41 laws of reflection diagram
Reflection of Light: Definition, Laws, Types and Diagrams Reflection follows two basic rules: (1) In reflection of light, the angle of incidence of the light is equal to the angle of reflection. (2) The incident ray, the normal, and the reflected ray all lie on the same plane. As far as plane mirrors are concerned, the images formed are virtual, erect, laterally inverted, and of the same size as the ... State The Laws Of Reflection Of Light - BYJUS The laws of reflection determine the reflection of incident light rays on reflecting surfaces, like mirrors, smooth metal surfaces, and clear water. Following are the laws of reflection: The incident ray, the reflected ray and the normal to the surface of the mirror all lie in the same plane. The angle of incidence is equal to the angle of ...
The Laws of Reflection and Refraction The law of reflection tells us that ? 2 = ? 3; on the basis of this and our conclusion about the relationship of ? 1 and ? 3, we can express ? 2 in terms of ? 1 as follows. Practice Problem : Complete the diagram to show (approximately) the path of the ray upon reflection by the mirror shown below.
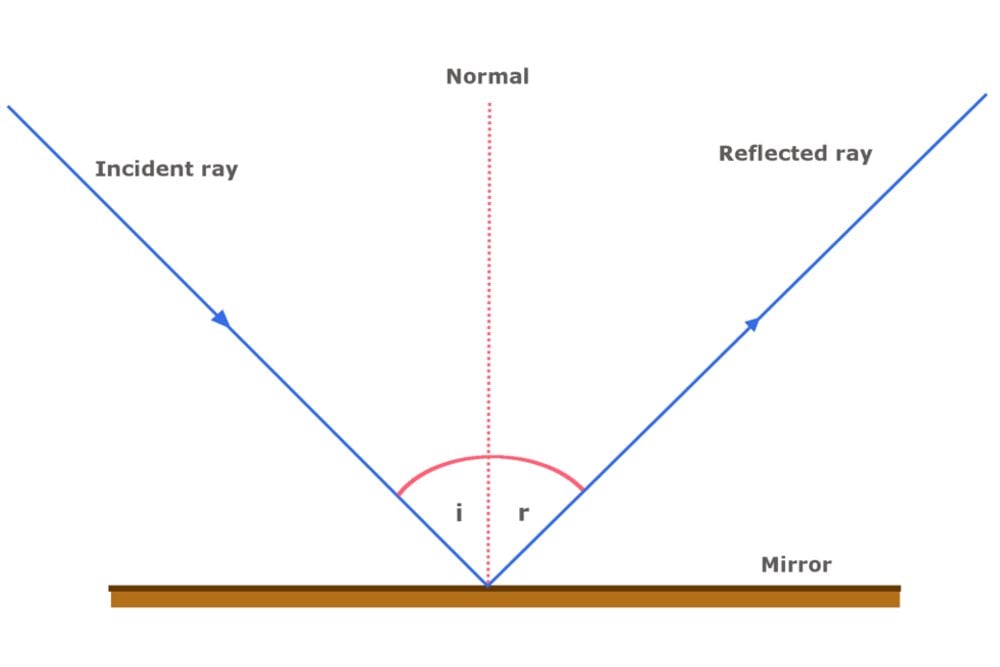
Laws of reflection diagram
Using the law of reflection - Ray diagram rules Use new ray diagram rules and create a virtual image Here we shall discuss method 2, using the laws of reflection. In the following diagram we will try to find the light rays from an object which travel to a mirror and then reflect from a mirror and then focus in the eye of an observer. Below shows you a convex mirror, an object and an observer. Law of reflection - Reflection and refraction of light ... the angle of reflection, r, is the angle between the normal and reflected ray. The law of reflection states that: angle of incidence i = angle of reflection r. For example, if a light ray hits a... What is law of reflection short definition? - Runyoncanyon ... The diagram below illustrates the law of reflection. In the diagram, the ray of light approaching the mirror is known as the incident ray (labeled I in the diagram). The law of reflection states that when a ray of light reflects off a surface, the angle of incidence is equal to the angle of reflection. What is reflection example?
Laws of reflection diagram. Laws Of Reflection: Definition, Types, Diagrams ... We know light is the form of energy which can undergo various phenomenons like refraction, reflection, diffraction, and interference. In this session, let us know more about laws of reflection (first law of reflection and second law of reflection), types of reflection, examples, differences, and total internal reflection. State the laws of Reflection along with a suitable diagram. State the laws of Reflection along with a suitable diagram. Easy Solution Verified by Toppr I = Incident ray R = Reflected ray N = Normal ∠ i = angle of incidence ∠ r = angle of reflection There are two basic laws of reflection of light - (i) The incident ray the reflected ray and the normal to the reflecting The Law of Reflection - Rensselaer Polytechnic Institute The Law of Reflection. In the figure to the left, a laser beam traveling through an optical fiber (shown in incredibly slow motion) reflects off the lower edge of the fiber. The normal to that edge is indicated by the dashed line. As the beam approaches the edge of the fiber, it makes an angle of incidence θi with respect to the normal. A. State the laws of reflection of light - Vedantu Laws of reflection: Incident ray, the reflected ray, and the normal to the surface of the mirror all lie in the same plane. The angle of reflection is equal ...
› Class › reflnPhysics Tutorial: The Law of Reflection Light is known to behave in a very predictable manner. If a ray of light could be observed approaching and reflecting off of a flat mirror, then the behavior of the light as it reflects would follow a predictable law known as the law of reflection. The diagram below illustrates the law of reflection. In the diagram, the ray of light approaching the mirror is known as the incident ray (labeled I in the diagram). › physics › laws-of-reflectionLaws of Reflection - First and Secons Law with Examples Law 1 - The primary law of reflection expresses that the reflection point is dependably comparable to the point of incidence. If the episode beam falls on the plane mirror along with the typical, for example, 90°, the reflected beam will go along a similar way. Law 2 - The reflected ray, incident ray, point of incidence, and reflection lie on ... Laws of Reflection | Definition, Examples, Diagrams Laws of verification can be experimentally verified by drawing the trace of a ray of light before and after reflection. This can be done by passing light through a small hole in a dark room or using two thin objects (like needles/pins) to trace a straight line and observe its reflection. Sample Problems for The Law of Reflection Sample Problems for The Law of Reflection Important Information When light is reflected from a surface, the angle of incidence is always equal to the angle of reflection, where both angles are measured from the path of the light to the normal to the surface at the point at which light strikes the surface. This equality is known as the law of reflection.
Law of Reflection (Diagram) Diagram | Quizlet Start studying Law of Reflection (Diagram). Learn vocabulary, terms, and more with flashcards, games, and other study tools. The reflection of light - Boston University To figure out where the image of this object is located, a ray diagram can be used. In a ray diagram, rays of light are drawn from the object to the mirror, along with the rays that reflect off the mirror. The image will be found where the reflected rays intersect. Note that the reflected rays obey the law of reflection. what are the laws of reflection? explain with diagram ... These are known as Laws of Reflection. 1. The incident ray, the reflected ray and normal at the point of incidence, lie in the same plane. 2. The angle of incidence is always equal to the angle of reflection (∠i = ∠r). [The law of refection is illustrated in figure-1] • Example -. The three laws of reflection - Mammoth Memory Incident ray and refracted ray are on different sides of the normal Law 1 explained The angle between the incident ray and the normal is equal to the angle between the reflected ray and the normal. This means that θi θ i equals θr θ r where θi = θ i = angle of incidence θr = θ r = angle of reflection
Laws of Reflection | Definition, Examples, Diagrams - Toppr Laws of reflection · The incident ray, the reflected ray and the normal at the point of incidence all lie in the same plane. · Angle of incidence is equal to the ...State the laws of reflection. Draw a diagram to show incident and reflected rays.What is reflection? Write the laws of reflection.
Laws of Reflection - Explanation and Experiment - Teachoo Laws of Reflection. There are 2 laws of Reflection. The Incident ray, Reflected ray and the Normal, all lie in the same plane. The Angle of Incidence is always equal to Angle of Reflection. So, in our figure above, Incident ray OP, reflected ray OQ and Normal ray ON all lie on the same plane. And,
Using the law of reflection - Mammoth Memory Here we shall discuss method 1, using the laws of reflection. In the following diagram we will try to find the light rays from an object which travel and focus in the eye of an observer: Place a protractor with its straight edge along the plane mirror. Use a ruler to extend the protracted lines.
The Law of Reflection Diagram | Quizlet Start studying The Law of Reflection. Learn vocabulary, terms, and more with flashcards, games, and other study tools.
Reflection: Definition, Laws of Reflection and Multiple ... Figure 12.3 shows the reflection of a ray of light which falls on a smooth surface at O. O is called the point of incidence of the ray. AO is the incident ray and OB is the reflected ray. ON is the perpendicular to the surface at O. It is called the normal to the surface at the point of incidence.
Physics Video Tutorial - Law of Reflection This video tutorial lesson introduces the vocabulary of reflection (incident ray, reflected ray, angle of incidence, and angle of reflection) and describes and illustrates the law of reflection. The application of the law of reflection to the viewing of images in plane mirrors is explained. Some examples of the use of geometry principles combined with the law of reflection are discussed.
The Law of Reflection Draw a ray diagram to show how the light ray interacts with the mirror. Label the normal line, the incident ray, and the reflected ray. Solution: 1. When we ...2 pages
Laws of reflection - Light | Term 3 Unit 1 | 7th Science Laws of reflection: 1. The angle of incidence is always equal to the angle of reflection. ∟i = ∟r. 2. The incident ray, the reflected ray and the normal at the point of incidence lie on the same plane. Example 1. In the figure, the incident ray makes 27° with the normal, then find the angle of reflection. Solution:
Law of Reflection diagram Diagram - Quizlet Start studying Law of Reflection diagram. Learn vocabulary, terms, and more with flashcards, games, and other study tools.
Laws of Reflection and the Phenomenon of Light Reflection ... Laws of Reflection. The most common example of the reflection of light in real life is the reflection of light off the shiny surface of a mirror. There are multiple laws of reflection elaborated further. When a ray of light strikes a plane mirror, the light ray reflects off the mirror. Reflection involves a change in the direction of the light ray.
Reflection and Mirrors - Law of Reflection Mission RM1: Law of Reflection. Mission RM1 pertains to the law of reflection, the terminology associated with it, and its use in predicting the value of the angle of reflection. The mission consists of 34 questions organized into 9 Question Groups. You must answer one question from each Question Group to complete the mission.
Physics Tutorial: Two Rules of Reflection for Concave Mirrors Two Rules of Reflection for Concave Mirrors. Light always reflects according to the law of reflection, regardless of whether the reflection occurs off a flat surface or a curved surface. Using reflection laws allows one to determine the image location for an object. The image location is the location where all reflected light appears to diverge ...
Reflection - Light waves - KS3 Physics Revision - BBC Bitesize Reflection A ray diagram shows how light travels, including what happens when it reaches a surface. In a ray diagram, you draw each ray as: a straight line with an arrowhead pointing in the...
Explain the laws of reflection with the help of a diagram ... According to Law of Reflection, 1- The angle of the incident light ray is equal to the angle of the reflected light ray:-When a ray of light strikes on the smooth surface it gets reflected. We draw a perpendicular line at the point of incidence, this line is called normal ray.
What is law of reflection short definition? - Runyoncanyon ... The diagram below illustrates the law of reflection. In the diagram, the ray of light approaching the mirror is known as the incident ray (labeled I in the diagram). The law of reflection states that when a ray of light reflects off a surface, the angle of incidence is equal to the angle of reflection. What is reflection example?
Law of reflection - Reflection and refraction of light ... the angle of reflection, r, is the angle between the normal and reflected ray. The law of reflection states that: angle of incidence i = angle of reflection r. For example, if a light ray hits a...
Using the law of reflection - Ray diagram rules Use new ray diagram rules and create a virtual image Here we shall discuss method 2, using the laws of reflection. In the following diagram we will try to find the light rays from an object which travel to a mirror and then reflect from a mirror and then focus in the eye of an observer. Below shows you a convex mirror, an object and an observer.

0 Response to "41 laws of reflection diagram"
Post a Comment