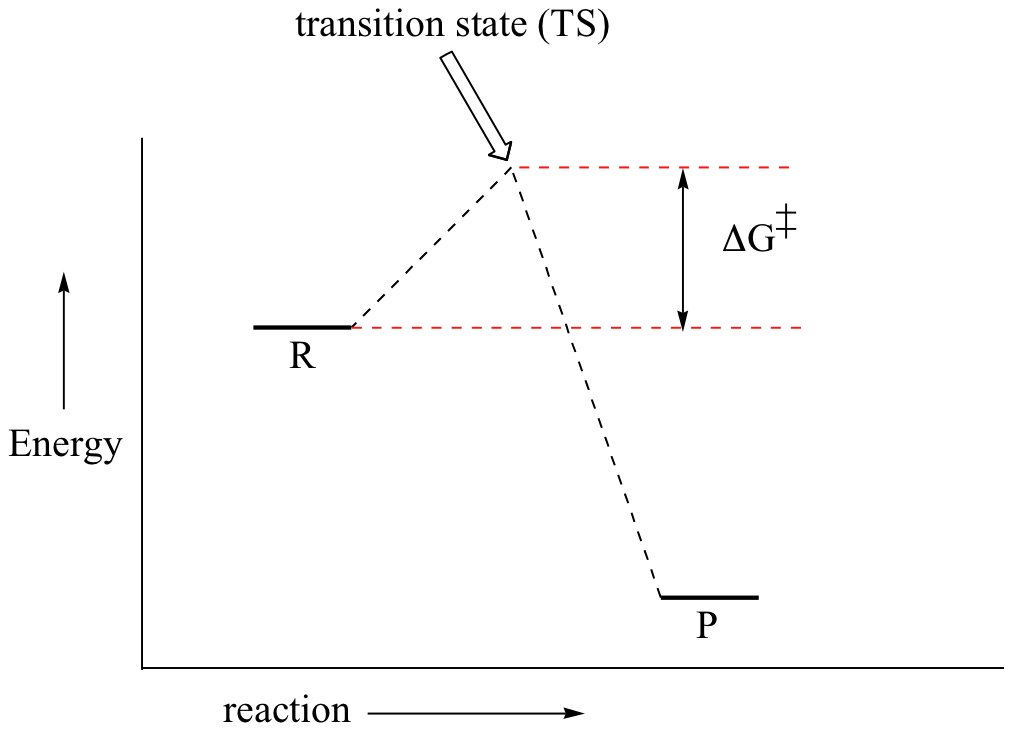
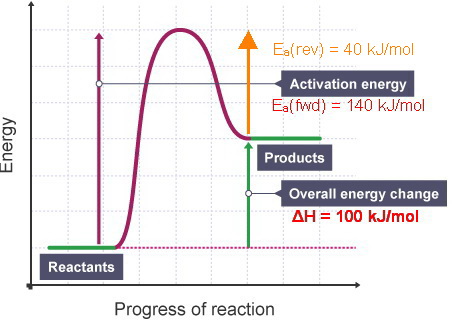
PDF 2.3.1 Enthalpy Changes - Shenfield Learning Site Include on your diagram labels for: • enthalpy change, ∆ H; • activation energy for the catalysed route, Ec; • activation energy for the uncatalysed route, Ea. enthalpy reactants progress of reaction [3] [Total 6 marks] 11. Enthalpy changes of reaction can be determined indirectly from average bond enthalpies and standard enthalpy changes.
Solved QUestion 4: Enthalpy of Reaction a. Use enthalpies ... QUestion 4: Enthalpy of Reaction. a. Use enthalpies of formation to determine the ?Hreaction for the reaction MgCl2(s) MgCl2(aq). (2 points) b. Use Hess's law and the following equations to calculate the ?Hreaction for the reaction CO(g) + 3H2(g) CH4(g) + H2O(g).
OneClass: Use average bond enthalpies from Table 8.4 to ... (b) By using the data tabulated here, sketch a quantitative energy profile for the catalyzed reaction represented by reactions 3 and 4. ( c ) By using bond enthalpies, estimate where the reactants, CH 4 ( g ) + Cl 2 ( g ), should be placed on your diagram in part (b).
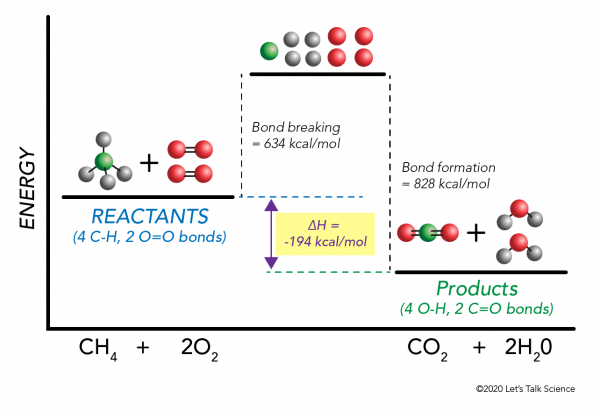
AP Chemistry: Midterm Review Flashcards - Quizlet The enthalpy of a reaction (ΔH) is estimated as the sum of the bond enthalpies of the bonds broken minus the sum of the bond enthalpies of the bonds formed. No bonds are formed during the dissociation reaction, so ΔH is equal to the energy required to break the O=O double bond, which is 495kJ/mol.
Chemistry 4.09 Quiz: Writing Thermochemical Equations ... Which of the following enthalpies of reaction would the reaction represented by the diagram have? ΔH < 0. Related questions. QUESTION. when 878 J of heat are absorbed by 125 g of silver, the temperature rises from 25.0 ºC to 54.9 ºC. what is the specific heat capacity of silver?
Chemistry 4.09: Writing Thermochemical Equations Flashcards ... Which of the following enthalpies of reaction would the reaction represented by the diagram have? ΔH < 0 ...
PDF CHAPTER 5: ANSWERS TO ASSIGNED PROBLEMS Hauser- General ... 5.69 The following is known as the thermite reaction 2 Al (s) + Fe 2O 3 (s) Al 2O 3 (s) + 2 Fe (s) This highly exothermic reaction is used for welding massive units, such as propellers for large ships. Using standard enthalpies of formation in Appendix C, calculate ΔH° for this reaction. Use Enthalpy of Formation data and equation:
PDF Enthalpy of Formation of Magnesium Oxide - University of Idaho Along with learning calorimetry techniques, you will use the data you collect, other reaction enthalpies, and Hess's Law, to determine o ΔHf for MgO(s). Read and/or review the thermochemistry chapter in your textbook. Enthalpy and Hess's Law The enthalpy change, o ΔHrxn , of a chemical reaction is called the enthalpy of reaction or the ...
PDF Tutorial 7 HEATS OF REACTION - Eastern Illinois University reaction performed at constant pressure is the enthalpy change for the reaction. This enthalpy change, ∆H, has units kJ/mol and is defined: (1) ∆H = H(products) - H(reactants) If energy is given off during a reaction, such as in the burning of a fuel, the products have less
Enthalpy - Wikipedia Enthalpy / ˈ ɛ n θ əl p i / (), a property of a thermodynamic system, is the sum of the system's internal energy and the product of its pressure and volume. It is a state function used in many measurements in chemical, biological, and physical systems at a constant pressure, which is conveniently provided by the large ambient atmosphere. The pressure-volume term expresses the work ...
ChemTeam: Hess' Law - using standard enthalpies of formation All the above values have units of kJ/mol because these are standard values. All standard enthalpies have the unit kJ/mol. As a brief reminder, here is the chemical reaction for the standard enthalpy of glucose: 6C(s, graphite) + 6H 2 (g) + 3O 2 (g) ---> C 6 H 12 O 6 (s) Each standard enthalpy value is associated with a chemical reaction.







:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/endergonic-vs-exergonic-609258_final-2904b2c359574dfcb65a9fca2d54179a.png)









0 Response to "40 which of the following enthalpies of reaction would the reaction represented by the diagram have"
Post a Comment