37 beta decay feynman diagram
Pion weak decay Feynman diagram for (42) π →e +ν e − − Matrix element: π μ π m p j ~ Pion currect – from Klein-Gordan equation for spinless particles: π− (43) G F is the coupling constant for the 4-point like fermion vertex (d u e ν e) − fπ is the pion decay constant: fπ =93 MeV In the rest frame of pion: p (m ,0) r μ= π (44) The corresponding Feynman diagram will be: This is a weak decay of the strange quark. It is an allowed diagonal change between quark generations. The Feynman diagram for the s to u transition is a combination of two quark-W vertices. The pion is derived from a same generation quark weak vertex. Return to top of page
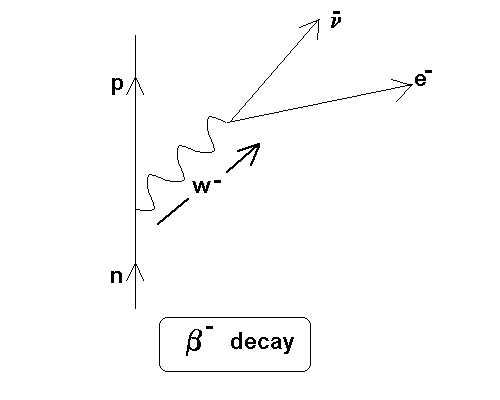
Beta decay occurs when, in a nucleus with too many protons or too many neutrons, one of the protons or neutrons is transformed into the other. In beta minus ...

Beta decay feynman diagram
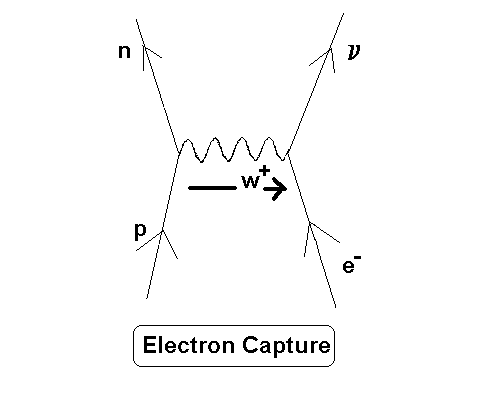
The leading-order Feynman diagrams for electron capture decay. ... The Q value is defined as the total energy released in a given nuclear decay. In beta decay, Q is therefore also the sum of the kinetic energies of the emitted beta particle, neutrino, and recoiling nucleus. (Because of the large mass of the nucleus compared to that of the beta ... (ii) Sketch the Feynman diagram that represents this reaction. The diagram has been started for you. times u du (ii) Energy is transferred to a hadron in an attempt to separate its quarks. Describe; Question: 2. (a) Silicon-30 (Si) can be formed from phosphorus-30 (SP) by a process of beta-plus decay. This weak force is believed to be carried by three fundamental particles: W-,W+ and Z bosons. Using the Feynman diagram, describe the beta-negative decay of a ...4 May 2014 · Uploaded by AK LECTURES
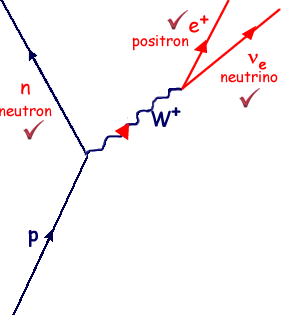
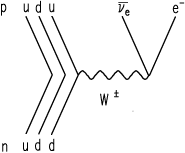
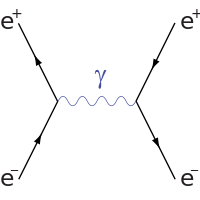
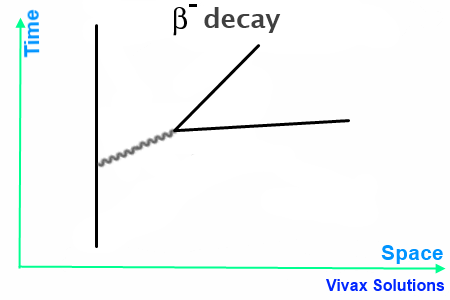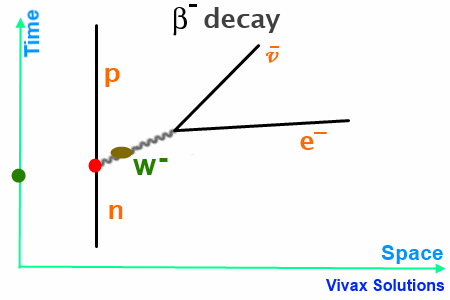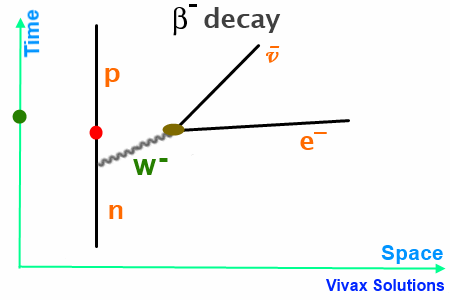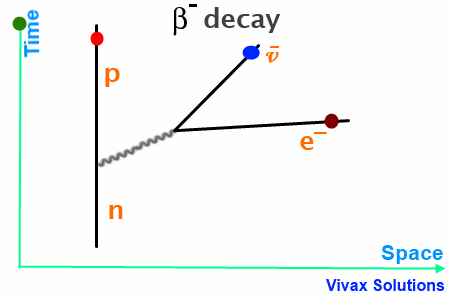
Beta decay feynman diagram. Feynman diagram 138 E ` m “ E1 ` a p2 ` m2 pE ` m ´ E1q“ a p2 ` m2 pE ` m ´ E1q2 “ E2 ` E12 ´ 2EE1 cos ` m2 E2 ` E12 ` m2 ` 2mE ´ 2mE1 ´ 2EE1 “ E2 ` E12 ´ 2EE1 cos ` m2 2mE ´ 2mE1 “ 2EE1p1 ´ cos q Think of time “passing” to the right, so initially, we start with an electron. And in the final state, we end with an electron ... Download scientific diagram | 1: Feynman diagram of Inverse Beta Decay (IBD) process. from publication: Neutrino Physics in Present and Future Kamioka ... Diagram Beta decay: beta particle is emitted from an atomic nucleus Compton scattering: scattering of a photon by a charged particle Neutrino-less double beta decay: If neutrinos are Majorana fermions (that is, their own antiparticle), Neutrino-less double beta decay is possible. Several experiments are searching for this. Pair creation and ... ⇒Feynman Diagrams are pictorial representations of the interactions of subatomic particles ⇒ For example, this shows a Feynman Diagram of beta (β-) decay (see our notes on nuclear equations if you have not done so already): ⇒ Usually, Feynman Diagrams are read from left to right ⇒ So, here, we can see a neutron decaying into a proton and a W-exchange particle, which subsequently ...
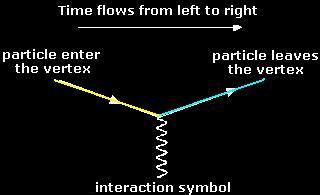
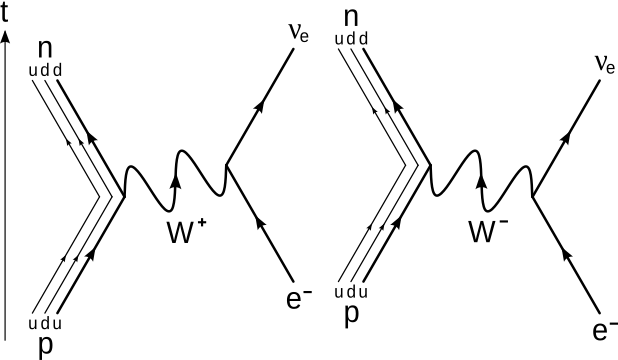
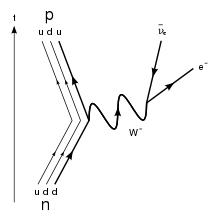
Like electrical circuit diagrams, every line in the diagram has a strict mathematical interpretation. For details of Feynman diagram calculation, take a Advanced Quantum or 880.02 course see Griffiths (e.g. sections 6.3, 6.6, and 7.5) Bjorken & Drell (Relativistic Quantum Mechanics). Feynman Diagrams µ decay € e+e−→µ+µ− scattering a particle with no spin, the Feynman propagator is a factor 1 Q Q m2 where Q Q = E2 Q q is the four-momentum-squared of the internal virtual particle4. These intermediate particles are called virtual particles. They do not satisfy the usual relativistic energy-momentum constraint Q Q = m2. For an intermediate virtual particle, Q Q = E2 Q qq 6= m2: Like muon decay, the theory of neutron beta decay based on the Feynman diagram of gure 3 is still a V-A theory and produces surprisingly good results. However, a more 6. sophisticated theory will take into consideration the observed generational mixing of quarks associated with the weak interaction. Moreover, since a neutron is composite The Feynman-diagram of the neutron beta decay is shown in the left figure. A down-quark changes its flavour to an up-quark emitting a W-boson.
This weak force is believed to be carried by three fundamental particles: W-,W+ and Z bosons. Using the Feynman diagram, describe the beta-negative decay of a ...4 May 2014 · Uploaded by AK LECTURES (ii) Sketch the Feynman diagram that represents this reaction. The diagram has been started for you. times u du (ii) Energy is transferred to a hadron in an attempt to separate its quarks. Describe; Question: 2. (a) Silicon-30 (Si) can be formed from phosphorus-30 (SP) by a process of beta-plus decay. The leading-order Feynman diagrams for electron capture decay. ... The Q value is defined as the total energy released in a given nuclear decay. In beta decay, Q is therefore also the sum of the kinetic energies of the emitted beta particle, neutrino, and recoiling nucleus. (Because of the large mass of the nucleus compared to that of the beta ...
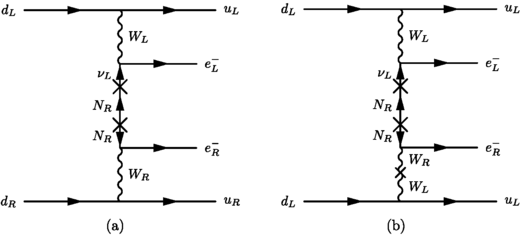
Figure 3 Linear Collider Test Of A Neutrinoless Double Beta Decay Mechanism In Left Right Symmetric Theories Springerlink
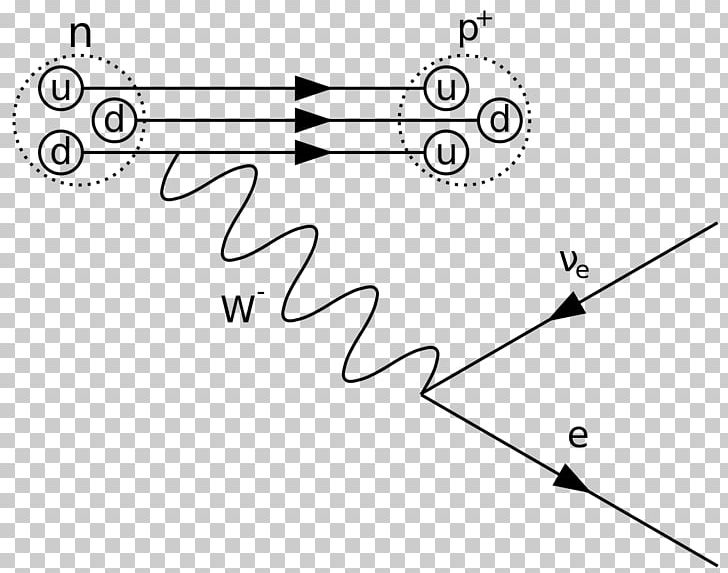
Feynman Diagram Beta Particle Beta Decay Positron Emission Quantum Mechanics Png Clipart Angle Area Beta Decay
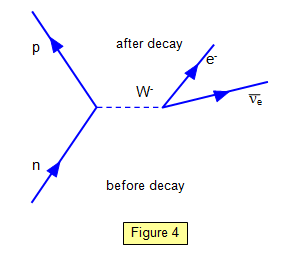














0 Response to "37 beta decay feynman diagram"
Post a Comment