39 a cause-and-effect diagram helps identify the sources of a problem.
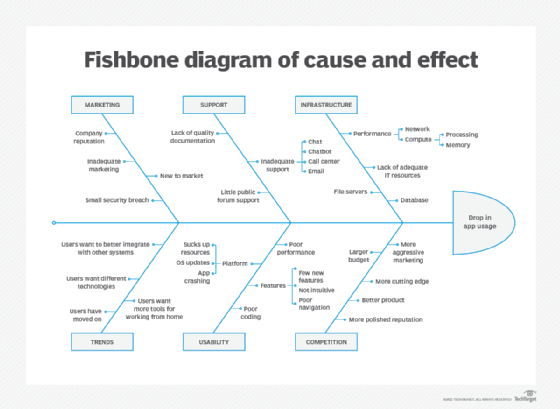
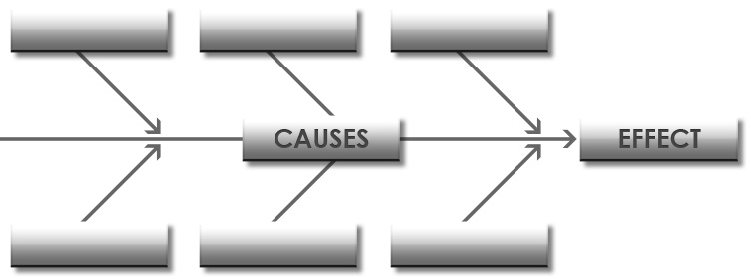
The cause and effect diagram is an easy yet powerful tool commonly used in a cross functional setting to visually describe the potential root causes for a specific problem in question. The tool lends itself to enabling a team to readily organize the causes behind the problem into useful categories, providing a structured brainstorming session. A Fishbone diagram is the final outcome of any cause and effect analysis carried out for determining causes and finding solutions of a problem. In fact, it is a way to look at all these causes and their effect on business visually.
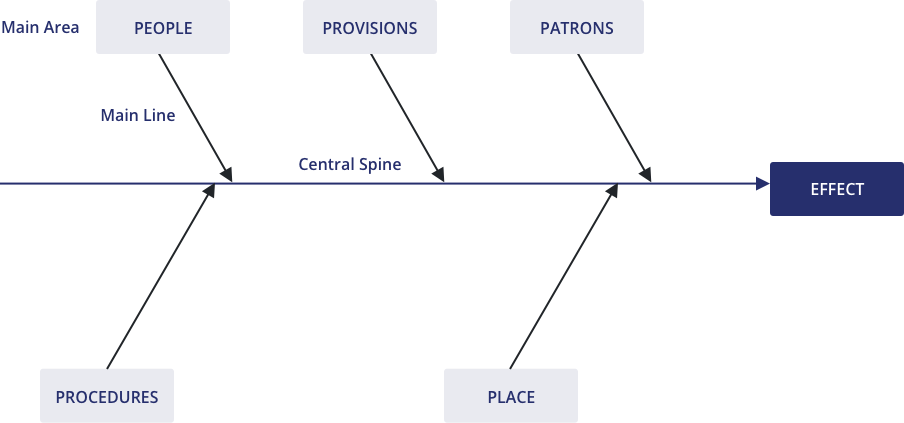
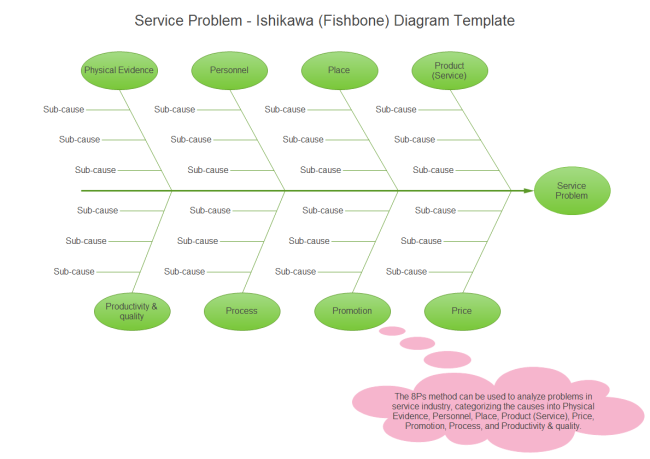
The cause and effect diagram is an analytical approach where a problem or outcome is examined in the light of potential causes that are organized or broken down into smaller causes or contributing factors. It helps to showcase the relationship between these factors. It is used in quality control and is one of the basic tools, commonly referred to as Ishikawa or fishbone diagram.

A cause-and-effect diagram helps identify the sources of a problem.
Source: Adam Kelleher on Medium ... helps identify the root cause of a problem; ... Cause and effect diagrams. The Fishbone diagram is an example of cause and effect diagrams. Many similar tools try to map the relationship between causes and effects in a system. ... These are the best and most common practices when creating cause and effect diagrams. Identify the problem. Define the process or issue to be examined. Brainstorm. Discuss all possible causes and group them into categories. Draw the backbone. Once the topic is identified, draw a straight, horizontal line (this is called the spine or backbone ... Scatter diagram; Cause-and-effect diagram ; Quality tools are used to collect data, analyze data, identify root causes, and measure results in problem-solving and process improvement. The use of these tools helps people involved easily generate new ideas, solve problems, and do proper planning.
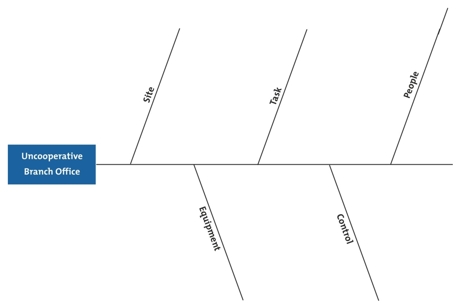
A cause-and-effect diagram helps identify the sources of a problem.. A cause and effect diagram, often called a "fishbone" diagram, can help in brainstorming to identify possible causes of a problem and in sorting ideas into useful categories. A fishbone diagram is a visual way to look at cause and effect. It is a more structured approach than some other tools available for brainstorming causes of a problem ... A cause and effect diagram is a visual map that functions as a problem-solving tool. As the name suggests, its main purpose is to help you identify the cause of a troubling situation in relation to the effect (or results) you've observed. To clarify the cause and effect diagram definition further, it may help to understand that this tool is ... Fishbone diagram can be grouped into major categories to identify sources of variation causes. Fishbone diagram shows factors of Equipment, Process, People, Materials, Environment and Management, all affecting the overall problem in one drawing for the further analysis. Typically, a cause and effect diagram is composed of problem (effect ... A cause and effect diagram, also known as a fishbone diagram, helps a team identify the different causes of a problem to determine the root causes of a problem. Using a fishbone diagram allows a team to focus on the problem instead of the issues associated with the problem. It challenges the team members to explore the causes rather than the ...
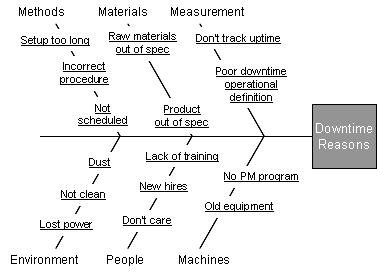
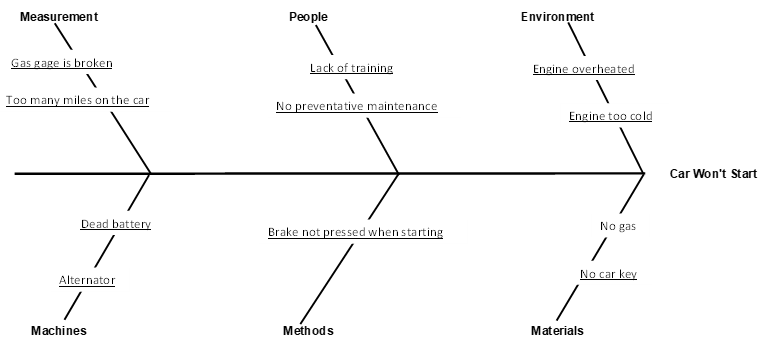
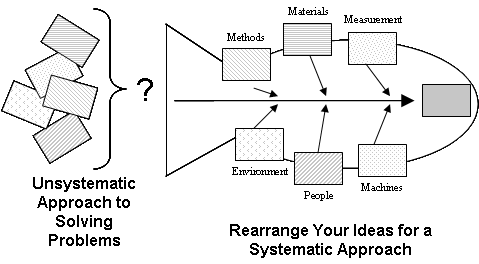
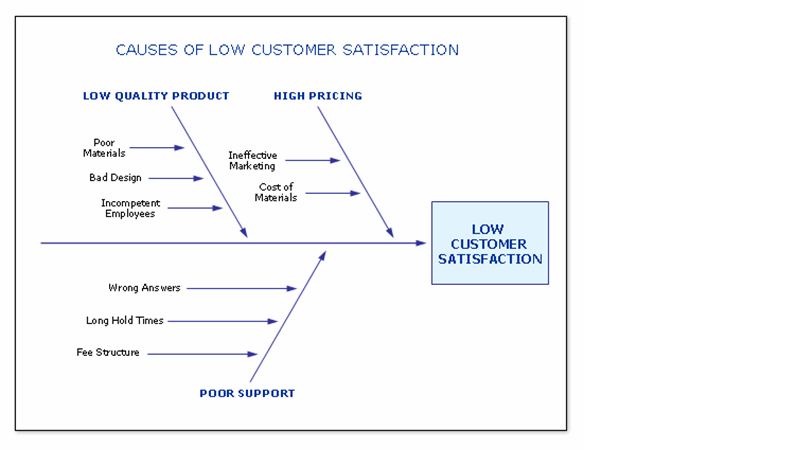
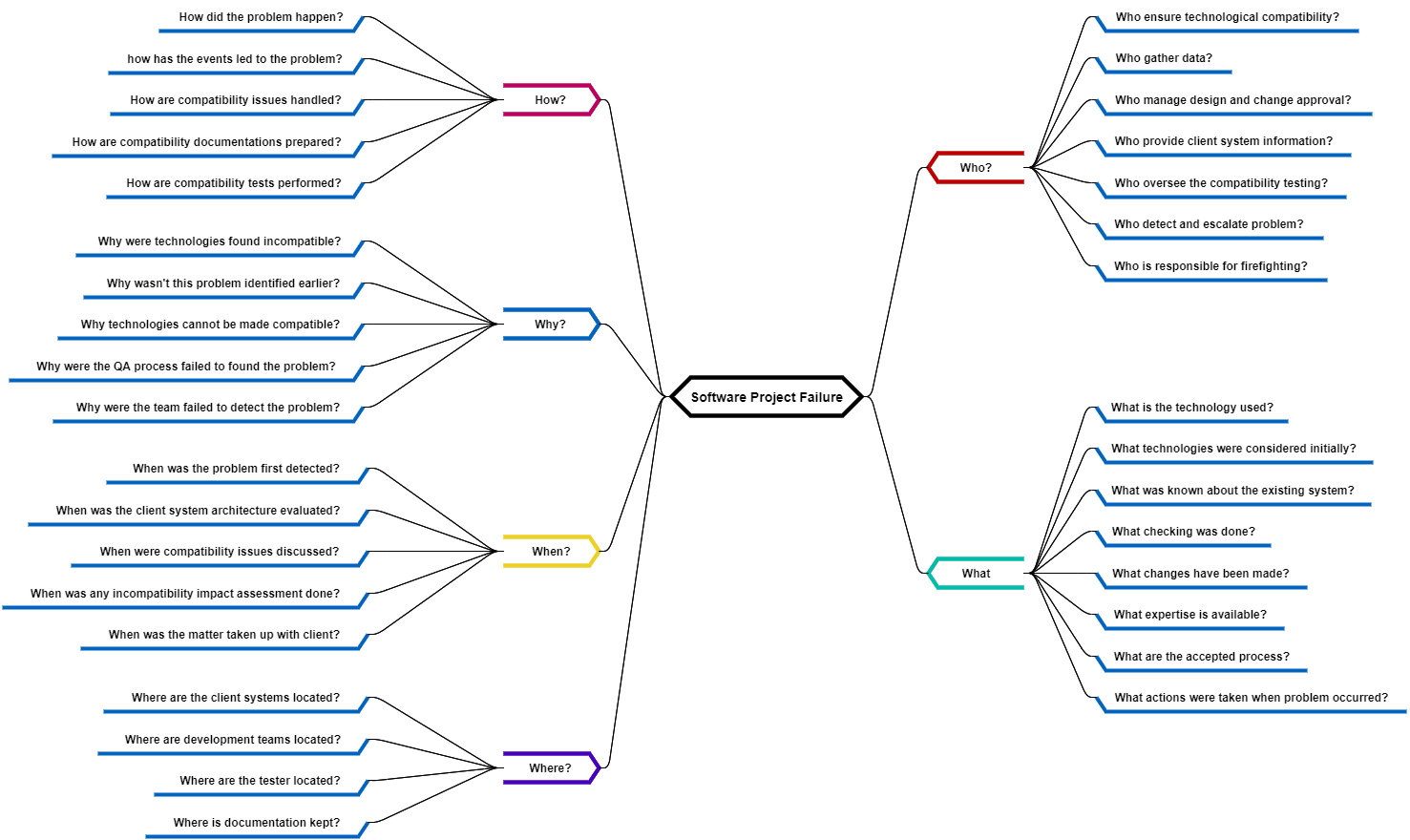
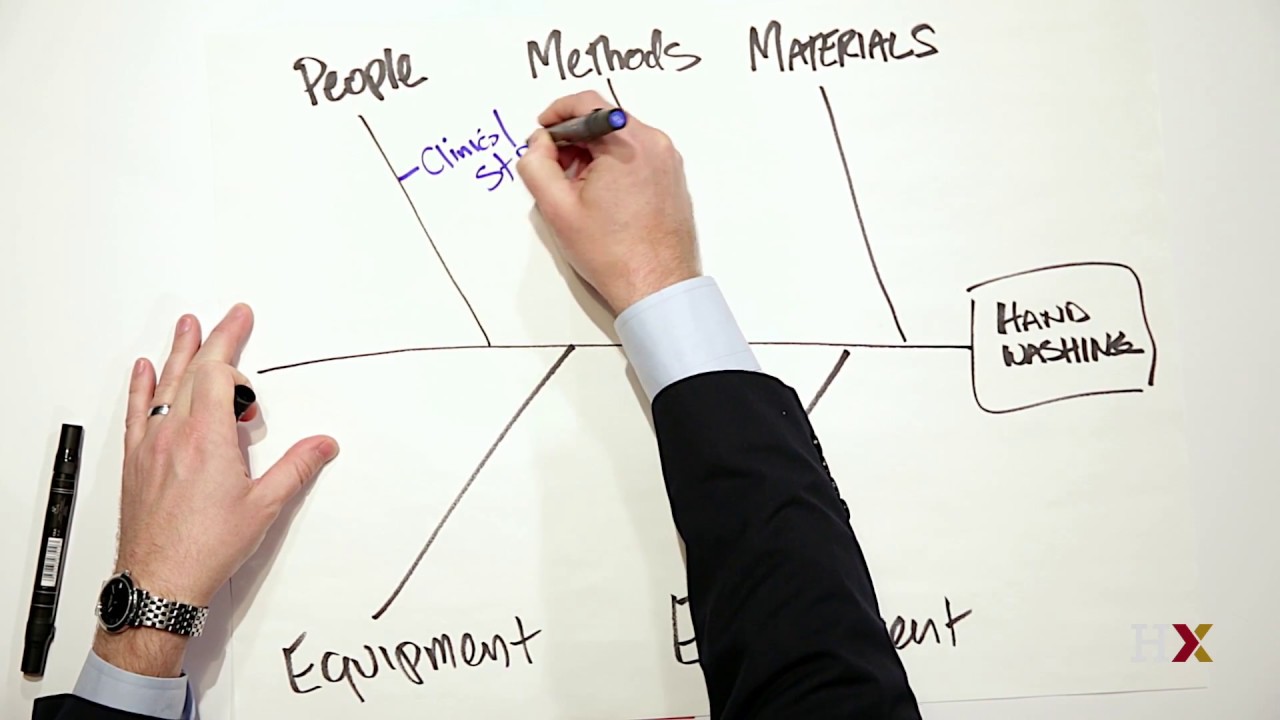
The Cause and Effect Diagram can be implemented during the brainstorming session of development to discover the roots of a specific problem or identify the bottleneck in a specific process through categorizing problems into six main types: people, methods, machines, materials, measurements, and environment. The categorization of the cause of a ... A Cause-and-Effect Diagram is a tool that helps identify, sort, and display possible causes of a specific problem or quality characteristic (Viewgraph 1). It graphically illustrates the relationship between a given outcome and all the factors that influence the outcome. This type of diagram is sometimes called an "Ishikawa diagram" A fishbone diagram is a tool that can help you perform a cause and effect analysis for a problem you are trying to solve. This type of analysis enables you to discover the root cause of a problem. This tool is also called a cause and effect diagram or an Ishikawa diagram.These names can be used interchangeably. Cause and effect analysis helps you to think through the causes of a problem thoroughly, including its possible root causes. It is only by identifying the main causes that you can permanently remove the problem, or reduce the delay. A cause and effect diagram is a tool that helps you do this. The 'effect' is the problem you are working on ...
Cause and Effect Diagrams for PMP. Project teams need to actively identify a problem and understand the root cause of the problem if they are to solve it. In the Project Management Professional ® (PMP) certification exam, cause and effect diagrams are a tool used to better understand the root of a problem. The Cause and Effect Diagram (aka Ishikawa, Fishbone) introduced by Kaoru Ishikawa (1968) that show the causes of a specific event. He also introduced the company-wide quality control (CWQC) and also Quality circles concept in Japan. Common uses of the Ishikawa diagram are product design and quality defect prevention, to identify potential factors causing an overall effect. •Also known as Cause and Effect Diagram or Ishikawa Diagram •Visually displays multiple causes for a problem •Helps identify stakeholder ideas about the causes of problems •Allows the user to immediately categorize ideas into themes for analysis or further data gathering •Uses the "five-whys" technique in conjunction with the fishbone A Fishbone diagram is a kind of widely used Cause-and-Effect tool that helps identify, sort, and display possible causes of a specific problem or quality characteristic. It graphically illustrates the relationship between a given outcome and all the factors that influence the outcome.
The cause-effect diagram helps organize the search for the causes, but it does not identify the causes. Other tools, such as Pareto analysis , scatter diagrams, and histograms, will be used to analyze data to establish the causality empirically.
The Cause and Effect diagram introduced by Kaoru Ishikawa in 1968 is a method for analyzing process dispersion. It can help you to dive into a problem and find an effective solution, identify and represent the possible causes for an effect, analyze the complex business problems and successfully solve them.
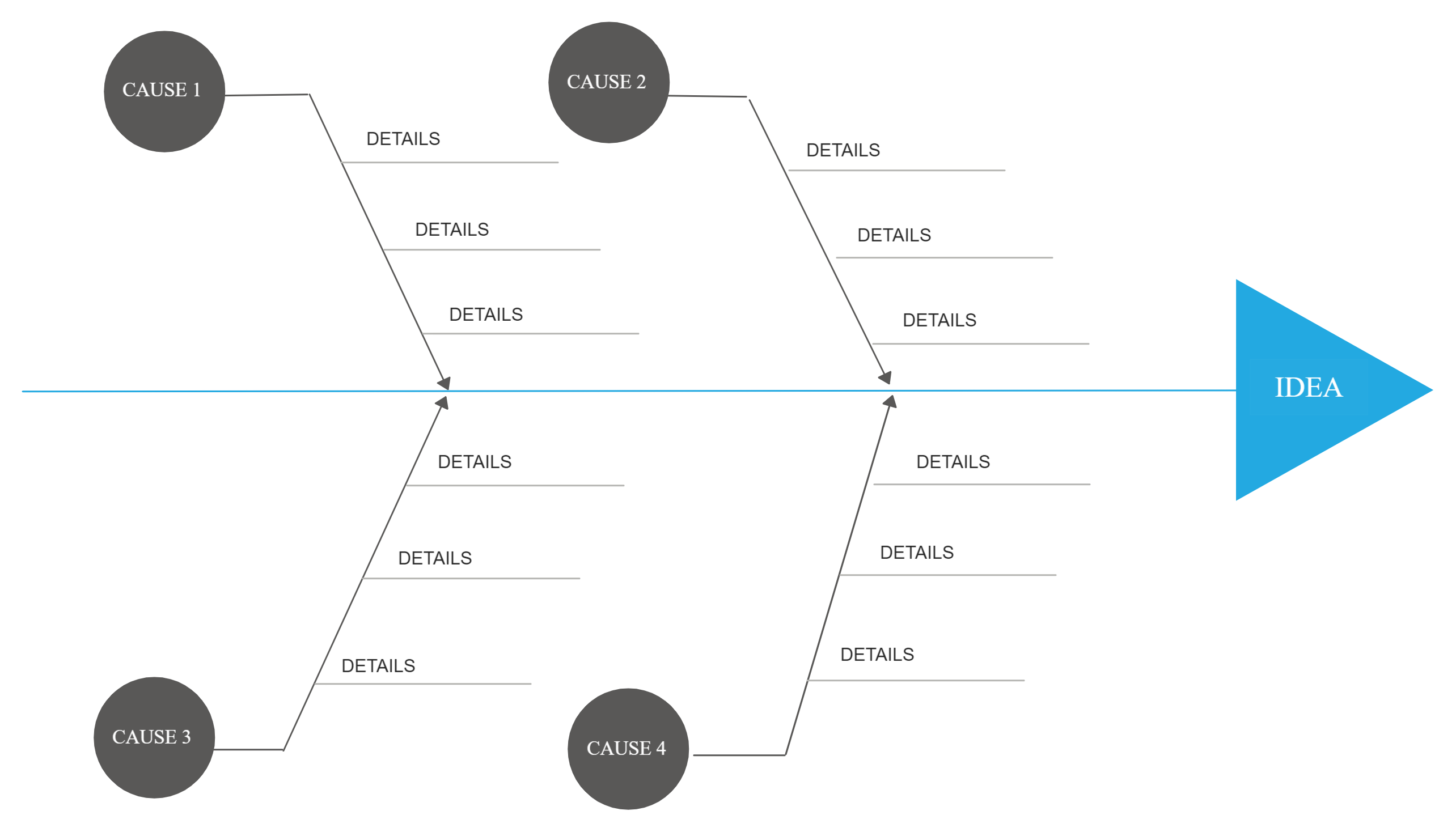
Cause and Effect Analysis is a technique that helps you identify all the likely causes of a problem. This means that you can find and fix the main cause, first time around, without the problem running on and on. The diagrams you create with this type of analysis are sometimes known as fishbone diagrams, because they look like the skeleton of a fish.
A cause-and -effect diagram helps identify the sources of a problem. TRUR or FALSE 2. Typically, a more expensive shipping option is A. faster, but holding cost is unaffected by delivery speed. B. faster with a higher holding cost c. Slower with a lower holding cost D. slower with a higher holding cost 3.
Also called: cause-and-effect diagram, Ishikawa diagram. This cause analysis tool is considered one of the seven basic quality tools. The fishbone diagram identifies many possible causes for an effect or problem. It can be used to structure a brainstorming session. It immediately sorts ideas into useful categories.
Professor Kaoru Ishikawa created Cause and Effect Analysis in the 1960s. The technique uses a diagram-based approach for thinking through all of the possible causes of a problem. This helps you to carry out a thorough analysis of the situation. There are four steps to using the tool. Identify the problem.
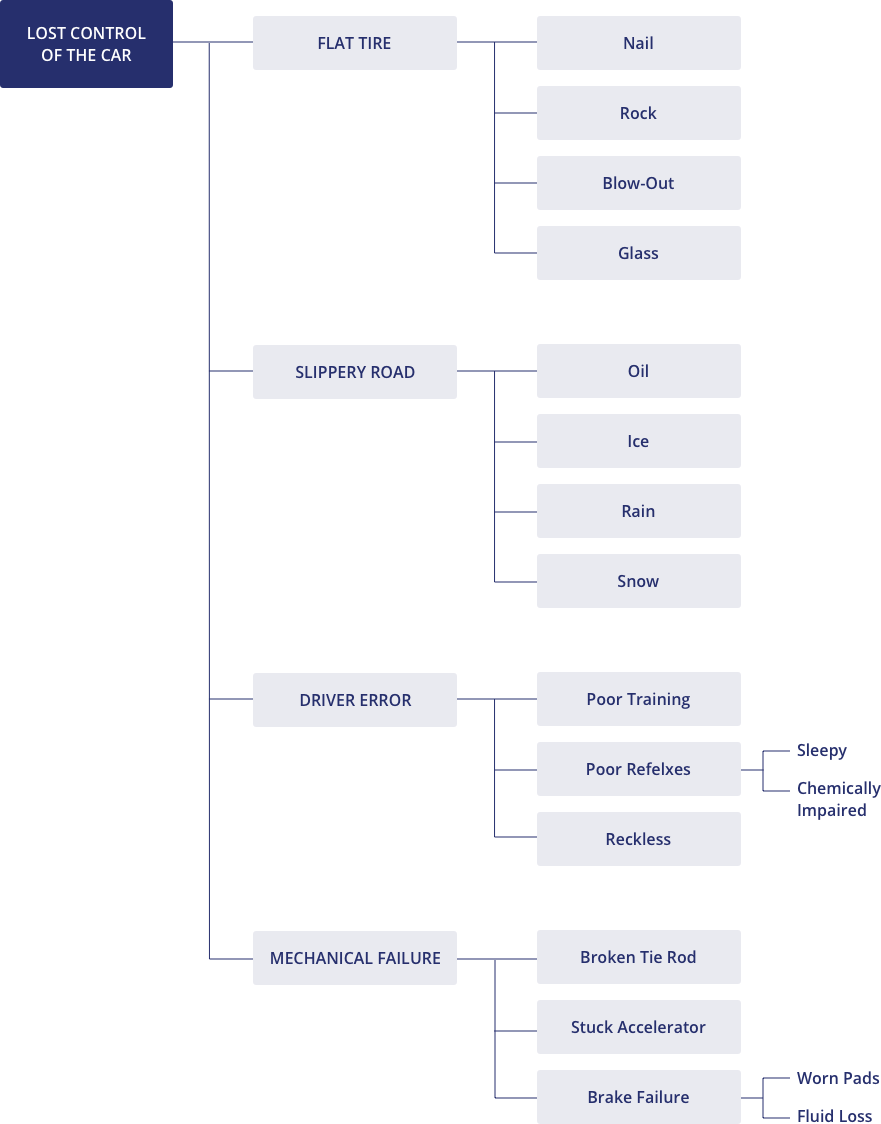
The cause and effect analysis uses brainstorming and critical analysis by way of visual representation to enable problem-solving. The main problem is drawn out on the left while the main causes are drawn out an extension of the problem. This then calls for a look at the sub causes which are written out as branches of the main problems.
The Cause and Effect diagram introduced by Kaoru Ishikawa in 1968 is a method for analyzing process dispersion. It can help you to dive into a problem and find an effective solution, identify and represent the possible causes for an effect, analyze the complex business problems and successfully solve them.
A cause-and-effect diagram helps identify the sources of a problem. True. Pareto charts are used to. ... The 4 M's of cause-and-effect diagrams are. material, machinery, manpower, and methods. Among the tools of TQM, the tool ordinarily used to aid in understanding the sequence of events through which a product travels is a. flowchart.
1) Pareto charts are a graphical way of identifying the few critical items from the many less important ones. Answer: TRUE 2) A cause-and-effect diagram helps identify the sources of a problem.
Scatter diagram; Cause-and-effect diagram ; Quality tools are used to collect data, analyze data, identify root causes, and measure results in problem-solving and process improvement. The use of these tools helps people involved easily generate new ideas, solve problems, and do proper planning.
These are the best and most common practices when creating cause and effect diagrams. Identify the problem. Define the process or issue to be examined. Brainstorm. Discuss all possible causes and group them into categories. Draw the backbone. Once the topic is identified, draw a straight, horizontal line (this is called the spine or backbone ...
Source: Adam Kelleher on Medium ... helps identify the root cause of a problem; ... Cause and effect diagrams. The Fishbone diagram is an example of cause and effect diagrams. Many similar tools try to map the relationship between causes and effects in a system. ...

:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/IshikawaDiagram2-386e9108096f4149b67cb5a803c45dd0.png)

















0 Response to "39 a cause-and-effect diagram helps identify the sources of a problem."
Post a Comment